USB Host Maintainers Notes (Introduction)
This document contains information regarding the implementation details of the USB Host stack. This document is intended for the maintainers and third-party contributors of the USB Host stack. Users of the USB Host stack should refer to USB Host instead.
Warning
The implementations details of the USB Host stack is categorized as private API. Thus, all layers (other than the USB Host Library) do not adhere to ESP-IDF's versioning scheme (i.e., breaking changes are permitted).
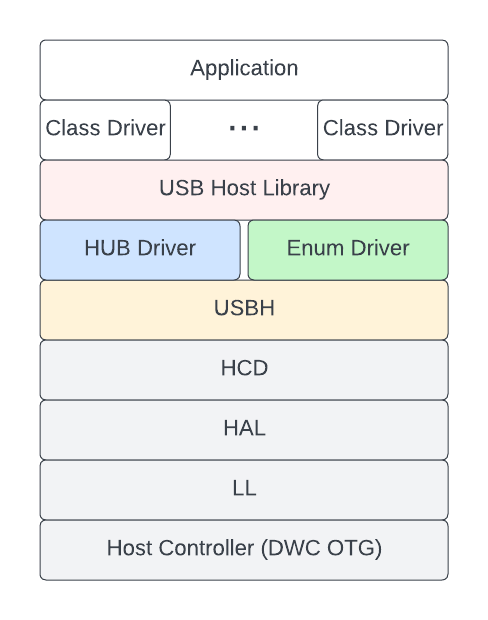
This document is split into the following sections:
Todo:
USB Host Maintainers Notes (HAL & LL)
USB Host Maintainers Notes (HCD)
USB Host Maintainers Notes (Hub)
USB Host Maintainers Notes (USB Host Library)
Introduction
The ESP-IDF USB Host Stack allows the ESP32-S2 to operate as a USB Host. Operating as a USB Host allows the ESP32-S2 to communicate with a wide range of USB devices. However, most USB Host Stack implementations do not run on embedded hardware (i.e., runs on PCs and smartphones), thus have comparatively more resources (i.e., memory and CPU speed).
The implementation of the ESP-IDF USB Host Stack (henceforth referred to as the Host Stack) takes into account the embedded nature of the ESP32-S2 which is reflected in various aspects of the Host Stack's design.