ESP32-LyraT V4 Getting Started Guide¶
This guide provide users with functional descriptions, configuration options for ESP32-LyraT V4 audio development board, as well as how to get started with ESP32-LyraT board.
The ESP32-LyraT development board is a hardware platform specifically designed for the dual-core ESP32 audio applications, e.g., Wi-Fi or BT audio speakers, speech-based remote controllers, smart-home appliances with audio functionality(ies), etc.
If you like to start using this board right now, go directly to section Start Application Development.
What You Need¶
- 1 × ESP32-LyraT V4 board
- 2 x 4-ohm speakers with Dupont female jumper wires or headphones with a 3.5 mm jack
- 1 x Micro USB 2.0 Cable, Type A to Micro B
- 1 × PC loaded with Windows, Linux or Mac OS
Overview¶
The ESP32-LyraT V4 is an audio development board produced by Espressif built around ESP32. It is intended for audio applications, by providing hardware for audio processing and additional RAM on top of what is already onboard of the ESP32 chip. The specific hardware includes:
- ESP32-WROVER Module
- Audio Codec Chip
- Dual Microphones on board
- Headphone input
- 2 x 3 Watt Speaker output
- Dual Auxiliary Input
- MicroSD Card slot (1 line or 4 lines)
- 6 buttons (2 physical buttons and 4 touch buttons)
- JTAG header
- Integrated USB-UART Bridge Chip
- Li-ion Battery-Charge Management
Block diagram below presents main components of the ESP32-LyraT and interconnections between components.
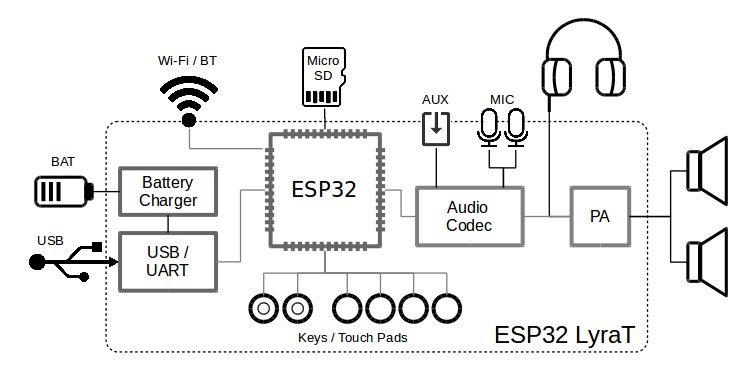
ESP32-LyraT block diagram
Functional Description¶
The following list and figure below describe key components, interfaces and controls of the ESP32-LyraT board.
- ESP32-WROVER Module
- The ESP32-WROVER module contains ESP32 chip to provide Wi-Fi / BT connectivity and data processing power as well as integrates 32 Mbit SPI flash and 32 Mbit PSRAM for flexible data storage.
- Green and Red LEDs
- Two general purpose LEDs controlled by ESP32-WROVER Module to indicate certain operation states of the audio application using dedicated API.
- Function DIP Switch
- Used to configure function of GPIO12 to GPIO15 pins that are shared between devices, primarily between JTAG Header and MicroSD Card. By default MicroSD Card is enabled with all switches in OFF position. To enable JTAG Header instead, switches in positions 3, 4, 5 and 6 should be put ON. If JTAG is not used and MicroSD Card is operated in one-line mode, then GPIO12 and GPIO13 may be assigned to other functions. Please refer to ESP32 LyraT V4 schematic for more details.
- JTAG Header
- Provides access to the JTAG interface of ESP32-WROVER Module. May be used for debugging, application upload, as well as implementing several other functions, e.g., Application Level Tracing. See JTAG Header / JP7 for pinout details. Before using JTAG signals to the header, Function DIP Switch should be enabled. Please note that when JTAG is in operation, MicroSD Card cannot be used and should be disconnected because some of JTAG signals are shared by both devices.
- UART Header
- Serial port provides access to the serial TX/RX signals between ESP32-WROVER Module and USB-UART Bridge Chip.
- I2C Header
- Provides access to the I2C interface. Both ESP32-WROVER Module and Audio Codec Chip are connected to this interface. See I2C Header / JP5 for pinout details.
- MicroSD Card
- The development board supports a MicroSD card in SPI/1-bit/4-bit modes, and can store or play audio files in the MicroSD card. See MicroSD Card / J5 for pinout details. Note that JTAG cannot be used and should be disconnected by setting Function DIP Switch when MicroSD Card is in operation, because some of the signals are shared by both devices.
- I2S Header
- Provides access to the I2S interface. Both ESP32-WROVER Module and Audio Codec Chip are connected to this interface. See I2S Header / JP4 for pinout details.
- Left Microphone
- Onboard microphone connected to IN1 of the Audio Codec Chip.
- AUX Input
- Auxiliary input socket connected to IN2 (left and right channels) of the Audio Codec Chip. Use a 3.5 mm stereo jack to connect to this socket.
- Headphone Output
- Output socket to connect headphones with a 3.5 mm stereo jack.
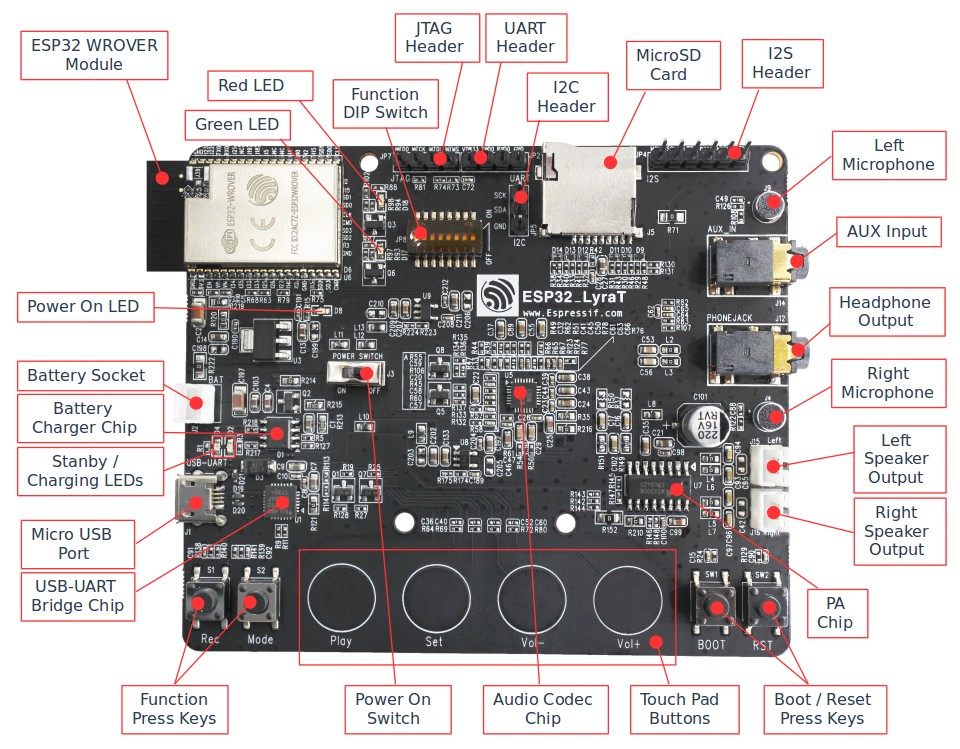
ESP32 LyraT V4 board layout
- Right Microphone
- Onboard microphone connected to IN1 of the Audio Codec Chip.
- Left Speaker Output
- Output socket to connect 4 ohm speaker. The pins have a standard 2.54 mm / 0.1” pitch.
- Right Speaker Output
- Output socket to connect 4 ohm speaker. The pins have a standard 2.54 mm / 0.1” pitch.
- PA Chip
- A power amplifier used to amplify stereo audio signal from the Audio Codec Chip for driving two 4-ohm speakers.
- Boot/Reset Press Keys
- Boot: holding down the Boot button and momentarily pressing the Reset button initiates the firmware upload mode. Then user can upload firmware through the serial port. Reset: pressing this button alone resets the system.
- Touch Pad Buttons
- Four touch pads labeled Play, Sel, Vol+ and Vol-. They are routed to ESP32-WROVER Module and intended for development and testing of a UI for audio applications using dedicated API.
- Audio Codec Chip
- The Audio Codec Chip, ES8388, is a low-power stereo audio codec with headphone amplifier. It consists of 2-channel ADC, 2-channel DAC, microphone amplifier, headphone amplifier, digital sound effects, analog mixing and gain functions. It is interfaced with ESP32-WROVER Module over I2S and I2S buses to provide audio processing in hardware independently from the audio application.
- Function Press Keys
- Two key labeled Rec and Mode. They are routed to ESP32-WROVER Module and intended for developing and testing a UI for audio applications using dedicated API.
- USB-UART Bridge Chip
- A single chip USB-UART bridge provides up to 1 Mbps transfer rate.
- Micro USB Port
- USB interface. It functions as the power supply for the board and the communication interface between a PC and the ESP32 module.
- Standby / Charging LEDs
- The Standby green LED indicates that power has been applied to the Micro USB Port. The Charging red LED indicates that a battery connected to the Battery Socket is being charged.
- Battery Charger Chip
- Constant current & constant voltage linear charger for single cell lithium-ion batteries AP5056. Used for charging of a battery connected to the Battery Socket over the Micro USB Port.
- Power On Switch
- Power on/off knob: toggling it to the left powers the board on; toggling it to the right powers the board off.
- Battery Socket
- Two pins socket to connect a single cell Li-ion battery.
- Power On LED
Red LED indicating that Power On Switch is turned on.
Note
The Power On Switch does not affect / disconnect the Li-ion battery charging.
Hardware Setup Options¶
There are couple of options to change the hardware configuration of the ESP32-LyraT board. The options are selectable with the Function DIP Switch.
Enable MicroSD Card in 1-wire Mode¶
| DIP SW | Position |
|---|---|
| 1 | OFF |
| 2 | OFF |
| 3 | OFF |
| 4 | OFF |
| 5 | OFF |
| 6 | OFF |
| 7 | OFF 1 |
| 8 | n/a |
- AUX Input detection may be enabled by toggling the DIP SW 7 ON
In this mode:
- JTAG functionality is not available
- Vol- touch button is available for use with the API
Enable MicroSD Card in 4-wire Mode¶
| DIP SW | Position |
|---|---|
| 1 | ON |
| 2 | ON |
| 3 | OFF |
| 4 | OFF |
| 5 | OFF |
| 6 | OFF |
| 7 | OFF |
| 8 | n/a |
In this mode:
- JTAG functionality is not available
- Vol- touch button is not available for use with the API
- AUX Input detection from the API is not available
Enable JTAG¶
| DIP SW | Position |
|---|---|
| 1 | OFF |
| 2 | OFF |
| 3 | ON |
| 4 | ON |
| 5 | ON |
| 6 | ON |
| 7 | ON |
| 8 | n/a |
In this mode:
- MicroSD Card functionality is not available, remove the card from the slot
- Vol- touch button is not available for use with the API
- AUX Input detection from the API is not available
Allocation of ESP32 Pins¶
Several pins / terminals of ESP32 modules are allocated to the onboard hardware. Some of them, like GPIO0 or GPIO2, have multiple functions. Please refer to tables below or ESP32 LyraT V4 schematic for specific details.
Red / Green LEDs¶
| ESP32 Pin | LED Color | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GPIO19 | Red LED |
| 2 | GPIO22 | Green LED |
Touch Pads¶
| ESP32 Pin | Touch Pad Function | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GPIO33 | Play |
| 2 | GPIO32 | Set |
| 3 | GPIO13 | Vol- 1 |
| 4 | GPIO27 | Vol+ |
- Vol- function is not available if JTAG is used. It is also not available for the MicroSD Card configured to operate in 4-wire mode.
MicroSD Card / J5¶
| ESP32 Pin | MicroSD Signal | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MTDI / GPIO12 | DATA2 |
| 2 | MTCK / GPIO13 | CD / DATA3 |
| 3 | MTDO / GPIO15 | CMD |
| 4 | MTMS / GPIO14 | CLK |
| 5 | GPIO2 | DATA0 |
| 6 | GPIO4 | DATA1 |
| 7 | GPIO21 | CD |
UART Header / JP2¶
| Header Pin | |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3V |
| 2 | TX |
| 3 | RX |
| 4 | GND |
I2S Header / JP4¶
| I2C Header Pin | ESP32 Pin | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MCLK | GPI0 |
| 2 | SCLK | GPIO5 |
| 1 | LRCK | GPIO25 |
| 2 | DSDIN | GPIO26 |
| 3 | ASDOUT | GPIO35 |
| 3 | GND | GND |
I2C Header / JP5¶
| I2C Header Pin | ESP32 Pin | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SCL | GPIO23 |
| 2 | SDA | GPIO18 |
| 3 | GND | GND |
JTAG Header / JP7¶
| ESP32 Pin | JTAG Signal | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MTDO / GPIO15 | TDO |
| 2 | MTCK / GPIO13 | TCK |
| 3 | MTDI / GPIO12 | TDI |
| 4 | MTMS / GPIO14 | TMS |
Function DIP Switch / JP8¶
| Switch OFF | Switch ON | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GPIO12 not allocated | MicroSD Card 4-wire |
| 2 | Touch Vol- enabled | MicroSD Card 4-wire |
| 3 | MicroSD Card | JTAG |
| 4 | MicroSD Card | JTAG |
| 5 | MicroSD Card | JTAG |
| 6 | MicroSD Card | JTAG |
| 7 | MicroSD Card 4-wire | AUX IN detect 1 |
| 8 | not used | not used |
- The AUX Input signal pin should not be plugged in when the system powers up. Otherwise the ESP32 may not be able to boot correctly.
Start Application Development¶
Before powering up the ESP32-LyraT, please make sure that the board has been received in good condition with no obvious signs of damage.
Initial Setup¶
Prepare the board for loading of the first sample application:
- Connect 4-ohm speakers to the Right and Left Speaker Output. Optionally connect headphones to the Headphone Output.
- Plug in the Micro-USB cable to the PC and to the Micro USB Port of the ESP32-LyraT.
- The Standby LED (green) should turn on. Assuming that a battery is not connected, the Charging LED will momentarily blink every couple of seconds.
- Toggle left the Power On Switch.
- The red Power On LED should turn on.
If this is what you see on the LEDs, the board should be ready for application upload. Now prepare the PC by loading and configuring development tools what is discussed in the next section.
Develop Applications¶
If the ESP32-LyraT is initially set up and checked, you can proceed with preparation of the development tools. Go to section Get Started, which will walk you through the following steps:
- Set up ESP-IDF in your PC that provides a common framework to develop applications for the ESP32 in C language;
- Get ESP-ADF to have the API specific for the audio applications;
- Setup Path to ESP-ADF to make the framework aware of the audio specific API;
- Start a Project that will provide a sample audio application for the ESP32-LyraT board;
- Connect and Configure to prepare the application for loading;
- Build, Flash and Monitor this will finally run the application and play some music.