Analog to Digital Converter (ADC)
ADC Channels
The ESP32 integrates 2 SAR (Successive Approximation Register) ADCs, supporting a total of 18 measurement channels (analog enabled pins).
These channels are supported:
- ADC1:
8 channels: GPIO32 - GPIO39
- ADC2:
10 channels: GPIO0, GPIO2, GPIO4, GPIO12 - GPIO15, GOIO25 - GPIO27
ADC Attenuation
Vref is the reference voltage used internally by ESP32 ADCs for measuring the input voltage. The ESP32 ADCs can measure analog voltages from 0 V to Vref. Among different chips, the Vref varies, the median is 1.1 V. In order to convert voltages larger than Vref, input voltages can be attenuated before being input to the ADCs. There are 4 available attenuation options, the higher the attenuation is, the higher the measurable input voltage could be.
Attenuation |
Measurable input voltage range |
|---|---|
|
100 mV ~ 950 mV |
|
100 mV ~ 1250 mV |
|
150 mV ~ 1750 mV |
|
150 mV ~ 2450 mV |
ADC Conversion
An ADC conversion is to convert the input analog voltage to a digital value. The ADC conversion results provided by the ADC driver APIs are raw data. Resolution of ESP32 ADC raw results under Single Read mode is 12-bit.
To calculate the voltage based on the ADC raw results, this formula can be used:
Vout = Dout * Vmax / Dmax (1)
where:
Vout |
Digital output result, standing for the voltage. |
Dout |
ADC raw digital reading result. |
Vmax |
Maximum measurable input analog voltage, see ADC Attenuation. |
Dmax |
Maximum of the output ADC raw digital reading result, which is 4095 under Single Read mode, 4095 under Continuous Read mode. |
For boards with eFuse ADC calibration bits, esp_adc_cal_raw_to_voltage() can be used to get the calibrated conversion results. These results stand for the actual voltage (in mV). No need to transform these data via the formula (1).
If ADC calibration APIs are used on boards without eFuse ADC calibration bits, warnings will be generated. See ADC Calibration.
ADC Limitations
Note
Some of the ADC2 pins are used as strapping pins (GPIO 0, 2, 15) thus cannot be used freely. Such is the case in the following official Development Kits:
ESP32 DevKitC: GPIO 0 cannot be used due to external auto program circuits.
ESP-WROVER-KIT: GPIO 0, 2, 4 and 15 cannot be used due to external connections for different purposes.
Since the ADC2 module is also used by the Wi-Fi, only one of them could get the preemption when using together, which means the
adc2_get_raw()may get blocked until Wi-Fi stops, and vice versa.
Driver Usage
Both of the ADC units support single read mode, which is suitable for low-frequency sampling operations.
Note
ADC readings from a pin not connected to any signal are random.
ADC Single Read mode
The ADC should be configured before reading is taken.
For ADC1, configure desired precision and attenuation by calling functions
adc1_config_width()andadc1_config_channel_atten().For ADC2, configure the attenuation by
adc2_config_channel_atten(). The reading width of ADC2 is configured every time you take the reading.
Attenuation configuration is done per channel, see adc1_channel_t and adc2_channel_t, set as a parameter of above functions.
Then it is possible to read ADC conversion result with adc1_get_raw() and adc2_get_raw(). Reading width of ADC2 should be set as a parameter of adc2_get_raw() instead of in the configuration functions.
Single Read mode ADC example can be found in peripherals/adc/single_read directory of ESP-IDF examples.
It is also possible to read the internal hall effect sensor via ADC1 by calling dedicated function hall_sensor_read(). Note that even the hall sensor is internal to ESP32, reading from it uses channels 0 and 3 of ADC1 (GPIO 36 and 39). Do not connect anything else to these pins and do not change their configuration. Otherwise it may affect the measurement of low value signal from the sensor.
This API provides convenient way to configure ADC1 for reading from ULP. To do so, call function adc1_ulp_enable() and then set precision and attenuation as discussed above.
There is another specific function adc_vref_to_gpio() used to route internal reference voltage to a GPIO pin. It comes handy to calibrate ADC reading and this is discussed in section ADC Calibration.
Note
See ADC Limitations for the limitation of using ADC single read mode.
Minimizing Noise
The ESP32 ADC can be sensitive to noise leading to large discrepancies in ADC readings. Depending on the usage scenario, users may connect a bypass capacitor (e.g. a 100 nF ceramic capacitor) to the ADC input pad in use, to minimize noise. Besides, multisampling may also be used to further mitigate the effects of noise.
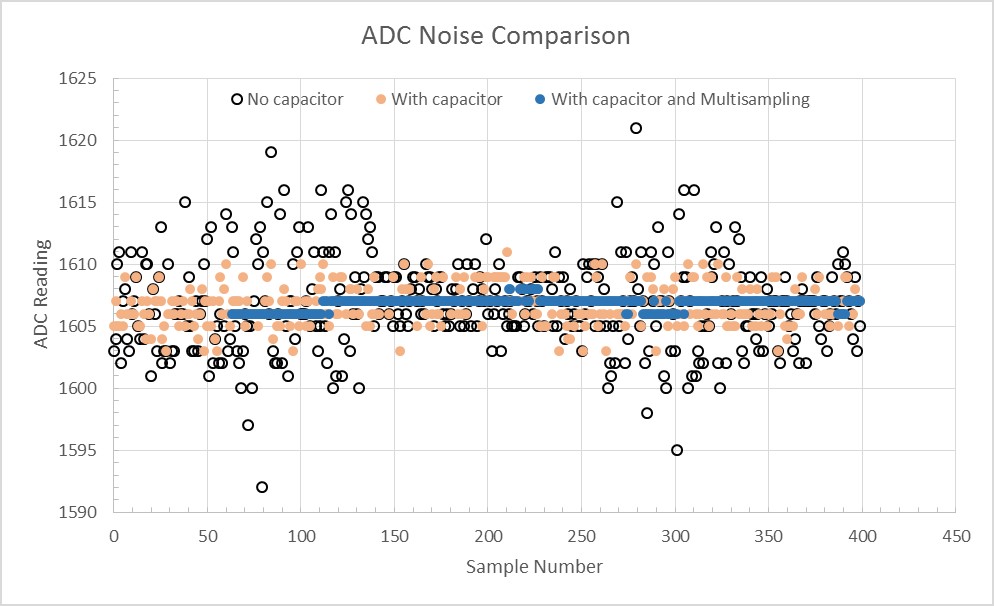
Graph illustrating noise mitigation using capacitor and multisampling of 64 samples.
ADC Calibration
The esp_adc_cal/include/esp_adc_cal.h API provides functions to correct for differences in measured voltages caused by variation of ADC reference voltages (Vref) between chips. Per design the ADC reference voltage is 1100 mV, however the true reference voltage can range from 1000 mV to 1200 mV amongst different ESP32s.
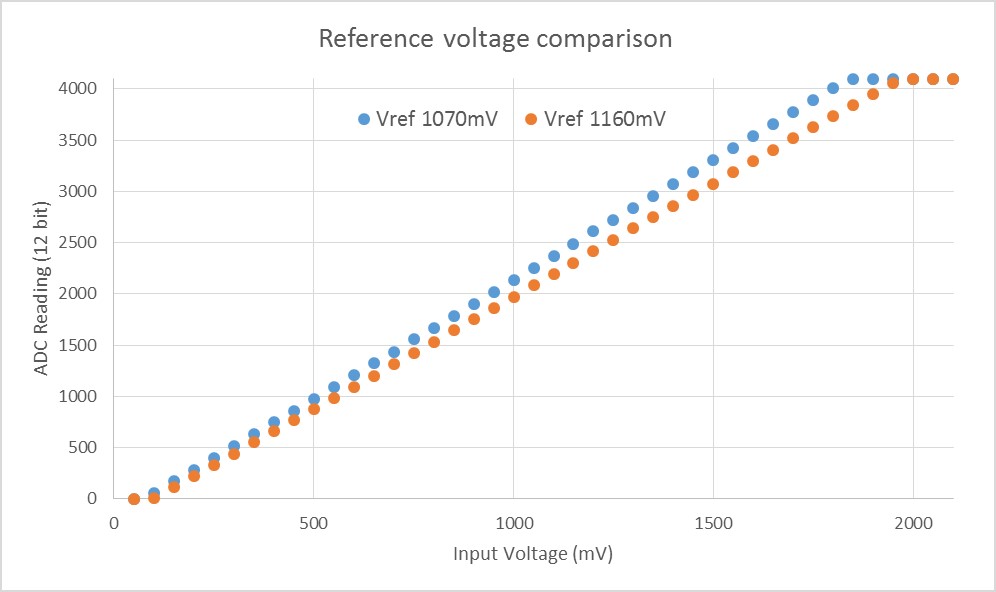
Graph illustrating effect of differing reference voltages on the ADC voltage curve.
Correcting ADC readings using this API involves characterizing one of the ADCs at a given attenuation to obtain a characteristics curve (ADC-Voltage curve) that takes into account the difference in ADC reference voltage. The characteristics curve is in the form of y = coeff_a * x + coeff_b and is used to convert ADC readings to voltages in mV. Calculation of the characteristics curve is based on calibration values which can be stored in eFuse or provided by the user.
Calibration Values
Calibration values are used to generate characteristic curves that account for the variation of ADC reference voltage of a particular ESP32 chip. There are currently 3 source(s) of calibration values on ESP32. The availability of these calibration values will depend on the type and production date of the ESP32 chip/module.
Two Point values represent each of the ADCs’ readings at 150 mV and 850 mV. To obtain more accurate calibration results these values should be measured by user and burned into eFuse
BLOCK3.eFuse Vref represents the true ADC reference voltage. This value is measured and burned into eFuse
BLOCK0during factory calibration.Default Vref is an estimate of the ADC reference voltage provided by the user as a parameter during characterization. If Two Point or eFuse Vref values are unavailable, Default Vref will be used.
Individual measurement and burning of the eFuse Vref has been applied to ESP32-D0WD and ESP32-D0WDQ6 chips produced on/after the 1st week of 2018. Such chips may be recognized by date codes on/later than 012018 (see Line 4 on figure below).
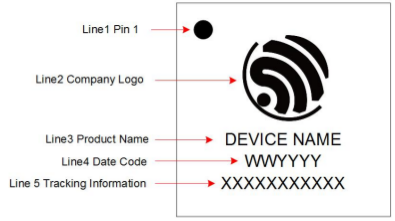
ESP32 Chip Surface Marking
If you would like to purchase chips or modules with calibration, double check with distributor or Espressif (sales@espressif.com) directly.
If you are unable to check the date code (i.e. the chip may be enclosed inside a canned module, etc.), you can still verify if eFuse Vref is present by running the espefuse.py tool with
adc_infoparameter$IDF_PATH/components/esptool_py/esptool/espefuse.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 adc_info
Replace
/dev/ttyUSB0with ESP32 board’s port name.A chip that has specific eFuse Vref value programmed (in this case 1093 mV) will be reported as follows:
ADC VRef calibration: 1093 mV
In another example below the eFuse Vref is not programmed:
ADC VRef calibration: None (1100 mV nominal)
For a chip with two point calibration the message will look similar to:
ADC VRef calibration: 1149 mV ADC readings stored in efuse BLK3: ADC1 Low reading (150 mV): 306 ADC1 High reading (850 mV): 3153 ADC2 Low reading (150 mV): 389 ADC2 High reading (850 mV): 3206
Application Extensions
For a full example see esp-idf: peripherals/adc/single_read
Characterizing an ADC at a particular attenuation:
#include "driver/adc.h"
#include "esp_adc_cal.h"
...
//Characterize ADC at particular atten
esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t *adc_chars = calloc(1, sizeof(esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t));
esp_adc_cal_value_t val_type = esp_adc_cal_characterize(unit, atten, ADC_WIDTH_BIT_12, DEFAULT_VREF, adc_chars);
//Check type of calibration value used to characterize ADC
if (val_type == ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF) {
printf("eFuse Vref");
} else if (val_type == ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP) {
printf("Two Point");
} else {
printf("Default");
}
Reading an ADC then converting the reading to a voltage:
#include "driver/adc.h"
#include "esp_adc_cal.h"
...
uint32_t reading = adc1_get_raw(ADC1_CHANNEL_5);
uint32_t voltage = esp_adc_cal_raw_to_voltage(reading, adc_chars);
Routing ADC reference voltage to GPIO, so it can be manually measured (for Default Vref):
#include "driver/adc.h"
...
esp_err_t status = adc_vref_to_gpio(ADC_UNIT_1, GPIO_NUM_25);
if (status == ESP_OK) {
printf("v_ref routed to GPIO\n");
} else {
printf("failed to route v_ref\n");
}
GPIO Lookup Macros
There are macros available to specify the GPIO number of a ADC channel, or vice versa. e.g.
ADC1_CHANNEL_0_GPIO_NUMis the GPIO number of ADC1 channel 0.ADC1_GPIOn_CHANNELis the ADC1 channel number of GPIO n.
API Reference
This reference covers three components:
ADC driver
Header File
Functions
-
void adc_power_on(void)
Enable ADC power.
- Deprecated:
Use adc_power_acquire and adc_power_release instead.
-
void adc_power_off(void)
Power off SAR ADC.
- Deprecated:
Use adc_power_acquire and adc_power_release instead. This function will force power down for ADC. This function is deprecated because forcing power ADC power off may disrupt operation of other components which may be using the ADC.
-
void adc_power_acquire(void)
Increment the usage counter for ADC module. ADC will stay powered on while the counter is greater than 0. Call adc_power_release when done using the ADC.
-
void adc_power_release(void)
Decrement the usage counter for ADC module. ADC will stay powered on while the counter is greater than 0. Call this function when done using the ADC.
-
esp_err_t adc1_pad_get_io_num(adc1_channel_t channel, gpio_num_t *gpio_num)
Get the GPIO number of a specific ADC1 channel.
- Parameters
channel – Channel to get the GPIO number
gpio_num – output buffer to hold the GPIO number
- Returns
ESP_OK if success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG if channel not valid
-
esp_err_t adc1_config_channel_atten(adc1_channel_t channel, adc_atten_t atten)
Set the attenuation of a particular channel on ADC1, and configure its associated GPIO pin mux.
The default ADC voltage is for attenuation 0 dB and listed in the table below. By setting higher attenuation it is possible to read higher voltages.
Due to ADC characteristics, most accurate results are obtained within the “suggested range” shown in the following table.
+----------+-------------+-----------------+ | | attenuation | suggested range | | SoC | (dB) | (mV) | +==========+=============+=================+ | | 0 | 100 ~ 950 | | +-------------+-----------------+ | | 2.5 | 100 ~ 1250 | | ESP32 +-------------+-----------------+ | | 6 | 150 ~ 1750 | | +-------------+-----------------+ | | 11 | 150 ~ 2450 | +----------+-------------+-----------------+ | | 0 | 0 ~ 750 | | +-------------+-----------------+ | | 2.5 | 0 ~ 1050 | | ESP32-S2 +-------------+-----------------+ | | 6 | 0 ~ 1300 | | +-------------+-----------------+ | | 11 | 0 ~ 2500 | +----------+-------------+-----------------+
For maximum accuracy, use the ADC calibration APIs and measure voltages within these recommended ranges.
Note
For any given channel, this function must be called before the first time
adc1_get_raw()is called for that channel.Note
This function can be called multiple times to configure multiple ADC channels simultaneously. You may call
adc1_get_raw()only after configuring a channel.- Parameters
channel – ADC1 channel to configure
atten – Attenuation level
- Returns
ESP_OK success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
-
esp_err_t adc1_config_width(adc_bits_width_t width_bit)
Configure ADC1 capture width, meanwhile enable output invert for ADC1. The configuration is for all channels of ADC1.
- Parameters
width_bit – Bit capture width for ADC1
- Returns
ESP_OK success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
-
int adc1_get_raw(adc1_channel_t channel)
Take an ADC1 reading from a single channel.
Note
ESP32: When the power switch of SARADC1, SARADC2, HALL sensor and AMP sensor is turned on, the input of GPIO36 and GPIO39 will be pulled down for about 80ns. When enabling power for any of these peripherals, ignore input from GPIO36 and GPIO39. Please refer to section 3.11 of ‘ECO_and_Workarounds_for_Bugs_in_ESP32’ for the description of this issue. As a workaround, call adc_power_acquire() in the app. This will result in higher power consumption (by ~1mA), but will remove the glitches on GPIO36 and GPIO39.
Note
Call
adc1_config_width()before the first time this function is called.Note
For any given channel, adc1_config_channel_atten(channel) must be called before the first time this function is called. Configuring a new channel does not prevent a previously configured channel from being read.
- Parameters
channel – ADC1 channel to read
- Returns
-1: Parameter error
Other: ADC1 channel reading.
-
esp_err_t adc_set_data_inv(adc_unit_t adc_unit, bool inv_en)
Set ADC data invert.
- Parameters
adc_unit – ADC unit index
inv_en – whether enable data invert
- Returns
ESP_OK success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
-
esp_err_t adc_set_clk_div(uint8_t clk_div)
Set ADC source clock.
- Parameters
clk_div – ADC clock divider, ADC clock is divided from APB clock
- Returns
ESP_OK success
-
esp_err_t adc_set_data_width(adc_unit_t adc_unit, adc_bits_width_t width_bit)
Configure ADC capture width.
- Parameters
adc_unit – ADC unit index
width_bit – Bit capture width for ADC unit.
- Returns
ESP_OK success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
-
void adc1_ulp_enable(void)
Configure ADC1 to be usable by the ULP.
This function reconfigures ADC1 to be controlled by the ULP. Effect of this function can be reverted using
adc1_get_raw()function.Note that adc1_config_channel_atten,
adc1_config_width()functions need to be called to configure ADC1 channels, before ADC1 is used by the ULP.
-
esp_err_t adc2_pad_get_io_num(adc2_channel_t channel, gpio_num_t *gpio_num)
Get the GPIO number of a specific ADC2 channel.
- Parameters
channel – Channel to get the GPIO number
gpio_num – output buffer to hold the GPIO number
- Returns
ESP_OK if success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG if channel not valid
-
esp_err_t adc2_config_channel_atten(adc2_channel_t channel, adc_atten_t atten)
Configure the ADC2 channel, including setting attenuation.
The default ADC voltage is for attenuation 0 dB and listed in the table below. By setting higher attenuation it is possible to read higher voltages.
Due to ADC characteristics, most accurate results are obtained within the “suggested range” shown in the following table.
+----------+-------------+-----------------+ | | attenuation | suggested range | | SoC | (dB) | (mV) | +==========+=============+=================+ | | 0 | 100 ~ 950 | | +-------------+-----------------+ | | 2.5 | 100 ~ 1250 | | ESP32 +-------------+-----------------+ | | 6 | 150 ~ 1750 | | +-------------+-----------------+ | | 11 | 150 ~ 2450 | +----------+-------------+-----------------+ | | 0 | 0 ~ 750 | | +-------------+-----------------+ | | 2.5 | 0 ~ 1050 | | ESP32-S2 +-------------+-----------------+ | | 6 | 0 ~ 1300 | | +-------------+-----------------+ | | 11 | 0 ~ 2500 | +----------+-------------+-----------------+
For maximum accuracy, use the ADC calibration APIs and measure voltages within these recommended ranges.
Note
This function also configures the input GPIO pin mux to connect it to the ADC2 channel. It must be called before calling
adc2_get_raw()for this channel.Note
For any given channel, this function must be called before the first time
adc2_get_raw()is called for that channel.- Parameters
channel – ADC2 channel to configure
atten – Attenuation level
- Returns
ESP_OK success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
-
esp_err_t adc2_get_raw(adc2_channel_t channel, adc_bits_width_t width_bit, int *raw_out)
Take an ADC2 reading on a single channel.
Note
ESP32: When the power switch of SARADC1, SARADC2, HALL sensor and AMP sensor is turned on, the input of GPIO36 and GPIO39 will be pulled down for about 80ns. When enabling power for any of these peripherals, ignore input from GPIO36 and GPIO39. Please refer to section 3.11 of ‘ECO_and_Workarounds_for_Bugs_in_ESP32’ for the description of this issue. As a workaround, call adc_power_acquire() in the app. This will result in higher power consumption (by ~1mA), but will remove the glitches on GPIO36 and GPIO39.
Note
ESP32: For a given channel,
adc2_config_channel_atten()must be called before the first time this function is called. If Wi-Fi is started viaesp_wifi_start(), this function will always fail withESP_ERR_TIMEOUT.Note
ESP32-S2: ADC2 support hardware arbiter. The arbiter is to improve the use efficiency of ADC2. After the control right is robbed by the high priority, the low priority controller will read the invalid ADC2 data. Default priority: Wi-Fi > RTC > Digital;
- Parameters
channel – ADC2 channel to read
width_bit – Bit capture width for ADC2
raw_out – the variable to hold the output data.
- Returns
ESP_OK if success
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT ADC2 is being used by other controller and the request timed out.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE The controller status is invalid. Please try again.
-
esp_err_t adc_vref_to_gpio(adc_unit_t adc_unit, gpio_num_t gpio)
Output ADC1 or ADC2’s reference voltage to
adc2_channe_t’s IO.This function routes the internal reference voltage of ADCn to one of ADC2’s channels. This reference voltage can then be manually measured for calibration purposes.
Note
ESP32 only supports output of ADC2’s internal reference voltage.
- Parameters
adc_unit – [in] ADC unit index
gpio – [in] GPIO number (Only ADC2’s channels IO are supported)
- Returns
ESP_OK: v_ref successfully routed to selected GPIO
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Unsupported GPIO
-
esp_err_t adc2_vref_to_gpio(gpio_num_t gpio)
Output ADC2 reference voltage to
adc2_channe_t’s IO.This function routes the internal reference voltage of ADCn to one of ADC2’s channels. This reference voltage can then be manually measured for calibration purposes.
- Deprecated:
Use
adc_vref_to_gpioinstead.
- Parameters
gpio – [in] GPIO number (ADC2’s channels are supported)
- Returns
ESP_OK: v_ref successfully routed to selected GPIO
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Unsupported GPIO
-
esp_err_t adc_digi_initialize(const adc_digi_init_config_t *init_config)
Initialize the Digital ADC.
- Parameters
init_config – Pointer to Digital ADC initilization config. Refer to
adc_digi_init_config_t.- Returns
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND No free interrupt found with the specified flags
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM If out of memory
ESP_OK On success
-
esp_err_t adc_digi_read_bytes(uint8_t *buf, uint32_t length_max, uint32_t *out_length, uint32_t timeout_ms)
Read bytes from Digital ADC through DMA.
- Parameters
buf – [out] Buffer to read from ADC.
length_max – [in] Expected length of data read from the ADC.
out_length – [out] Real length of data read from the ADC via this API.
timeout_ms – [in] Time to wait for data via this API, in millisecond.
- Returns
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid. Usually it means the ADC sampling rate is faster than the task processing rate.
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT Operation timed out
ESP_OK On success
-
esp_err_t adc_digi_start(void)
Start the Digital ADC and DMA peripherals. After this, the hardware starts working.
- Returns
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
ESP_OK On success
-
esp_err_t adc_digi_stop(void)
Stop the Digital ADC and DMA peripherals. After this, the hardware stops working.
- Returns
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
ESP_OK On success
-
esp_err_t adc_digi_deinitialize(void)
Deinitialize the Digital ADC.
- Returns
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
ESP_OK On success
-
esp_err_t adc_digi_controller_configure(const adc_digi_configuration_t *config)
Setting the digital controller.
- Parameters
config – Pointer to digital controller paramter. Refer to
adc_digi_config_t.- Returns
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_OK On success
-
int hall_sensor_read(void)
Read Hall Sensor.
Note
When the power switch of SARADC1, SARADC2, HALL sensor and AMP sensor is turned on, the input of GPIO36 and GPIO39 will be pulled down for about 80ns. When enabling power for any of these peripherals, ignore input from GPIO36 and GPIO39. Please refer to section 3.11 of ‘ECO_and_Workarounds_for_Bugs_in_ESP32’ for the description of this issue.
Note
The Hall Sensor uses channels 0 and 3 of ADC1. Do not configure these channels for use as ADC channels.
Note
The ADC1 module must be enabled by calling adc1_config_width() before calling hall_sensor_read(). ADC1 should be configured for 12 bit readings, as the hall sensor readings are low values and do not cover the full range of the ADC.
- Returns
The hall sensor reading.
-
esp_err_t adc_set_i2s_data_source(adc_i2s_source_t src)
Set I2S data source.
- Parameters
src – I2S DMA data source, I2S DMA can get data from digital signals or from ADC.
- Returns
ESP_OK success
-
esp_err_t adc_i2s_mode_init(adc_unit_t adc_unit, adc_channel_t channel)
Initialize I2S ADC mode.
- Parameters
adc_unit – ADC unit index
channel – ADC channel index
- Returns
ESP_OK success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Parameter error
Structures
-
struct adc_digi_init_config_s
ADC DMA driver configuration.
Public Members
-
uint32_t max_store_buf_size
Max length of the converted data that driver can store before they are processed.
-
uint32_t conv_num_each_intr
Bytes of data that can be converted in 1 interrupt.
-
uint32_t adc1_chan_mask
Channel list of ADC1 to be initialized.
-
uint32_t adc2_chan_mask
Channel list of ADC2 to be initialized.
-
uint32_t max_store_buf_size
-
struct adc_digi_configuration_t
ADC digital controller settings.
Public Members
-
bool conv_limit_en
To limit ADC conversion times. Conversion stops after finishing
conv_limit_numtimes conversion.
-
uint32_t conv_limit_num
Set the upper limit of the number of ADC conversion triggers. Range: 1 ~ 255.
-
uint32_t pattern_num
Number of ADC channels that will be used.
-
adc_digi_pattern_config_t *adc_pattern
List of configs for each ADC channel that will be used.
-
uint32_t sample_freq_hz
The expected ADC sampling frequency in Hz. Range: 611Hz ~ 83333Hz Fs = Fd / interval / 2 Fs: sampling frequency; Fd: digital controller frequency, no larger than 5M for better performance interval: interval between 2 measurement trigger signal, the smallest interval should not be smaller than the ADC measurement period, the largest interval should not be larger than 4095
-
adc_digi_convert_mode_t conv_mode
ADC DMA conversion mode, see
adc_digi_convert_mode_t.
-
adc_digi_output_format_t format
ADC DMA conversion output format, see
adc_digi_output_format_t.
-
bool conv_limit_en
Macros
-
ADC_ATTEN_0db
ADC rtc controller attenuation option.
Note
This definitions are only for being back-compatible
-
ADC_ATTEN_2_5db
-
ADC_ATTEN_6db
-
ADC_ATTEN_11db
-
ADC_WIDTH_BIT_DEFAULT
The default (max) bit width of the ADC of current version. You can also get the maximum bitwidth by
SOC_ADC_MAX_BITWIDTHdefined in soc_caps.h.
-
ADC_WIDTH_9Bit
-
ADC_WIDTH_10Bit
-
ADC_WIDTH_11Bit
-
ADC_WIDTH_12Bit
-
ADC_MAX_DELAY
Digital ADC DMA read max timeout value, it may make the
adc_digi_read_bytesblock forever if the OS supports.
Type Definitions
-
typedef struct adc_digi_init_config_s adc_digi_init_config_t
ADC DMA driver configuration.
Enumerations
-
enum adc1_channel_t
Values:
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_0
ADC1 channel 0 is GPIO36
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_1
ADC1 channel 1 is GPIO37
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_2
ADC1 channel 2 is GPIO38
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_3
ADC1 channel 3 is GPIO39
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_4
ADC1 channel 4 is GPIO32
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_5
ADC1 channel 5 is GPIO33
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_6
ADC1 channel 6 is GPIO34
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_7
ADC1 channel 7 is GPIO35
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_MAX
-
enumerator ADC1_CHANNEL_0
-
enum adc2_channel_t
Values:
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_0
ADC2 channel 0 is GPIO4 (ESP32), GPIO11 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_1
ADC2 channel 1 is GPIO0 (ESP32), GPIO12 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_2
ADC2 channel 2 is GPIO2 (ESP32), GPIO13 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_3
ADC2 channel 3 is GPIO15 (ESP32), GPIO14 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_4
ADC2 channel 4 is GPIO13 (ESP32), GPIO15 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_5
ADC2 channel 5 is GPIO12 (ESP32), GPIO16 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_6
ADC2 channel 6 is GPIO14 (ESP32), GPIO17 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_7
ADC2 channel 7 is GPIO27 (ESP32), GPIO18 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_8
ADC2 channel 8 is GPIO25 (ESP32), GPIO19 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_9
ADC2 channel 9 is GPIO26 (ESP32), GPIO20 (ESP32-S2)
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_MAX
-
enumerator ADC2_CHANNEL_0
-
enum adc_i2s_encode_t
ADC digital controller encode option.
- Deprecated:
The ESP32-S2 doesn’t use I2S DMA. Call
adc_digi_output_format_tinstead.
Values:
-
enumerator ADC_ENCODE_12BIT
ADC to DMA data format, , [15:12]-channel [11:0]-12 bits ADC data
-
enumerator ADC_ENCODE_11BIT
ADC to DMA data format, [15]-unit, [14:11]-channel [10:0]-11 bits ADC data
-
enumerator ADC_ENCODE_MAX
Header File
Structures
-
struct adc_digi_pattern_config_t
ADC digital controller pattern configuration.
-
struct adc_digi_output_data_t
ADC digital controller (DMA mode) output data format. Used to analyze the acquired ADC (DMA) data.
Note
ESP32: Only
type1is valid. ADC2 does not support DMA mode.Note
ESP32-S2: Member
channelcan be used to judge the validity of the ADC data, because the role of the arbiter may get invalid ADC data.Public Members
-
uint16_t data
ADC real output data info. Resolution: 12 bit.
ADC real output data info. Resolution: 11 bit.
-
uint16_t channel
ADC channel index info.
ADC channel index info. For ESP32-S2: If (channel < ADC_CHANNEL_MAX), The data is valid. If (channel > ADC_CHANNEL_MAX), The data is invalid.
-
struct adc_digi_output_data_t::[anonymous]::[anonymous] type1
ADC type1
-
uint16_t unit
ADC unit index info. 0: ADC1; 1: ADC2.
-
struct adc_digi_output_data_t::[anonymous]::[anonymous] type2
When the configured output format is 11bit.
ADC_DIGI_FORMAT_11BIT
-
uint16_t val
Raw data value
-
uint16_t data
Enumerations
-
enum adc_unit_t
ADC unit enumeration.
Note
For ADC digital controller (DMA mode), ESP32 doesn’t support
ADC_UNIT_2,ADC_UNIT_BOTH,ADC_UNIT_ALTER.Values:
-
enumerator ADC_UNIT_1
SAR ADC 1.
-
enumerator ADC_UNIT_2
SAR ADC 2.
-
enumerator ADC_UNIT_BOTH
SAR ADC 1 and 2.
-
enumerator ADC_UNIT_ALTER
SAR ADC 1 and 2 alternative mode.
-
enumerator ADC_UNIT_MAX
-
enumerator ADC_UNIT_1
-
enum adc_channel_t
ADC channels handle. See
adc1_channel_t,adc2_channel_t.Note
For ESP32 ADC1, don’t use
ADC_CHANNEL_8,ADC_CHANNEL_9. Seeadc1_channel_t.Values:
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_0
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_1
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_2
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_3
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_4
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_5
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_6
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_7
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_8
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_9
ADC channel
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_MAX
-
enumerator ADC_CHANNEL_0
-
enum adc_atten_t
ADC attenuation parameter. Different parameters determine the range of the ADC. See
adc1_config_channel_atten.Values:
-
enumerator ADC_ATTEN_DB_0
No input attenumation, ADC can measure up to approx. 800 mV.
-
enumerator ADC_ATTEN_DB_2_5
The input voltage of ADC will be attenuated extending the range of measurement by about 2.5 dB (1.33 x)
-
enumerator ADC_ATTEN_DB_6
The input voltage of ADC will be attenuated extending the range of measurement by about 6 dB (2 x)
-
enumerator ADC_ATTEN_DB_11
The input voltage of ADC will be attenuated extending the range of measurement by about 11 dB (3.55 x)
-
enumerator ADC_ATTEN_MAX
-
enumerator ADC_ATTEN_DB_0
-
enum adc_bits_width_t
ADC resolution setting option.
Note
Only used in single read mode
Values:
-
enumerator ADC_WIDTH_BIT_9
ADC capture width is 9Bit.
-
enumerator ADC_WIDTH_BIT_10
ADC capture width is 10Bit.
-
enumerator ADC_WIDTH_BIT_11
ADC capture width is 11Bit.
-
enumerator ADC_WIDTH_BIT_12
ADC capture width is 12Bit.
-
enumerator ADC_WIDTH_MAX
-
enumerator ADC_WIDTH_BIT_9
-
enum adc_digi_convert_mode_t
ADC digital controller (DMA mode) work mode.
Values:
-
enumerator ADC_CONV_SINGLE_UNIT_1
Only use ADC1 for conversion.
-
enumerator ADC_CONV_SINGLE_UNIT_2
Only use ADC2 for conversion.
-
enumerator ADC_CONV_BOTH_UNIT
Use Both ADC1 and ADC2 for conversion simultaneously.
-
enumerator ADC_CONV_ALTER_UNIT
Use both ADC1 and ADC2 for conversion by turn. e.g. ADC1 -> ADC2 -> ADC1 -> ADC2 …..
-
enumerator ADC_CONV_UNIT_MAX
-
enumerator ADC_CONV_SINGLE_UNIT_1
-
enum adc_digi_output_format_t
ADC digital controller (DMA mode) output data format option.
Values:
-
enumerator ADC_DIGI_FORMAT_12BIT
ADC to DMA data format, [15:12]-channel, [11: 0]-12 bits ADC data (
adc_digi_output_data_t). Note: For single convert mode.
-
enumerator ADC_DIGI_FORMAT_11BIT
ADC to DMA data format, [15]-adc unit, [14:11]-channel, [10: 0]-11 bits ADC data (
adc_digi_output_data_t). Note: For multi or alter convert mode.
-
enumerator ADC_DIGI_FORMAT_MAX
-
enumerator ADC_DIGI_OUTPUT_FORMAT_TYPE1
-
enumerator ADC_DIGI_OUTPUT_FORMAT_TYPE2
-
enumerator ADC_DIGI_FORMAT_12BIT
ADC Calibration
Header File
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_adc_cal_check_efuse(esp_adc_cal_value_t value_type)
Checks if ADC calibration values are burned into eFuse.
This function checks if ADC reference voltage or Two Point values have been burned to the eFuse of the current ESP32
Note
in ESP32S2, only ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP is supported. Some old ESP32S2s do not support this, either. In which case you have to calibrate it manually, possibly by performing your own two-point calibration on the chip.
- Parameters
value_type – Type of calibration value (ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF or ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP)
- Returns
ESP_OK: The calibration mode is supported in eFuse
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: Error, eFuse values are not burned
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Error, invalid argument (ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_DEFAULT_VREF)
-
esp_adc_cal_value_t esp_adc_cal_characterize(adc_unit_t adc_num, adc_atten_t atten, adc_bits_width_t bit_width, uint32_t default_vref, esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t *chars)
Characterize an ADC at a particular attenuation.
This function will characterize the ADC at a particular attenuation and generate the ADC-Voltage curve in the form of [y = coeff_a * x + coeff_b]. Characterization can be based on Two Point values, eFuse Vref, or default Vref and the calibration values will be prioritized in that order.
Note
For ESP32, Two Point values and eFuse Vref calibration can be enabled/disabled using menuconfig. For ESP32s2, only Two Point values calibration and only ADC_WIDTH_BIT_13 is supported. The parameter default_vref is unused.
- Parameters
adc_num – [in] ADC to characterize (ADC_UNIT_1 or ADC_UNIT_2)
atten – [in] Attenuation to characterize
bit_width – [in] Bit width configuration of ADC
default_vref – [in] Default ADC reference voltage in mV (Only in ESP32, used if eFuse values is not available)
chars – [out] Pointer to empty structure used to store ADC characteristics
- Returns
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF: eFuse Vref used for characterization
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP: Two Point value used for characterization (only in Linear Mode)
ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_DEFAULT_VREF: Default Vref used for characterization
-
uint32_t esp_adc_cal_raw_to_voltage(uint32_t adc_reading, const esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t *chars)
Convert an ADC reading to voltage in mV.
This function converts an ADC reading to a voltage in mV based on the ADC’s characteristics.
Note
Characteristics structure must be initialized before this function is called (call esp_adc_cal_characterize())
- Parameters
adc_reading – [in] ADC reading
chars – [in] Pointer to initialized structure containing ADC characteristics
- Returns
Voltage in mV
-
esp_err_t esp_adc_cal_get_voltage(adc_channel_t channel, const esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t *chars, uint32_t *voltage)
Reads an ADC and converts the reading to a voltage in mV.
This function reads an ADC then converts the raw reading to a voltage in mV based on the characteristics provided. The ADC that is read is also determined by the characteristics.
Note
The Characteristics structure must be initialized before this function is called (call esp_adc_cal_characterize())
- Parameters
channel – [in] ADC Channel to read
chars – [in] Pointer to initialized ADC characteristics structure
voltage – [out] Pointer to store converted voltage
- Returns
ESP_OK: ADC read and converted to mV
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Error due to invalid arguments
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Reading result is invalid. Try to read again.
Structures
-
struct esp_adc_cal_characteristics_t
Structure storing characteristics of an ADC.
Note
Call esp_adc_cal_characterize() to initialize the structure
Public Members
-
adc_unit_t adc_num
ADC number
-
adc_atten_t atten
ADC attenuation
-
adc_bits_width_t bit_width
ADC bit width
-
uint32_t coeff_a
Gradient of ADC-Voltage curve
-
uint32_t coeff_b
Offset of ADC-Voltage curve
-
uint32_t vref
Vref used by lookup table
-
const uint32_t *low_curve
Pointer to low Vref curve of lookup table (NULL if unused)
-
const uint32_t *high_curve
Pointer to high Vref curve of lookup table (NULL if unused)
-
uint8_t version
ADC Calibration
-
adc_unit_t adc_num
Enumerations
-
enum esp_adc_cal_value_t
Type of calibration value used in characterization.
Values:
-
enumerator ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF
Characterization based on reference voltage stored in eFuse
-
enumerator ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP
Characterization based on Two Point values stored in eFuse
-
enumerator ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_DEFAULT_VREF
Characterization based on default reference voltage
-
enumerator ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_TP_FIT
Characterization based on Two Point values and fitting curve coefficients stored in eFuse
-
enumerator ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_MAX
-
enumerator ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_NOT_SUPPORTED
-
enumerator ESP_ADC_CAL_VAL_EFUSE_VREF
GPIO Lookup Macros
Header File
Macros
-
ADC1_GPIO36_CHANNEL
-
ADC1_CHANNEL_0_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC1_GPIO37_CHANNEL
-
ADC1_CHANNEL_1_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC1_GPIO38_CHANNEL
-
ADC1_CHANNEL_2_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC1_GPIO39_CHANNEL
-
ADC1_CHANNEL_3_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC1_GPIO32_CHANNEL
-
ADC1_CHANNEL_4_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC1_GPIO33_CHANNEL
-
ADC1_CHANNEL_5_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC1_GPIO34_CHANNEL
-
ADC1_CHANNEL_6_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC1_GPIO35_CHANNEL
-
ADC1_CHANNEL_7_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO4_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_0_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO0_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_1_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO2_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_2_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO15_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_3_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO13_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_4_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO12_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_5_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO14_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_6_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO27_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_7_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO25_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_8_GPIO_NUM
-
ADC2_GPIO26_CHANNEL
-
ADC2_CHANNEL_9_GPIO_NUM