RF Coexistence
Overview
ESP boards now support three modules: Bluetooth (BT & BLE), IEEE 802.15.4 (Thread / Zigbee), and Wi-Fi. Each type of board has only one 2.4 GHz ISM band RF module, shared by two or three modules. Consequently, a module cannot receive or transmit data while another module is engaged in data transmission or reception. In such scenarios, ESP32 employs the time-division multiplexing method to manage the reception and transmission of packets.
Supported Coexistence Scenario for ESP32
BLE |
|||||
Scan |
Advertising |
Connected |
|||
Wi-Fi |
STA |
Scan |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Connecting |
Y |
Y |
Y |
||
Connected |
Y |
Y |
Y |
||
SOFTAP |
TX Beacon |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Connecting |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
||
Connected |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
||
Sniffer |
RX |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
|
ESP-NOW |
RX |
S |
S |
S |
|
TX |
Y |
Y |
Y |
||
BR/EDR |
|||||||
Inquiry |
Inquiry scan |
Page |
Page scan |
Connected |
|||
Wi-Fi |
STA |
Scan |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Connecting |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
||
Connected |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
||
SOFTAP |
TX Beacon |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
Connecting |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
||
Connected |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
||
Sniffer |
RX |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
C1 |
|
ESP-NOW |
RX |
S |
S |
S |
S |
S |
|
TX |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |
||
Note
Y: supported and the performance is stable
C1: supported but the performance is unstable
X: not supported
S: supported and the performance is stable in STA mode, otherwise not supported
Coexistence Mechanism and Policy
Coexistence Mechanism
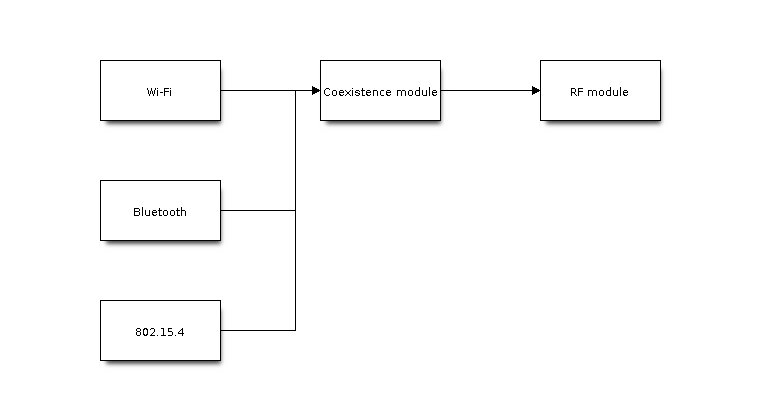
The RF resource allocation mechanism is based on priority. As shown below, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and 802.15.4 modules request RF resources from the coexistence module, and the coexistence module decides who will use the RF resource based on their priority.
Coexistence Mechanism
Coexistence Policy
Coexistence Period and Time Slice
Wi-Fi, BT, and BLE have their fixed time slice to use the RF. A coexistence period is divided into 3 time slices in the order of Wi-Fi, BT, and BLE. In the Wi-Fi slice, Wi-Fi's request to the coexistence arbitration module will have higher priority. Similarly, BT/BLE can enjoy higher priority at their own time slices. The duration of the coexistence period and the proportion of each time slice are divided into four categories according to the Wi-Fi status:
IDLE status: the coexistence of BT and BLE is controlled by Bluetooth module.
CONNECTED status: the coexistence period starts at the Target Beacon Transmission Time (TBTT) and is more than 100 ms.
SCAN status: Wi-Fi slice and coexistence period are longer than in the CONNECTED status. To ensure Bluetooth performance, the Bluetooth time slice will also be adjusted accordingly.
CONNECTING status: Wi-Fi slice is longer than in the CONNECTED status. To ensure Bluetooth performance, the Bluetooth time slice will also be adjusted accordingly.
According to the coexistence logic, different coexistence periods and time slice strategies will be selected based on the Wi-Fi and Bluetooth usage scenarios. A Coexistence policy corresponding to a certain usage scenarios is called a "coexistence scheme". For example, the scenario of Wi-Fi CONNECTED and BLE CONNECTED has a corresponding coexistence scheme. In this scheme, the time slices of Wi-Fi and BLE in a coexistence period each account for 50%. The time allocation is shown in the following figure:
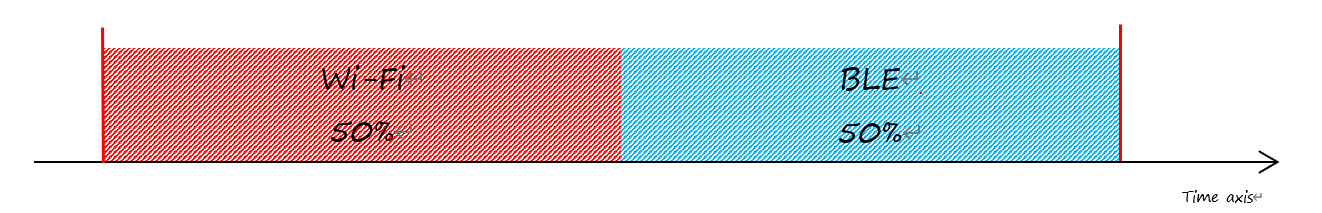
Time Slice Under the Status of Wi-Fi CONNECTED and BLE CONNECTED
Dynamic Priority
The coexistence module assigns varying priorities to different statuses of each module, and these priorities are dynamic. For example, in every N BLE Advertising events, there is always one event with high priority. If a high-priority BLE Advertising event occurs within the Wi-Fi time slice, the right to use the RF may be preempted by BLE.
Wi-Fi Connectionless Modules Coexistence
To some extent, some combinations of connectionless power-saving parameters Window and Interval would lead to extra Wi-Fi priority request out of Wi-Fi time slice. It`s for obtaining RF resources at coexistence for customized parameters, while leading to impact on Bluetooth performance.
If connectionless power-saving parameters are configured with default values, the coexistence module would perform in stable mode and the behaviour above would not happen. So please configure Wi-Fi connectionless power-saving parameters to default values unless you have plenty of coexistence performance tests for customized parameters.
Please refer to connectionless module power save to get more detail.
How to Use the Coexistence Feature
Coexistence API
For most coexistence cases, ESP32 will switch the coexistence status automatically without calling API. However, ESP32 provides two APIs for the coexistence of BLE MESH and Wi-Fi. When the status of BLE MESH changes, call esp_coex_status_bit_clear to clear the previous status first and then call esp_coex_status_bit_set to set the current status.
BLE MESH Coexistence Status
As the firmware of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are not aware of the current scenario of the upper layer application, some coexistence schemes require application code to call the coexistence API to take effect. The application layer needs to pass the working status of BLE MESH to the coexistence module for selecting the coexistence scheme.
ESP_COEX_BLE_ST_MESH_CONFIG: network is provisioning
ESP_COEX_BLE_ST_MESH_TRAFFIC: data is transmitting
ESP_COEX_BLE_ST_MESH_STANDBY: in idle status with no significant data interaction
Coexistence API Error Codes
All coexistence APIs have custom return values, i.e., error codes. These error codes can be categorized as:
No error. For example, the return value ESP_OK siginifies the API returned successfully.
Recoverable errors. For example, the return value ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG signifies API parameter errors.
Setting Coexistence Compile-time Options
After writing the coexistence program, you must check CONFIG_ESP_COEX_SW_COEXIST_ENABLE option through menuconfig to open coexistence configuration on software, otherwise the coexistence function mentioned above cannot be used.
To ensure better communication performance of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth in the case of coexistence, run the task of the Wi-Fi protocol stack, the task of the Bluetooth Controller and Host protocol stack on different CPUs. You can use CONFIG_BTDM_CTRL_PINNED_TO_CORE_CHOICE and CONFIG_BT_BLUEDROID_PINNED_TO_CORE_CHOICE (or CONFIG_BT_NIMBLE_PINNED_TO_CORE_CHOICE) to put the tasks of the Bluetooth controller and the host protocol stack on the same CPU, and then use CONFIG_ESP_WIFI_TASK_CORE_ID to place the task of the Wi-Fi protocol stack on another CPU.
In the case of coexistence, BLE SCAN may be interrupted by Wi-Fi and Wi-Fi releases RF resources before the end of the current BLE scan window. In order to make BLE acquire RF resources again within the current scan window, you can check the FULL SCAN configuration option through CONFIG_BTDM_CTRL_FULL_SCAN_SUPPORTED.
You can reduce the memory consumption by configuring the following options on menuconfig.
CONFIG_BT_BLE_DYNAMIC_ENV_MEMORY: enable the configuration of dynamic memory for Bluetooth protocol stack.
CONFIG_ESP_WIFI_STATIC_RX_BUFFER_NUM: reduce the number of Wi-Fi static RX buffers.
CONFIG_ESP_WIFI_DYNAMIC_RX_BUFFER_NUM: reduce the number of Wi-Fi dynamic RX buffers.
CONFIG_ESP_WIFI_TX_BUFFER: enable the configuration of dynamic allocation TX buffers.
CONFIG_ESP_WIFI_DYNAMIC_TX_BUFFER_NUM: reduce the number of Wi-Fi dynamic TX buffers.
CONFIG_ESP_WIFI_TX_BA_WIN: reduce the number of Wi-Fi Block Ack TX windows.
CONFIG_ESP_WIFI_RX_BA_WIN: reduce the number of Wi-Fi Block Ack RX windows.
CONFIG_ESP_WIFI_MGMT_SBUF_NUM: reduce the number of Wi-Fi Management Short Buffer.
CONFIG_ESP_WIFI_RX_IRAM_OPT: turning off this configuration option will reduce the IRAM memory by approximately 17 KB.
CONFIG_LWIP_TCP_SND_BUF_DEFAULT: reduce the default TX buffer size for TCP sockets.
CONFIG_LWIP_TCP_WND_DEFAULT: reduce the default size of the RX window for TCP sockets.
CONFIG_LWIP_TCP_RECVMBOX_SIZE: reduce the size of the TCP receive mailbox. Receive mailbox buffers data within active connections and handles data flow during connections。
CONFIG_LWIP_TCP_ACCEPTMBOX_SIZE: reduce the size of the TCP accept mailbox. Accept mailbox queues incoming connection requests and manages the initiation of new connections.
CONFIG_LWIP_UDP_RECVMBOX_SIZE: reduce the size of the UDP receive mailbox.
CONFIG_LWIP_TCPIP_RECVMBOX_SIZE: reduce the size of TCPIP task receive mailbox.
Note
As the coexistence configuration option relies on the presence of any two enabled modules, please ensure that both modules are activated before configuring any coexistence features.