Image Signal Processor
Introduction
ESP32-P4 includes an Image Signal Processor (ISP), which is a feature pipeline that consists of many image processing algorithms. ISP receives image data from the DVP camera or MIPI-CSI camera, or system memory, and writes the processed image data to the system memory through DMA. The ISP is designed to work with other camera controller modules and cannot operate independently.
Terminology
MIPI-CSI: Camera serial interface, a high-speed serial interface for cameras compliant with MIPI specifications
DVP: Digital video parallel interface, generally composed of vsync, hsync, de, and data signals
RAW: Unprocessed data directly output from an image sensor, typically divided into R, Gr, Gb, and B four channels classified into RAW8, RAW10, RAW12, etc., based on bit width
RGB: Colored image format composed of red, green, and blue colors classified into RGB888, RGB565, etc., based on the bit width of each color
YUV: Colored image format composed of luminance and chrominance classified into YUV444, YUV422, YUV420, etc., based on the data arrangement
AF: Auto-focus
AWB: Auto-white balance
BF: Bayer noise filter
CCM: Color correction matrix
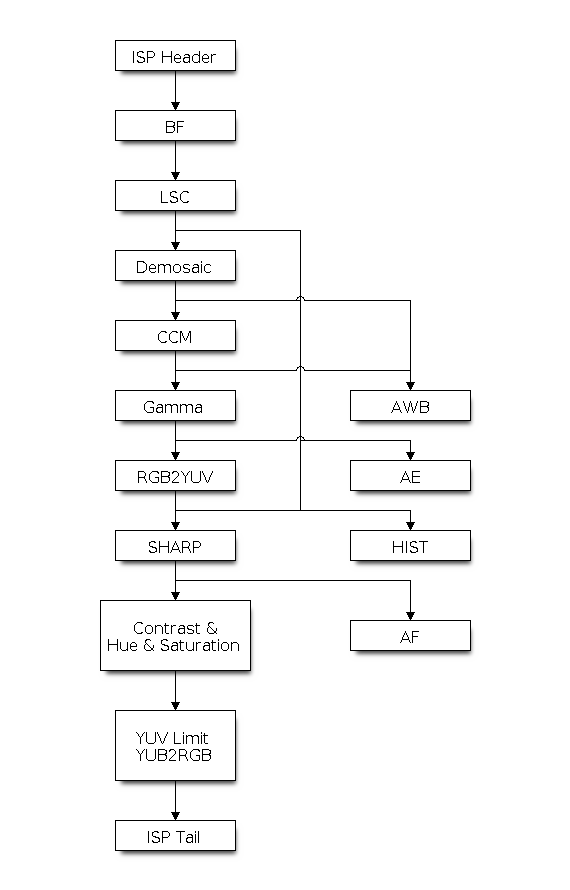
ISP Pipeline
ISP Pipeline
Functional Overview
The ISP driver offers following services:
Resource Allocation - covers how to allocate ISP resources with properly set of configurations. It also covers how to recycle the resources when they finished working.
Enable and disable ISP processor - covers how to enable and disable an ISP processor.
Get AF statistics in one shot or continuous way - covers how to get AF statistics one-shot or continuously.
Get AE statistics in one shot or continuous way - covers how to get AE statistics one-shot or continuously.
Get AWB statistics in one shot or continuous way - covers how to get AWB white patches statistics one-shot or continuously.
Get histogram statistics in one shot or continuous way - covers how to get histogram statistics one-shot or continuously.
Enable BF function - covers how to enable and configure BF function.
Enable LSC function - covers how to enable and configure LSC function.
Configure CCM - covers how to configure the Color Correction Matrix.
Configure Demosaic - covers how to config the Demosaic function.
Enable Gamma Correction - covers how to enable and configure gamma correction.
Configure Sharpen - covers how to config the Sharpen function.
Register callback - covers how to hook user specific code to ISP driver event callback function.
Thread Safety - lists which APIs are guaranteed to be thread safe by the driver.
Kconfig Options - lists the supported Kconfig options that can bring different effects to the driver.
IRAM SAFE - describes tips on how to make the ISP interrupt and control functions work better along with a disabled cache.
Resource Allocation
Install ISP Driver
ISP driver requires the configuration that specified by esp_isp_processor_cfg_t.
If the configurations in esp_isp_processor_cfg_t is specified, users can call esp_isp_new_processor() to allocate and initialize an ISP processor. This function will return an ISP processor handle if it runs correctly. You can take following code as reference.
esp_isp_processor_cfg_t isp_config = {
.clk_src = ISP_CLK_SRC_DEFAULT,
...
};
isp_proc_handle_t isp_proc = NULL;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_new_processor(&isp_config, &isp_proc));
You can use the created handle to do driver enable / disable the ISP driver and do other ISP module installation.
Install ISP Auto-Focus (AF) Driver
ISP auto-focus (AF) driver requires the configuration that specified by esp_isp_af_config_t.
If the configurations in esp_isp_af_config_t is specified, users can call esp_isp_new_af_controller() to allocate and initialize an ISP AF processor. This function will return an ISP AF processor handle if it runs correctly. You can take following code as reference.
esp_isp_af_config_t af_config = {
.edge_thresh = 128,
};
isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr = NULL;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_new_af_controller(isp_proc, &af_config, &af_ctrlr));
You can use the created handle to do driver enable / disable the ISP AF driver and ISP AF Env module installation.
Install ISP Auto-White-Balance (AWB) Driver
ISP auto-white-balance (AWB) driver requires the configuration specified by esp_isp_awb_config_t.
If an esp_isp_awb_config_t configuration is specified, you can call esp_isp_new_awb_controller() to allocate and initialize an ISP AWB processor. This function will return an ISP AWB processor handle on success. You can take following code as reference.
isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr = NULL;
uint32_t image_width = 800;
uint32_t image_height = 600;
/* The AWB configuration, please refer to the API comment for how to tune these parameters */
esp_isp_awb_config_t awb_config = {
.sample_point = ISP_AWB_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_CCM,
...
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_new_awb_controller(isp_proc, &awb_config, &awb_ctlr));
The AWB handle created in this step is required by other AWB APIs and AWB scheme.
Install ISP Auto-Exposure (AE) Driver
ISP auto-exposure (AE) driver requires the configuration that specified by esp_isp_ae_config_t.
If the configurations in esp_isp_ae_config_t is specified, users can call esp_isp_new_ae_controller() to allocate and initialize an ISP AE processor. This function will return an ISP AE processor handle if it runs correctly. You can take following code as reference.
esp_isp_ae_config_t ae_config = {
.sample_point = ISP_AE_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_DEMOSAIC,
...
};
isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr = NULL;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_new_ae_controller(isp_proc, &ae_config, &ae_ctlr));
You can use the created handle to do driver enable / disable the ISP AE driver and ISP AE environment detector setup.
Install ISP histogram (HIST) Driver
ISP histogram (HIST) driver requires the configuration that specified by esp_isp_hist_config_t.
If the configurations in esp_isp_hist_config_t is specified, users can call esp_isp_new_hist_controller() to allocate and initialize an ISP Histogram processor. This function will return an ISP HIST processor handle if it runs correctly. You can take following code as reference.
The sum of all subwindows weight's decimal value should be 256 or the statistics will be small, and integer value should be 0.
The sum of all RGB coefficients' decimal value should be 256 or the statistics will be small, and integer value should be 0.
The segment_threshold must be 0 ~ 255 and in order
esp_isp_hist_config_t hist_cfg = {
.segment_threshold = {16, 32, 48, 64, 80, 96, 112, 128, 144, 160, 176, 192, 208, 224, 240},
.hist_mode = ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_RGB,
.rgb_coefficient.coeff_r = {
.integer = 0,
.decimal = 86,
},
.rgb_coefficient.coeff_g = {
.integer = 0,
.decimal = 85,
},
.rgb_coefficient.coeff_b = {
.integer = 0,
.decimal = 85,
},
.window_weight = {
{{16, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}},
{{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}},
{{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}},
{{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}},
{{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}}, {{10, 0}},
},
};
isp_hist_ctlr_t hist_ctlr_ctlr = NULL;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_new_hist_controller(isp_proc, &hist_config, &hist_ctlr));
You can use the created handle to do driver enable / disable the ISP HIST driver setup.
Uninstall ISP Driver(s)
If a previously installed ISP driver(s) are not needed, it's recommended to recycle the resource by following APIs to release the underlying hardware:
esp_isp_del_processor(), for ISP processor.esp_isp_del_af_controller(), for ISP AF processor.esp_isp_del_awb_controller(), for ISP AWB processor.esp_isp_del_ae_controller(), for ISP AE processor.esp_isp_del_hist_controller(), for ISP Histogram processor.
Enable and Disable ISP
ISP
Before doing ISP pipeline, you need to enable the ISP processor first, by calling esp_isp_enable(). This function:
Switches the driver state from init to enable.
Calling esp_isp_disable() does the opposite, that is, put the driver back to the init state.
ISP AF Processor
Before doing ISP AF, you need to enable the ISP AF processor first, by calling esp_isp_af_controller_enable(). This function:
Switches the driver state from init to enable.
Calling esp_isp_af_controller_disable() does the opposite, that is, put the driver back to the init state.
AF One-shot and Continuous Statistics
Calling esp_isp_af_controller_get_oneshot_statistics() to get oneshot AF statistics result. You can take following code as reference.
Aside from the above oneshot API, the ISP AF driver also provides a way to start AF statistics continuously. Calling esp_isp_af_controller_start_continuous_statistics() to start the continuous statistics and esp_isp_af_controller_stop_continuous_statistics() to stop it.
Note that if you want to use the continuous statistics, you need to register the esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_env_statistics_done or esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_env_change callback to get the statistics result. See how to register in Register Event Callbacks
Note
When you use the continuous statistics, AF Environment Detector will be invalid.
esp_isp_af_config_t af_config = {
.edge_thresh = 128,
};
isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr = NULL;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_new_af_controller(isp_proc, &af_config, &af_ctrlr));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_af_controller_enable(af_ctrlr));
isp_af_result_t result = {};
/* Trigger the AF statistics and get its result for one time with timeout value 2000ms. */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_af_controller_get_oneshot_statistics(af_ctrlr, 2000, &result));
/* Start continuous AF statistics */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_af_controller_start_continuous_statistics(af_ctrlr));
// You can do other stuffs here, the statistics result can be obtained in the callback
// ......
// vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
/* Stop continuous AF statistics */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_af_controller_stop_continuous_statistics(af_ctrlr));
/* Disable the af controller */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_af_controller_disable(af_ctrlr));
/* Delete the af controller and free the resources */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_del_af_controller(af_ctrlr));
Set AF Environment Detector
Calling esp_isp_af_controller_set_env_detector() to set an ISP AF environment detector. You can take following code as reference.
esp_isp_af_env_config_t env_config = {
.interval = 10,
};
isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr = NULL;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_new_af_controller(isp_proc, &af_config, &af_ctrlr));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_af_controller_set_env_detector(af_ctrlr, &env_config));
Set AF Environment Detector Threshold
Calling esp_isp_af_env_detector_set_threshold() to set the threshold of an ISP AF environment detector.
int definition_thresh = 0;
int luminance_thresh = 0;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_af_env_detector_set_threshold(env_detector, definition_thresh, luminance_thresh));
ISP AE Processor
Before doing ISP AE, you need to enable the ISP AE processor first, by calling esp_isp_ae_controller_enable(). This function:
Switches the driver state from init to enable.
Calling esp_isp_ae_controller_disable() does the opposite, that is, put the driver back to the init state.
AE One-shot and Continuous Statistics
Calling esp_isp_ae_controller_get_oneshot_statistics() to get oneshot AE statistics result. You can take following code as reference.
When you use AE oneshot statistics, the AE continuous mode need to be disabled otherwise the result may be overwritten by the environment detector. After oneshot operation finishes, you need to restart continuous mode again.
Aside from the above oneshot API, the ISP AE driver also provides a way to start AE statistics continuously. Calling esp_isp_ae_controller_start_continuous_statistics() to start the continuous statistics and esp_isp_ae_controller_stop_continuous_statistics() to stop it.
Note that if you want to use the continuous statistics, you need to register the esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_statistics_done or esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_change callback to get the statistics result. See how to register in Register Event Callbacks
Note
When using oneshot statistics, the AE Environment Detector will be temporarily disabled and will automatically recover once the oneshot is complete.
esp_isp_ae_config_t ae_config = {
.sample_point = ISP_AE_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_DEMOSAIC,
};
isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr = NULL;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_new_ae_controller(isp_proc, &ae_config, &ae_ctlr));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ae_controller_enable(ae_ctlr));
isp_ae_result_t result = {};
/* Trigger the AE statistics and get its result for one time with timeout value 2000ms. */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ae_controller_get_oneshot_statistics(ae_ctlr, 2000, &result));
/* Start continuous AE statistics */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ae_controller_start_continuous_statistics(ae_ctlr));
// You can do other stuffs here, the statistics result can be obtained in the callback
// ......
// vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
/* Stop continuous AE statistics */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ae_controller_stop_continuous_statistics(ae_ctlr));
/* Disable the ae controller */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ae_controller_disable(ae_ctlr));
/* Delete the ae controller and free the resources */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_del_ae_controller(ae_ctlr));
Set AE Environment Detector
Calling esp_isp_ae_controller_set_env_detector() to set an ISP AE environment detector. You can take following code as reference.
esp_isp_ae_env_config_t env_config = {
.interval = 10,
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ae_controller_set_env_detector(ae_ctlr, &env_config));
Set AE Environment Detector Threshold
Calling esp_isp_ae_controller_set_env_detector_threshold() to set the thresholds(1-255) of an ISP AE environment detector.
esp_isp_ae_env_thresh_t env_thresh = {
.low_thresh = 110,
.high_thresh = 130,
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ae_controller_set_env_detector_threshold(ae_ctlr, env_thresh));
ISP AWB Processor
Before doing ISP AWB, you need to enable the ISP AWB processor first, by calling esp_isp_awb_controller_enable(). This function:
Switches the driver state from init to enable.
Calling esp_isp_awb_controller_disable() does the opposite, that is, put the driver back to the init state.
AWB One-shot and Continuous Statistics
Calling esp_isp_awb_controller_get_oneshot_statistics() to get oneshot AWB statistics result of white patches. You can take following code as reference.
Aside from the above oneshot API, the ISP AWB driver also provides a way to start AWB statistics continuously. Calling esp_isp_awb_controller_start_continuous_statistics() starts the continuous statistics and esp_isp_awb_controller_stop_continuous_statistics() stops it.
Note that if you want to use the continuous statistics, you need to register the esp_isp_awb_cbs_t::on_statistics_done callback to get the statistics result. See how to register it in Register Event Callbacks
bool example_isp_awb_on_statistics_done_cb(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr, const esp_isp_awb_evt_data_t *edata, void *user_data);
// ...
isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr = NULL;
uint32_t image_width = 800;
uint32_t image_height = 600;
/* The AWB configuration, please refer to the API comment for how to tune these parameters */
esp_isp_awb_config_t awb_config = {
.sample_point = ISP_AWB_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_CCM,
...
};
isp_awb_stat_result_t stat_res = {};
/* Create the awb controller */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_new_awb_controller(isp_proc, &awb_config, &awb_ctlr));
/* Register AWB callback */
esp_isp_awb_cbs_t awb_cb = {
.on_statistics_done = example_isp_awb_on_statistics_done_cb,
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_awb_register_event_callbacks(awb_ctlr, &awb_cb, NULL));
/* Enabled the awb controller */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_awb_controller_enable(awb_ctlr));
/* Get oneshot AWB statistics result */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_awb_controller_get_oneshot_statistics(awb_ctlr, -1, &stat_res));
/* Start continuous AWB statistics, note that continuous statistics requires `on_statistics_done` callback */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_awb_controller_start_continuous_statistics(awb_ctlr));
// You can do other stuffs here, the statistics result can be obtained in the callback
// ......
// vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
/* Stop continuous AWB statistics */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_awb_controller_stop_continuous_statistics(awb_ctlr));
/* Disable the awb controller */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_awb_controller_disable(awb_ctlr));
/* Delete the awb controller and free the resources */
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_del_awb_controller(awb_ctlr));
ISP histogram Processor
Before doing ISP histogram statistics, you need to enable the ISP histogram processor first, by calling esp_isp_hist_controller_enable(). This function:
Switches the driver state from init to enable.
Calling esp_isp_hist_controller_disable() does the opposite, that is, put the driver back to the init state.
Histogram One-shot and Continuous Statistics
Calling esp_isp_hist_controller_get_oneshot_statistics() to get oneshot histogram statistics result. You can take following code as reference.
Aside from the above oneshot API, the ISP histogram driver also provides a way to start histogram statistics continuously. Calling esp_isp_hist_controller_start_continuous_statistics() starts the continuous statistics and esp_isp_hist_controller_stop_continuous_statistics() stops it.
Note that if you want to use the continuous statistics, you need to register the esp_isp_hist_cbs_t::on_statistics_done callback to get the statistics result. See how to register it in Register Event Callbacks
static bool s_hist_scheme_on_statistics_done_callback(isp_hist_ctlr_t awb_ctrlr, const esp_isp_hist_evt_data_t *edata, void *user_data)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
esp_rom_printf(DRAM_STR("val %d is %x\n"), i, edata->hist_result.hist_value[i]); // get the histogram statistic value
}
return true;
}
esp_isp_hist_cbs_t hist_cbs = {
.on_statistics_done = s_hist_scheme_on_statistics_done_callback,
};
esp_isp_hist_register_event_callbacks(hist_ctlr, &hist_cbs, hist_ctlr);
esp_isp_hist_controller_enable(hist_ctlr);
ISP BF Processor
This pipeline is used for doing image input denoising under bayer mode.
Calling esp_isp_bf_configure() to configure BF function, you can take following code as reference.
esp_isp_bf_config_t bf_config = {
.denoising_level = 5,
.bf_template = {
{1, 2, 1},
{2, 4, 2},
{1, 2, 1},
},
...
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_bf_configure(isp_proc, &bf_config));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_bf_enable(isp_proc));
esp_isp_bf_config_t::bf_template is used for bayer denoise. You can set the esp_isp_bf_config_t::bf_template with a Gaussian filter template or an average filter template.
After calling esp_isp_bf_configure(), you need to enable the ISP BF processor, by calling esp_isp_bf_enable(). This function:
Switches the driver state from init to enable.
Calling esp_isp_bf_disable() does the opposite, that is, put the driver back to the init state.
ISP LSC Controller
Lens Shading Correction (LSC) aims for the issues caused by the uneven refraction of light through the camera lens.
Calling esp_isp_lsc_configure() to configure the LSC module to do the correction. The esp_isp_lsc_gain_array_t is necessary for the hardware to do the correction related calculation. esp_isp_lsc_allocate_gain_array() is a helper function to help allocate proper size of memory for the gains.
esp_isp_lsc_gain_array_t gain_array = {};
size_t gain_size = 0;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_lsc_allocate_gain_array(isp_proc, &gain_array, &gain_size));
esp_isp_lsc_config_t lsc_config = {
.gain_array = &gain_array,
};
isp_lsc_gain_t gain_val = {
.decimal = 204,
.integer = 0,
};
for (int i = 0; i < gain_size; i++) {
gain_array.gain_r[i].val = gain_val.val;
gain_array.gain_gr[i].val = gain_val.val;
gain_array.gain_gb[i].val = gain_val.val;
gain_array.gain_b[i].val = gain_val.val;
}
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_lsc_configure(isp_proc, &lsc_config));
After calling esp_isp_lsc_configure(), you need to enable the ISP LSC controller, by calling esp_isp_lsc_enable(). The LSC can be disabled by calling esp_isp_lsc_disable(). It's allowed to call esp_isp_lsc_configure() when the LSC isn't enabled, but the LSC function will only take effect when it's enabled.
ISP Color Processor
This pipeline is used to adjust the image contrast, saturation, hue and brightness.
Calling esp_isp_color_configure() to configure color function, you can take following code as reference.
Contrast value should be 0 ~ 1.0, default 1.0
Saturation value should be 0 ~ 1.0, default 1.0
Hue value should be 0 ~ 360, default 0
Brightness value should be --127 ~ 128, default 0
esp_isp_color_config_t color_config = {
.color_contrast = {
.integer = 1,
.decimal = 0,
},
.color_saturation = {
.integer = 1,
.decimal = 0,
},
.color_hue = 0,
.color_brightness = 0,
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_color_configure(isp_proc, &color_config));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_color_enable(isp_proc));
After calling esp_isp_color_configure(), you need to enable the ISP color processor, by calling esp_isp_color_enable(). This function:
Switches the driver state from init to enable.
Calling esp_isp_color_disable() does the opposite, that is, put the driver back to the init state.
Configure CCM
Color Correction Matrix can scale the color ratio of RGB888 pixels. It can be used for adjusting the image color via some algorithms, for example, used for white balance by inputting the AWB computed result, or used as a Filter with some filter algorithms.
To adjust the color correction matrix, here is the formula:
[ R' ] [ RR RG RB ] [ R ]
[ G' ] = [ GR GG GB ] * [ G ]
[ B' ] [ BR BG BB ] [ B ]
, and you can refer to the following code:
// ...
// Configure CCM
esp_isp_ccm_config_t ccm_cfg = {
.matrix = {
1.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0
},
.saturation = false,
...
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ccm_configure(isp_proc, &ccm_cfg));
// The configured CCM will be applied to the image once the CCM module is enabled
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ccm_enable(isp_proc));
// CCM can also be configured after it is enabled
ccm_cfg.matrix[0][0] = 2.0;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ccm_configure(isp_proc, &ccm_cfg));
// Disable CCM if no longer needed
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_ccm_disable(isp_proc));
ISP Demosaic Processor
This pipeline is used for doing image demosaic algorithm to convert RAW image to RGB mode.
Calling esp_isp_demosaic_configure() to configure Demosaic function, you can take following code as reference.
esp_isp_demosaic_config_t demosaic_config = {
.grad_ratio = {
.integer = 2,
.decimal = 5,
},
...
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_demosaic_configure(isp_proc, &sharpen_config));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_demosaic_enable(isp_proc));
After calling esp_isp_demosaic_configure(), you need to enable the ISP Sharpen processor, by calling esp_isp_demosaic_enable(). This function:
Switches the driver state from init to enable.
Calling esp_isp_demosaic_disable() does the opposite, that is, put the driver back to the init state.
esp_isp_demosaic_configure() is allowed to be called even if the driver is in init state, but the demosaic configurations will only be taken into effect when in enable state.
Enable Gamma Correction
The human visual system is non-linearly sensitive to the physical luminance. Adding gamma correction to the ISP pipeline to transforms RGB coordinates into a space in which coordinates are proportional to subjective brightness.
The driver provides a helper API esp_isp_gamma_fill_curve_points() to fill isp_gamma_curve_points_t, which is a group of points used to describe the gamma correction curve. Or you can manually declare the points as your desired 'gamma' correction curve. Each R / G / B component can have its own gamma correction curve, you can set the configuration by calling esp_isp_gamma_configure().
A typical code example is:
#include <math.h>
// Set the camera gamma to be 0.7, so the gamma correction curve is y = 256 * (x / 256) ^ 0.7
static uint32_t s_gamma_curve(uint32_t x)
{
return pow((double)x / 256, 0.7) * 256;
}
isp_gamma_curve_points_t pts = {};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_gamma_fill_curve_points(s_gamma_curve, &pts));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_gamma_configure(isp_proc, COLOR_COMPONENT_R, &pts));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_gamma_configure(isp_proc, COLOR_COMPONENT_G, &pts));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_gamma_configure(isp_proc, COLOR_COMPONENT_B, &pts));
// Enable gamma module after curve parameters configured
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_gamma_enable(isp_proc));
// Disable gamma if no longer needed
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_gamma_disable(isp_proc));
ISP Sharpen Processor
This pipeline is used for doing image input sharpening under YUV mode.
Calling esp_isp_sharpen_configure() to configure Sharpen function, you can take following code as reference.
esp_isp_sharpen_config_t sharpen_config = {
.h_thresh = 255,
.sharpen_template = {
{1, 2, 1},
{2, 4, 2},
{1, 2, 1},
},
...
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_sharpen_configure(isp_proc, &sharpen_config));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(esp_isp_sharpen_enable(isp_proc));
esp_isp_sharpen_config_t::sharpen_template is used for sharpening. You can set the esp_isp_sharpen_config_t::sharpen_template with a Gaussian filter template or an average filter template.
After calling esp_isp_sharpen_configure(), you need to enable the ISP Sharpen processor, by calling esp_isp_sharpen_enable(). This function:
Switches the driver state from init to enable.
Calling esp_isp_sharpen_disable() does the opposite, that is, put the driver back to the init state.
esp_isp_sharpen_configure() is allowed to be called even if the driver is in init state, but the sharpen configurations will only be taken into effect when in enable state.
Register Event Callbacks
After an ISP module starts up, it can generate a specific event dynamically.
You can save your own context to callback function as well, via the parameter user_data. The user data will be directly passed to the callback function.
Note
The below mentioned callback functions are called within an ISR context, you must ensure that the functions do not attempt to block (e.g., by making sure that only FreeRTOS APIs with ISR suffix are called from within the function).
Register ISP Processor Event Callbacks
After the ISP processor is enabled, it can generate multiple events of multiple ISP submodules dynamically. You can hook your functions to the interrupt service routine by calling esp_isp_register_event_callbacks(). All supported event callbacks are listed in esp_isp_evt_cbs_t:
esp_isp_evt_cbs_t::on_sharpen_frame_done. sets a callback function for sharpen frame done. It will be called after the ISP sharpen submodule finishes its operation for one frame. The function prototype is declared inesp_isp_sharpen_callback_t.
Register ISP AF Environment Detector Event Callbacks
After the ISP AF environment detector starts up, it can generate a specific event dynamically. If you have some functions that should be called when the event happens, please hook your function to the interrupt service routine by calling esp_isp_af_env_detector_register_event_callbacks(). All supported event callbacks are listed in esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_cbs_t:
esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_env_statistics_donesets a callback function for environment statistics done. The function prototype is declared inesp_isp_af_env_detector_callback_t.esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_env_changesets a callback function for environment change. The function prototype is declared inesp_isp_af_env_detector_callback_t.
Register ISP AWB Statistics Done Event Callbacks
After the ISP AWB controller finished statistics of white patches, it can generate a specific event dynamically. If you want to be informed when the statistics done event takes place, please hook your function to the interrupt service routine by calling esp_isp_awb_register_event_callbacks(). All supported event callbacks are listed in esp_isp_awb_cbs_t:
esp_isp_awb_cbs_t::on_statistics_donesets a callback function when finished statistics of the white patches. The function prototype is declared inesp_isp_awb_callback_t.
Register ISP AE Environment Detector Event Callbacks
After the ISP AE environment detector starts up, it can generate a specific event dynamically. If you have some functions that should be called when the event happens, please hook your function to the interrupt service routine by calling esp_isp_ae_env_detector_register_event_callbacks(). All supported event callbacks are listed in esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_cbs_t:
esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_env_statistics_donesets a callback function for environment statistics done. . The function prototype is declared inesp_isp_ae_env_detector_callback_t.esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_env_changesets a callback function for environment change. . The function prototype is declared inesp_isp_ae_env_detector_callback_t.
Register ISP HIST Statistics Done Event Callbacks
After the ISP HIST controller finished statistics of brightness, it can generate a specific event dynamically. If you want to be informed when the statistics done event takes place, please hook your function to the interrupt service routine by calling esp_isp_hist_register_event_callbacks(). All supported event callbacks are listed in esp_isp_hist_cbs_t:
esp_isp_hist_cbs_t::on_statistics_donesets a callback function when finished statistics of the brightness. . The function prototype is declared inesp_isp_hist_callback_t.
Thread Safety
The factory function
are guaranteed to be thread safe by the driver, which means, user can call them from different RTOS tasks without protection by extra locks. Other APIs are not guaranteed to be thread-safe.
Kconfig Options
CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAFE controls whether the default ISR handler should be masked when the cache is disabled
IRAM Safe
By default, the ISP interrupt will be deferred when the cache is disabled because of writing or erasing the flash.
Kconfig option CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAFE will:
Enable the interrupt being serviced even when the cache is disabled
Place all functions that used by the ISR into IRAM
Place driver object into DRAM (in case it is mapped to PSRAM by accident)
This allows the interrupt to run while the cache is disabled, but comes at the cost of increased IRAM consumption. With this option enabled, the ISR callbacks will be running when cache is disabled. Therefore you should make sure the callbacks and its involved context are IRAM-safe as well.
Kconfig option CONFIG_ISP_CTRL_FUNC_IN_IRAM will:
Place some of ISP control functions into IRAM, function list:
Application Examples
peripherals/isp/multi_pipelines demonstrates how to use the ISP pipelines to process the image signals from camera sensors and display the video on LCD screen via DSI peripheral.
API Reference
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "hal/isp_types.h"
Unions
-
union isp_demosaic_grad_ratio_t
- #include <isp_types.h>
Gradient ratio.
-
union isp_sharpen_h_freq_coeff_t
- #include <isp_types.h>
High freq pixel sharpeness coeff.
-
union isp_sharpen_m_freq_coeff
- #include <isp_types.h>
Medium freq pixel sharpeness coeff.
-
union isp_hist_weight_t
- #include <isp_types.h>
ISP histogram weight value.
-
union isp_hist_coeff_t
- #include <isp_types.h>
ISP histogram coefficient value.
-
union isp_color_contrast_t
- #include <isp_types.h>
Color contrast value.
-
union isp_color_saturation_t
- #include <isp_types.h>
Color saturation value.
-
union isp_lsc_gain_t
- #include <isp_types.h>
LSC gain.
Structures
-
struct isp_coordinate_t
ISP coordinate type.
-
struct isp_window_t
The top left and bottom right coordinates of ISP full window.
Public Members
-
isp_coordinate_t top_left
The top left point coordinate.
-
isp_coordinate_t btm_right
The bottom right point coordinate.
-
isp_coordinate_t top_left
-
struct isp_gamma_curve_points_t
Structure that declares the points on an ISP gamma curve.
Constraint on pt[n].x: When n = 0, pt[n].x = 2 ^ a[n] When 0 < n < ISP_GAMMA_CURVE_POINTS_NUM-1, pt[n].x - pt[n-1].x = 2 ^ a[n] When n = ISP_GAMMA_CURVE_POINTS_NUM-1, pt[n].x = 255, (pt[n].x + 1) - pt[n-1].x = 2 ^ a[n] a[n] within [0, 7]
Public Members
-
uint8_t x
Raw value (0, 255].
-
uint8_t y
gamma-corrected value (0, 255]
-
struct isp_gamma_curve_points_t::[anonymous] pt[ISP_GAMMA_CURVE_POINTS_NUM]
Point (x, y)
-
uint8_t x
-
struct isp_hist_rgb_coefficient_t
ISP histogram r,g,b coefficient.
Public Members
-
isp_hist_coeff_t coeff_r
R coefficient.
-
isp_hist_coeff_t coeff_g
G coefficient.
-
isp_hist_coeff_t coeff_b
B coefficient.
-
isp_hist_coeff_t coeff_r
Macros
-
ISP_AE_BLOCK_X_NUM
-
ISP_AE_BLOCK_Y_NUM
-
ISP_AF_WINDOW_NUM
-
ISP_BF_TEMPLATE_X_NUMS
-
ISP_BF_TEMPLATE_Y_NUMS
-
ISP_CCM_DIMENSION
ISP Color Correction Matrix dimension.
-
ISP_DEMOSAIC_GRAD_RATIO_INT_BITS
-
ISP_DEMOSAIC_GRAD_RATIO_DEC_BITS
-
ISP_DEMOSAIC_GRAD_RATIO_RES_BITS
-
ISP_DVP_DATA_SIG_NUM
-
ISP_SHARPEN_TEMPLATE_X_NUMS
-
ISP_SHARPEN_TEMPLATE_Y_NUMS
-
ISP_SHARPEN_H_FREQ_COEF_INT_BITS
-
ISP_SHARPEN_H_FREQ_COEF_DEC_BITS
-
ISP_SHARPEN_H_FREQ_COEF_RES_BITS
-
ISP_SHARPEN_M_FREQ_COEF_INT_BITS
-
ISP_SHARPEN_M_FREQ_COEF_DEC_BITS
-
ISP_SHARPEN_M_FREQ_COEF_RES_BITS
-
ISP_GAMMA_CURVE_POINTS_NUM
Number of points to define a gamma correction curve.
-
ISP_HIST_BLOCK_X_NUM
-
ISP_HIST_BLOCK_Y_NUM
-
ISP_HIST_SEGMENT_NUMS
-
ISP_HIST_INTERVAL_NUMS
-
ISP_HIST_WEIGHT_INT_BITS
-
ISP_HIST_WEIGHT_DEC_BITS
-
ISP_HIST_WEIGHT_RES_BITS
-
ISP_HIST_COEFF_INT_BITS
-
ISP_HIST_COEFF_DEC_BITS
-
ISP_HIST_COEFF_RES_BITS
-
ISP_COLOR_CONTRAST_INT_BITS
-
ISP_COLOR_CONTRAST_DEC_BITS
-
ISP_COLOR_CONTRAST_RES_BITS
-
ISP_COLOR_SATURATION_INT_BITS
-
ISP_COLOR_SATURATION_DEC_BITS
-
ISP_COLOR_SATURATION_RES_BITS
-
ISP_LSC_GRAD_RATIO_INT_BITS
-
ISP_LSC_GRAD_RATIO_DEC_BITS
-
ISP_LSC_GRAD_RATIO_RES_BITS
Type Definitions
-
typedef soc_periph_isp_clk_src_t isp_clk_src_t
Clock source type of ISP.
Enumerations
-
enum isp_input_data_source_t
ISP Input Source.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_INPUT_DATA_SOURCE_CSI
Input data from CSI.
-
enumerator ISP_INPUT_DATA_SOURCE_DVP
Input data from DVP.
-
enumerator ISP_INPUT_DATA_SOURCE_DWGDMA
Input data from DW-GDMA.
-
enumerator ISP_INPUT_DATA_SOURCE_CSI
-
enum isp_color_t
ISP Color Type.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_RAW8
RAW8.
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_RAW10
RAW10.
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_RAW12
RAW12.
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_RGB888
RGB888.
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_RGB565
RGB565.
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_YUV422
YUV422.
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_YUV420
YUV420.
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_RAW8
-
enum isp_color_range_t
ISP color range.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_RANGE_LIMIT
Limited color range
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_RANGE_FULL
Full color range
-
enumerator ISP_COLOR_RANGE_LIMIT
-
enum isp_yuv_conv_std_t
The standard used for conversion between RGB and YUV.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_YUV_CONV_STD_BT601
YUV<->RGB conversion standard: BT.601
-
enumerator ISP_YUV_CONV_STD_BT709
YUV<->RGB conversion standard: BT.709
-
enumerator ISP_YUV_CONV_STD_BT601
-
enum isp_ae_sample_point_t
ISP AE input data source.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_AE_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_DEMOSAIC
AE input data after demosaic.
-
enumerator ISP_AE_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_GAMMA
AE input data after gamma.
-
enumerator ISP_AE_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_DEMOSAIC
-
enum isp_awb_sample_point_t
ISP AWB sample point in the ISP pipeline.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_AWB_SAMPLE_POINT_BEFORE_CCM
Sample AWB data before CCM (Color Correction Matrix)
-
enumerator ISP_AWB_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_CCM
Sample AWB data after CCM (Color Correction Matrix)
-
enumerator ISP_AWB_SAMPLE_POINT_BEFORE_CCM
-
enum isp_bf_edge_padding_mode_t
ISP BF edge padding mode.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_BF_EDGE_PADDING_MODE_SRND_DATA
Fill BF edge padding data with surrounding pixel data.
-
enumerator ISP_BF_EDGE_PADDING_MODE_CUSTOM_DATA
Fill BF edge padding data with custom pixel data.
-
enumerator ISP_BF_EDGE_PADDING_MODE_SRND_DATA
-
enum isp_demosaic_edge_padding_mode_t
ISP Demosaic edge padding mode.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_DEMOSAIC_EDGE_PADDING_MODE_SRND_DATA
Fill Demosaic edge padding data with surrounding pixel data.
-
enumerator ISP_DEMOSAIC_EDGE_PADDING_MODE_CUSTOM_DATA
Fill Demosaic edge padding data with custom pixel data.
-
enumerator ISP_DEMOSAIC_EDGE_PADDING_MODE_SRND_DATA
-
enum isp_sharpen_edge_padding_mode_t
ISP Sharpen edge padding mode.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_SHARPEN_EDGE_PADDING_MODE_SRND_DATA
Fill Sharpen edge padding data with surrounding pixel data.
-
enumerator ISP_SHARPEN_EDGE_PADDING_MODE_CUSTOM_DATA
Fill Sharpen edge padding data with custom pixel data.
-
enumerator ISP_SHARPEN_EDGE_PADDING_MODE_SRND_DATA
-
enum isp_hist_sampling_mode_t
ISP histogram mode.
Values:
-
enumerator ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_RAW_B
histogram mode for B component of raw image
-
enumerator ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_RAW_GB
histogram mode for GB component of raw image
-
enumerator ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_RAW_GR
histogram mode for GR component of raw image
-
enumerator ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_RAW_R
histogram mode for R component of raw image
-
enumerator ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_RGB
histogram mode for RGB
-
enumerator ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_YUV_Y
histogram mode for Y component for YUV
-
enumerator ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_YUV_U
histogram mode for U component for YUV
-
enumerator ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_YUV_V
histogram mode for V component for YUV
-
enumerator ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_RAW_B
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_types.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Structures
-
struct isp_u32_range_t
ISP unsigned integer range type.
Note
Whether the edge value are included depends on the variable itself
-
struct isp_float_range_t
ISP float range type.
Note
Whether the edge value are included depends on the variable itself
-
struct isp_af_result_t
ISP AF result.
-
struct isp_awb_stat_result_t
ISP AWB result.
-
struct isp_ae_result_t
ISP AE result.
Public Members
-
int luminance[ISP_AE_BLOCK_X_NUM][ISP_AE_BLOCK_Y_NUM]
Luminance, it refers how luminant an image is.
-
int luminance[ISP_AE_BLOCK_X_NUM][ISP_AE_BLOCK_Y_NUM]
-
struct esp_isp_sharpen_evt_data_t
Event data structure.
Public Members
-
uint8_t high_freq_pixel_max
high freq pixel max value
-
uint8_t high_freq_pixel_max
-
struct esp_isp_evt_cbs_t
Group of ISP event callbacks.
Note
These callbacks are all running in an ISR environment.
Note
When CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. Involved variables should be in internal RAM as well.
Public Members
-
esp_isp_sharpen_callback_t on_sharpen_frame_done
Event callback, invoked when sharpen frame done.
-
esp_isp_sharpen_callback_t on_sharpen_frame_done
Type Definitions
-
typedef struct isp_processor_t *isp_proc_handle_t
Type of ISP processor handle.
-
typedef struct isp_af_controller_t *isp_af_ctlr_t
Type of ISP AF controller handle.
-
typedef struct isp_awb_controller_t *isp_awb_ctlr_t
Type of ISP AWB controller handle.
-
typedef struct isp_ae_controller_t *isp_ae_ctlr_t
Type of ISP AE controller handle.
-
typedef struct isp_hist_controller_t *isp_hist_ctlr_t
Type of ISP HIST controller handle.
-
typedef bool (*esp_isp_sharpen_callback_t)(isp_proc_handle_t proc, const esp_isp_sharpen_evt_data_t *edata, void *user_data)
Prototype of ISP sharpen event callback.
- Param proc
[in] Processor handle
- Param edata
[in] ISP sharpen event data
- Param user_data
[in] User registered context, registered when in
esp_isp_register_event_callbacks()- Return
Whether a high priority task is woken up by this function
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_af.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_new_af_controller(isp_proc_handle_t isp_proc, const esp_isp_af_config_t *af_config, isp_af_ctlr_t *ret_hdl)
New an ISP AF controller.
- Parameters
isp_proc -- [in] ISP Processor handle
af_config -- [in] Pointer to AF config. Refer to
esp_isp_af_config_t.ret_hdl -- [out] AF controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Invalid state
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND No free interrupt found with the specified flags
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM If out of memory
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_del_af_controller(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr)
Delete an ISP AF controller.
- Parameters
af_ctrlr -- [in] AF controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_af_controller_enable(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr)
Enable an ISP AF controller.
- Parameters
af_ctrlr -- [in] AF controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_af_controller_disable(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr)
Disable an ISP AF controller.
- Parameters
af_ctrlr -- [in] AF controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_af_controller_get_oneshot_statistics(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr, int timeout_ms, isp_af_result_t *out_res)
Trigger AF luminance and definition statistics for one time and get the result.
- Parameters
af_ctrlr -- [in] AF controller handle
timeout_ms -- [in] Timeout in millisecond
timeout_ms < 0: Won't return until finished
timeout_ms = 0: No timeout, trigger one time statistics and return immediately, in this case, the result won't be assigned in this function, but you can get the result in the callback
esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_env_statistics_donetimeout_ms > 0: Wait for specified milliseconds, if not finished, then return timeout error
out_res -- [out] AF luminance and definition statistics result, can be NULL if
timeout_ms = 0
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT If the waiting time exceeds the specified timeout.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_af_controller_start_continuous_statistics(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr)
Start AF continuous statistics of the luminance and definition in the windows.
Note
This function is an asynchronous and non-block function, it will start the continuous statistics and return immediately. You have to register the AF callback and get the result from the callback event data.
Note
When continuous mode start, AF environment detector will be invalid
- Parameters
af_ctrlr -- [in] AF controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Null pointer
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_af_controller_stop_continuous_statistics(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr)
Stop AF continuous statistics of the luminance and definition in the windows.
- Parameters
af_ctrlr -- [in] AF controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Null pointer
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_af_controller_set_env_detector(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr, const esp_isp_af_env_config_t *env_config)
Set ISP AF environment detector.
Note
When continuous mode start, AF environment detector will be invalid
- Parameters
af_ctrlr -- [in] AF controller handle
env_config -- [in] AF Env detector configuration
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_af_controller_set_env_detector_threshold(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr, int definition_thresh, int luminance_thresh)
Set ISP AF environment detector detecting threshold.
- Parameters
af_ctrlr -- [in] AF controller handle
definition_thresh -- [in] Threshold for definition
luminance_thresh -- [in] Threshold for luminance
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_af_env_detector_register_event_callbacks(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr, const esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_cbs_t *cbs, void *user_data)
Register AF environment detector event callbacks.
Note
User can deregister a previously registered callback by calling this function and setting the to-be-deregistered callback member in the
cbsstructure to NULL.Note
When CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. Involved variables (including
user_data) should be in internal RAM as well.- Parameters
af_ctrlr -- [in] AF controller handle
cbs -- [in] Group of callback functions
user_data -- [in] User data, which will be delivered to the callback functions directly
- Returns
ESP_OK: On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Invalid arguments
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Driver state is invalid, you shouldn't call this API at this moment
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_af_config_t
AF controller config.
Public Members
-
isp_window_t window[ISP_AF_WINDOW_NUM]
The sampling windows of AF.
-
int edge_thresh
Edge threshold, definition higher than this value will be counted as a valid pixel for calculating AF result.
-
int intr_priority
The interrupt priority, range 0~3, if set to 0, the driver will try to allocate an interrupt with a relative low priority (1,2,3)
-
isp_window_t window[ISP_AF_WINDOW_NUM]
-
struct esp_isp_af_env_config_t
AF environment detector config.
Public Members
-
int interval
Interval between environment detection, in frames. i.e., AF controller will trigger the statistic periodically to detect the environment change.
-
int interval
-
struct esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_data_t
Event data structure.
Public Members
-
isp_af_result_t af_result
The AF statistics result
-
isp_af_result_t af_result
-
struct esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_cbs_t
Group of ISP AF Env detector callbacks.
Note
These callbacks are all running in an ISR environment.
Note
When CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. Involved variables should be in internal RAM as well.
Public Members
-
esp_isp_af_env_detector_callback_t on_env_statistics_done
Event callback, invoked when environment sample done.
-
esp_isp_af_env_detector_callback_t on_env_change
Event callback, invoked when environment change happens.
-
esp_isp_af_env_detector_callback_t on_env_statistics_done
Type Definitions
-
typedef bool (*esp_isp_af_env_detector_callback_t)(isp_af_ctlr_t af_ctrlr, const esp_isp_af_env_detector_evt_data_t *edata, void *user_data)
Prototype of ISP AF Env detector event callback.
- Param af_ctrlr
[in] ISP AF controller handle
- Param edata
[in] ISP AF Env detector event data
- Param user_data
[in] User registered context, registered when in
esp_isp_af_env_detector_register_event_callbacks()- Return
Whether a high priority task is woken up by this function
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_ae.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_new_ae_controller(isp_proc_handle_t isp_proc, const esp_isp_ae_config_t *ae_config, isp_ae_ctlr_t *ret_hdl)
New an ISP AE controller.
- Parameters
isp_proc -- [in] ISP Processor handle
ae_config -- [in] Pointer to AE config. Refer to
esp_isp_ae_config_t.ret_hdl -- [out] AE controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Invalid state
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND No free interrupt found with the specified flags
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM If out of memory
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_del_ae_controller(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr)
Delete an ISP AE controller.
- Parameters
ae_ctlr -- [in] AE controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ae_controller_enable(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr)
Enable an ISP AE controller.
- Parameters
ae_ctlr -- [in] AE controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ae_controller_disable(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr)
Disable an ISP AE controller.
- Parameters
ae_ctlr -- [in] AE controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ae_controller_get_oneshot_statistics(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr, int timeout_ms, isp_ae_result_t *out_res)
Trigger AE luminance statistics for one time and get the result.
- Parameters
ae_ctlr -- [in] AE controller handle
timeout_ms -- [in] Timeout in millisecond
timeout_ms < 0: Won't return until finished
timeout_ms = 0: No timeout, trigger one time statistics and return immediately, in this case, the result won't be assigned in this function, but you can get the result in the callback
esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_cbs_t::on_env_statistics_donetimeout_ms > 0: Wait for specified milliseconds, if not finished, then return timeout error
out_res -- [out] AE luminance statistics result, can be NULL if
timeout_ms = 0
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT If the waiting time exceeds the specified timeout.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ae_controller_start_continuous_statistics(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr)
Start AE continuous statistics of the luminance in the windows.
Note
This function is an asynchronous and non-block function, it will start the continuous statistics and return immediately. You have to register the AE callback and get the result from the callback event data.
Note
When using oneshot statistics, the AE Environment Detector will be temporarily disabled and will automatically recover once the oneshot is complete.
- Parameters
ae_ctlr -- [in] AE controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Null pointer
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ae_controller_stop_continuous_statistics(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr)
Stop AE continuous statistics of the luminance in the windows.
- Parameters
ae_ctlr -- [in] AE controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Null pointer
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ae_controller_set_env_detector(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr, const esp_isp_ae_env_config_t *env_config)
Set ISP AE environment detector.
- Parameters
ae_ctlr -- [in] AE controller handle
env_config -- [in] AE Env detector configuration
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ae_controller_set_env_detector_threshold(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr, const esp_isp_ae_env_thresh_t *env_thresh)
Set ISP AE environment detector detecting threshold.
- Parameters
ae_ctlr -- [in] AE controller handle
env_thresh -- [in] Luminance thresholds for AE env detector
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ae_env_detector_register_event_callbacks(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr, const esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_cbs_t *cbs, void *user_data)
Register AE Env detector event callbacks.
Note
User can deregister a previously registered callback by calling this function and setting the to-be-deregistered callback member in the
cbsstructure to NULL.Note
When CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAEE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. Involved variables (including
user_data) should be in internal RAM as well.- Parameters
ae_ctlr -- [in] AE controller handle
cbs -- [in] Group of callback functions
user_data -- [in] User data, which will be delivered to the callback functions directly
- Returns
ESP_OK: On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Invalid arguments
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Driver state is invalid, you shouldn't call this API at this moment
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_ae_config_t
AE controller config.
Public Members
-
isp_ae_sample_point_t sample_point
The input data source, ISP_AE_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_DEMOSAIC: AE input data after demosaic, ISP_AE_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_GAMMA: AE input data after gamma.
-
isp_window_t window
The sampling windows of AE.
-
int intr_priority
The interrupt priority, range 0~3, if set to 0, the driver will try to allocate an interrupt with a relative low priority (1,2,3)
-
isp_ae_sample_point_t sample_point
-
struct esp_isp_ae_env_config_t
AE environment detector config.
Public Members
-
int interval
Interval between environment detection, in frames. i.e., AE controller will trigger the statistic periodically to detect the environment change.
-
int interval
-
struct esp_isp_ae_env_thresh_t
AE environment detector config.
-
struct esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_data_t
Event data structure.
Public Members
-
isp_ae_result_t ae_result
The AE statistics result
-
isp_ae_result_t ae_result
-
struct esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_cbs_t
Group of ISP AE env_detector.
Note
These callbacks are all running in an ISR environment.
Note
When CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAEE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. Involved variables should be in internal RAM as well.
Public Members
-
esp_isp_ae_env_detector_callback_t on_env_statistics_done
Event callback, invoked when environment sample done.
-
esp_isp_ae_env_detector_callback_t on_env_change
Event callback, invoked when environment change happens.
-
esp_isp_ae_env_detector_callback_t on_env_statistics_done
Type Definitions
-
typedef bool (*esp_isp_ae_env_detector_callback_t)(isp_ae_ctlr_t ae_ctlr, const esp_isp_ae_env_detector_evt_data_t *edata, void *user_data)
Prototype of ISP AE Env detector event callback.
- Param ae_ctlr
[in] ISP AE controller handle
- Param edata
[in] ISP AE Env detector event data
- Param user_data
[in] User registered context, registered when in
esp_isp_ae_env_detector_register_event_callbacks()- Return
Whether a high priority task is woken up by this function
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_awb.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_new_awb_controller(isp_proc_handle_t isp_proc, const esp_isp_awb_config_t *awb_cfg, isp_awb_ctlr_t *ret_hdl)
New an ISP AWB controller.
- Parameters
isp_proc -- [in] ISP Processor handle
awb_cfg -- [in] Pointer to AWB config. Refer to
esp_isp_awb_config_t.ret_hdl -- [out] AWB controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Invalid state
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND No free interrupt found with the specified flags
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM If out of memory
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_del_awb_controller(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr)
Delete an ISP AWB controller.
- Parameters
awb_ctlr -- [in] AWB controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_awb_controller_reconfig(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr, const esp_isp_awb_config_t *awb_cfg)
Reconfigure the ISP AWB controller.
Note
This function is allowed to be called no matter the awb controller is enabled or not.
- Parameters
awb_ctlr -- [in] AWB controller handle
awb_cfg -- [in] Pointer to AWB config. Refer to
esp_isp_awb_config_t
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_awb_controller_enable(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr)
Enable an ISP AWB controller.
- Parameters
awb_ctlr -- [in] AWB controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_awb_controller_disable(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr)
Disable an ISP AWB controller.
- Parameters
awb_ctlr -- [in] AWB controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_awb_controller_get_oneshot_statistics(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr, int timeout_ms, isp_awb_stat_result_t *out_res)
Trigger AWB white patch statistics for one time and get the result.
- Parameters
awb_ctlr -- [in] AWB controller handle
timeout_ms -- [in] Timeout in millisecond
timeout_ms < 0: Won't return until finished
timeout_ms = 0: No timeout, trigger one time statistics and return immediately, in this case, the result won't be assigned in this function, but you can get the result in the callback
esp_isp_awb_cbs_t::on_statistics_donetimeout_ms > 0: Wait for specified milliseconds, if not finished, then return timeout error
out_res -- [out] AWB white patch statistics result
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT Wait for the result timeout
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_awb_controller_start_continuous_statistics(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr)
Start AWB continuous statistics of the white patch in the window.
Note
This function is an asynchronous and non-block function, it will start the continuous statistics and return immediately. You have to register the AWB callback and get the result from the callback event data.
- Parameters
awb_ctlr -- [in] AWB controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Null pointer
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_awb_controller_stop_continuous_statistics(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr)
Stop AWB continuous statistics of the white patch in the window.
- Parameters
awb_ctlr -- [in] AWB controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Null pointer
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_awb_register_event_callbacks(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr, const esp_isp_awb_cbs_t *cbs, void *user_data)
Register AWB event callbacks.
Note
User can deregister a previously registered callback by calling this function and setting the to-be-deregistered callback member in the
cbsstructure to NULL.Note
When CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. Involved variables (including
user_data) should be in internal RAM as well.- Parameters
awb_ctlr -- [in] AWB controller handle
cbs -- [in] Group of callback functions
user_data -- [in] User data, which will be delivered to the callback functions directly
- Returns
ESP_OK: On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Invalid arguments
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Driver state is invalid, you shouldn't call this API at this moment
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_awb_config_t
AWB controller config.
Public Members
-
isp_awb_sample_point_t sample_point
AWB sample point of the ISP pipeline. ISP_AWB_SAMPLE_POINT_BEFORE_CCM: sample before Color Correction Matrix(CCM). ISP_AWB_SAMPLE_POINT_AFTER_CCM: sample after Color Correction Matrix(CCM). If your camera support to set the manual gain to the RGB channels, then you can choose to sample before CCM, and set the gain to the camera registers. If your camera doesn't support the manual gain or don't want to change the camera configuration, then you can choose to sample after CCM, and set the calculated gain to the CCM
-
isp_window_t window
Statistic window of AWB. Suggest to set it at the middle of the image and a little smaller than the whole image. It will be more reliable because the edges of image are easily to be overexposure, the overexposure pixels are almost at maximum luminance, which are not good references to calculate the gain for white balance.
-
isp_u32_range_t luminance
Luminance range of the white patch. Range [0, 255 * 3] Not suggest to set the max value to 255 * 3, because these pixels are too bright, very possible to be overexposure. So the pixels that too bright should not be the reference of the white balance. And the minimum value better to be 0 to allow the white balance work under low luminance environment.
-
isp_float_range_t red_green_ratio
Red to green ratio of the white patch. Range [0, 4.0). The ratio could be as wider as possible, so that all the distorted pixels will be counted for the reference of white balance.
-
isp_float_range_t blue_green_ratio
Blue to green ratio of the white patch. Range [0, 4.0) The ratio could be as wider as possible, so that all the distorted pixels will be counted for the reference of white balance.
-
struct esp_isp_awb_config_t::[anonymous] white_patch
white patch configuration
-
int intr_priority
The interrupt priority, range 0~3, if set to 0, the driver will try to allocate an interrupt with a relative low priority (1,2,3)
-
isp_awb_sample_point_t sample_point
-
struct esp_isp_awb_evt_data_t
Event data of callbacks.
Public Members
-
isp_awb_stat_result_t awb_result
The AWB white patch statistics result
-
isp_awb_stat_result_t awb_result
-
struct esp_isp_awb_cbs_t
Group of ISP AWB callbacks.
Note
These callbacks are all running in an ISR environment.
Note
When CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. Involved variables should be in internal RAM as well.
Public Members
-
esp_isp_awb_callback_t on_statistics_done
Event callback, invoked when white patches statistic done.
-
esp_isp_awb_callback_t on_statistics_done
Type Definitions
-
typedef bool (*esp_isp_awb_callback_t)(isp_awb_ctlr_t awb_ctlr, const esp_isp_awb_evt_data_t *edata, void *user_data)
Prototype of ISP AWB event callback.
- Param awb_ctlr
[in] ISP AWB controller handle
- Param edata
[in] ISP AWB event data
- Param user_data
[in] User registered context, registered when in
esp_isp_awb_env_detector_register_event_callbacks()- Return
Whether a high priority task is woken up by this function
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_bf.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_bf_configure(isp_proc_handle_t proc, const esp_isp_bf_config_t *config)
ISP BF configuration.
Note
After calling this API, BF doesn't take into effect until
esp_isp_bf_enableis called- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
config -- [in] BF configurations, set NULL to de-configure the ISP BF
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Not allowed to be called under current state
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_bf_enable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Enable ISP BF function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_bf_disable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Disable ISP BF function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_bf_config_t
ISP BF configurations.
Public Members
-
isp_bf_edge_padding_mode_t padding_mode
BF edge padding mode.
-
uint8_t padding_data
BF edge padding pixel data.
-
uint8_t bf_template[ISP_BF_TEMPLATE_X_NUMS][ISP_BF_TEMPLATE_Y_NUMS]
BF template data.
-
uint8_t denoising_level
BF denoising level, from 2 to 20, the bigger the better denoising performance, but the worse detailed.
-
uint8_t padding_line_tail_valid_start_pixel
BF edge padding line tail valid start pixel, padding data will only be valid between the valid start pixel and the valid end pixel. Set both the start and end pixel to 0 to make all padding pixel valid.
-
uint8_t padding_line_tail_valid_end_pixel
BF edge padding line tail valid end pixel, padding data will only be valid between the valid start pixel and the valid end pixel. Set both the start and end pixel to 0 to make all padding pixel valid.
-
isp_bf_edge_padding_mode_t padding_mode
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_lsc.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_lsc_allocate_gain_array(isp_proc_handle_t isp_proc, esp_isp_lsc_gain_array_t *gain_array, size_t *out_array_size_per_channel)
Helper function to allocate gain array for LSC.
- Parameters
isp_proc -- [in] Processor handle
gain_array -- [in] Gain array to be allocated
out_array_size_per_channel -- [out] Array size
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Not allowed to be called under current state
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM Out of memory
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_lsc_configure(isp_proc_handle_t isp_proc, const esp_isp_lsc_config_t *config)
ISP LSC configuration.
Note
After calling this API, LSC doesn't take into effect until
esp_isp_lsc_enableis called- Parameters
isp_proc -- [in] Processor handle
config -- [in] LSC configurations
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Not allowed to be called under current state
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED Not supported
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_lsc_enable(isp_proc_handle_t isp_proc)
Enable ISP LSC function.
- Parameters
isp_proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_lsc_disable(isp_proc_handle_t isp_proc)
Disable ISP LSC function.
- Parameters
isp_proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_lsc_gain_array_t
LSC Gain array.
Public Members
-
isp_lsc_gain_t *gain_r
Gain for R channel.
-
isp_lsc_gain_t *gain_gr
Gain for GR channel.
-
isp_lsc_gain_t *gain_gb
Gain for GB channel.
-
isp_lsc_gain_t *gain_b
Gain for B channel.
-
isp_lsc_gain_t *gain_r
-
struct esp_isp_lsc_config_t
ISP LSC configurations.
Public Members
-
esp_isp_lsc_gain_array_t *gain_array
Gain array.
-
esp_isp_lsc_gain_array_t *gain_array
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_ccm.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ccm_configure(isp_proc_handle_t proc, const esp_isp_ccm_config_t *ccm_cfg)
ISP Color Correction Matrix (CCM) configuration.
Note
This function is allowed to be called before or after
esp_isp_ccm_enable, but it only takes effect untilesp_isp_ccm_enableis called- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
ccm_cfg -- [in] CCM configurations
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ccm_enable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Enable ISP CCM function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_ccm_disable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Disable ISP CCM function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_ccm_config_t
Color Correction Matrix configurations.
Public Members
-
float matrix[ISP_CCM_DIMENSION][ISP_CCM_DIMENSION]
The color correction matrix in float, range (-4.0, 4.0)
-
bool saturation
Whether to use saturation when the float data in the matrix is out of the range, For example, if one of the matrix data is 5.0, When saturation is true, and final value will be limited to 4.0, and won't rise error When saturation is false,
esp_isp_ccm_configurewill rise ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG error
-
float matrix[ISP_CCM_DIMENSION][ISP_CCM_DIMENSION]
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_demosaic.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_demosaic_configure(isp_proc_handle_t proc, const esp_isp_demosaic_config_t *config)
ISP Demosaic configuration.
Note
After calling this API, Demosaic doesn't take into effect until
esp_isp_demosaic_enableis called- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
config -- [in] Demosaic configurations, set NULL to de-configure the ISP Demosaic
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_demosaic_enable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Enable ISP Demosaic function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_demosaic_disable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Disable ISP Demosaic function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_demosaic_config_t
ISP Demosaic configurations.
Public Members
-
isp_demosaic_grad_ratio_t grad_ratio
Demosaic gradient ratio,
gradient_x * grad_ratio < gradient_y, use interpolation results in X direction
gradient_y * grad_ratio < gradient_x, use interpolation results in Y direction
else use the average results between X and Y
-
isp_demosaic_edge_padding_mode_t padding_mode
Demosaic edge padding mode.
-
uint8_t padding_data
Demosaic edge padding pixel data.
-
uint8_t padding_line_tail_valid_start_pixel
Demosaic edge padding line tail valid start pixel, padding data will only be valid between the valid start pixel and the valid end pixel. Set both the start and end pixel to 0 to make all padding pixel valid.
-
uint8_t padding_line_tail_valid_end_pixel
Demosaic edge padding line tail valid end pixel, padding data will only be valid between the valid start pixel and the valid end pixel. Set both the start and end pixel to 0 to make all padding pixel valid.
-
isp_demosaic_grad_ratio_t grad_ratio
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_sharpen.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_sharpen_configure(isp_proc_handle_t proc, const esp_isp_sharpen_config_t *config)
ISP Sharpen configuration.
Note
After calling this API, sharpen doesn't take into effect until
esp_isp_sharpen_enableis called- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
config -- [in] Sharpen configurations, set NULL to de-configure the ISP Sharpen
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_sharpen_enable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Enable ISP Sharpen function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_sharpen_disable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Disable ISP Sharpen function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_sharpen_config_t
ISP Sharpen configurations.
Public Members
-
isp_sharpen_h_freq_coeff_t h_freq_coeff
High freq pixel sharpeness coeff.
-
isp_sharpen_m_freq_coeff m_freq_coeff
Medium freq pixel sharpeness coeff.
-
uint8_t h_thresh
High threshold, pixel value higher than this threshold will be multiplied by
h_freq_coeff
-
uint8_t l_thresh
Low threshold, pixel value higher than this threshold but lower than
h_threshwill be multiplied bym_freq_coeff. Pixel value lower than this threshold will be set to 0.
-
isp_sharpen_edge_padding_mode_t padding_mode
Sharpen edge padding mode.
-
uint8_t padding_data
Sharpen edge padding pixel data.
-
uint8_t sharpen_template[ISP_SHARPEN_TEMPLATE_X_NUMS][ISP_SHARPEN_TEMPLATE_Y_NUMS]
Sharpen template data.
-
uint8_t padding_line_tail_valid_start_pixel
Sharpen edge padding line tail valid start pixel, padding data will only be valid between the valid start pixel and the valid end pixel. Set both the start and end pixel to 0 to make all padding pixel valid.
-
uint8_t padding_line_tail_valid_end_pixel
Sharpen edge padding line tail valid end pixel, padding data will only be valid between the valid start pixel and the valid end pixel. Set both the start and end pixel to 0 to make all padding pixel valid.
-
isp_sharpen_h_freq_coeff_t h_freq_coeff
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_gamma.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_gamma_configure(isp_proc_handle_t proc, color_component_t component, const isp_gamma_curve_points_t *pts)
ISP gamma Correction configuration.
Note
This function is allowed to be called before or after esp_isp_gamma_enable(), but it only takes effect until esp_isp_gamma_enable() is called
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
component -- [in] One of the R/G/B components, color_component_t
pts -- [in]
Group of points that describe the desired gamma correction curve;
Passing in NULL to reset to default parameters (no correction)
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_gamma_enable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Enable ISP gamma function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_gamma_disable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Disable ISP gamma function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_gamma_fill_curve_points(uint32_t (*gamma_correction_operator)(uint32_t), isp_gamma_curve_points_t *pts)
Helper function to fill the isp_gamma_curve_points_t structure, giving the mathematical function of the desired gamma correction curve.
Note
The raw values are sampled with equal spacing
- Parameters
gamma_correction_operator -- [in]
The desired gamma correction curve y = f(x).
x is the raw value, in [0, 256]; y is the gamma-corrected value, in [0, 256];
y can be equal to 256 only if x = 256. For any other x value, y should be always less than 256.
pts -- [out] Pointer to the to-be-filled isp_gamma_curve_points_t structure
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_hist.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_new_hist_controller(isp_proc_handle_t isp_proc, const esp_isp_hist_config_t *hist_cfg, isp_hist_ctlr_t *ret_hdl)
New an ISP hist controller.
- Parameters
isp_proc -- [in] ISP Processor handle
hist_cfg -- [in] Pointer to hist config. Refer to
esp_isp_hist_config_t.ret_hdl -- [out] hist controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Invalid state
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND No free interrupt found with the specified flags
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM If out of memory
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_del_hist_controller(isp_hist_ctlr_t hist_ctlr)
Delete an ISP hist controller.
- Parameters
hist_ctlr -- [in] hist controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_hist_controller_enable(isp_hist_ctlr_t hist_ctlr)
Enable an ISP hist controller.
- Parameters
hist_ctlr -- [in] hist controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_hist_controller_disable(isp_hist_ctlr_t hist_ctlr)
Disable an ISP hist controller.
- Parameters
hist_ctlr -- [in] hist controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_hist_controller_get_oneshot_statistics(isp_hist_ctlr_t hist_ctlr, int timeout_ms, isp_hist_result_t *out_res)
Trigger hist reference statistics for one time and get the result.
- Parameters
hist_ctlr -- [in] hist controller handle
timeout_ms -- [in] Timeout in millisecond
timeout_ms < 0: Won't return until finished
timeout_ms = 0: No timeout, trigger one time statistics and return immediately, in this case, the result won't be assigned in this function, but you can get the result in the callback
esp_isp_hist_cbs_t::on_statistics_donetimeout_ms > 0: Wait for specified milliseconds, if not finished, then return timeout error
out_res -- [out] hist reference statistics result
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT Wait for the result timeout
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_hist_controller_start_continuous_statistics(isp_hist_ctlr_t hist_ctlr)
Start hist continuous statistics of the reference in the window.
Note
This function is an asynchronous and non-block function, it will start the continuous statistics and return immediately. You have to register the hist callback and get the result from the callback event data.
- Parameters
hist_ctlr -- [in] hist controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Null pointer
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_hist_controller_stop_continuous_statistics(isp_hist_ctlr_t hist_ctlr)
Stop hist continuous statistics of the reference in the window.
- Parameters
hist_ctlr -- [in] hist controller handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG Null pointer
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_hist_register_event_callbacks(isp_hist_ctlr_t hist_ctlr, const esp_isp_hist_cbs_t *cbs, void *user_data)
Register hist event callbacks.
Note
User can deregister a previously registered callback by calling this function and setting the to-be-deregistered callback member in the
cbsstructure to NULL.Note
When CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. Involved variables (including
user_data) should be in internal RAM as well.- Parameters
hist_ctlr -- [in] hist controller handle
cbs -- [in] Group of callback functions
user_data -- [in] User data, which will be delivered to the callback functions directly
- Returns
ESP_OK: On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Invalid arguments
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Driver state is invalid, you shouldn't call this API at this moment
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_hist_config_t
Hist controller config.
Public Members
-
isp_window_t window
The sampling window of histogram, see
isp_window_t
-
isp_hist_sampling_mode_t hist_mode
ISP histogram sampling mode
-
isp_hist_rgb_coefficient_t rgb_coefficient
RGB coefficients, adjust the sensitivity to red, geen, and blue colors in the image, only effect when hist_mode is ISP_HIST_SAMPLING_RGB, the sum of all coefficients decimal should be 256
-
isp_hist_weight_t window_weight[ISP_HIST_BLOCK_X_NUM * ISP_HIST_BLOCK_Y_NUM]
Weights of histogram's each subwindows, the sum of all subwindows's weight decimal should be 256
-
uint32_t segment_threshold[ISP_HIST_INTERVAL_NUMS]
Threshold to segment the histogram into intervals, range 0~255
-
isp_window_t window
-
struct esp_isp_hist_evt_data_t
Event data of callbacks.
Public Members
-
isp_hist_result_t hist_result
The histogram reference statistics result
-
isp_hist_result_t hist_result
-
struct esp_isp_hist_cbs_t
Group of ISP hist callbacks.
Note
These callbacks are all running in an ISR environment.
Note
When CONFIG_ISP_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. Involved variables should be in internal RAM as well.
Public Members
-
esp_isp_hist_callback_t on_statistics_done
Event callback, invoked when histogram statistic done.
-
esp_isp_hist_callback_t on_statistics_done
Type Definitions
-
typedef bool (*esp_isp_hist_callback_t)(isp_hist_ctlr_t hist_ctlr, const esp_isp_hist_evt_data_t *edata, void *user_data)
Prototype of ISP hist event callback.
- Param hist_ctlr
[in] ISP hist controller handle
- Param edata
[in] ISP hist event data
- Param user_data
[in] User registered context, registered when in
esp_isp_hist_register_event_callbacks()- Return
Whether a high priority task is woken up by this function
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "driver/isp_color.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_driver_ispcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_driver_isp, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_driver_isp
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_color_configure(isp_proc_handle_t proc, const esp_isp_color_config_t *config)
ISP Color configuration.
Note
After calling this API, Color doesn't take into effect until
esp_isp_color_enableis calledNote
API is ISR available
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
config -- [in] Color configurations, set NULL to de-configure the ISP Color
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_color_enable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Enable ISP color function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
-
esp_err_t esp_isp_color_disable(isp_proc_handle_t proc)
Disable ISP color function.
- Parameters
proc -- [in] Processor handle
- Returns
ESP_OK On success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG If the combination of arguments is invalid.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Driver state is invalid.
Structures
-
struct esp_isp_color_config_t
ISP color configurations.
Public Members
-
isp_color_contrast_t color_contrast
The color contrast value, defines the contrast level of the image, which controls the difference in luminance between the lightest and darkest parts of the image Range 0 ~ 1, decimal value should be 0~127, default 1
-
isp_color_saturation_t color_saturation
The color saturation value, controls the intensity of colors in the image, affecting how vivid or muted the colors appear. Range 0 ~ 1, decimal value should be 0~127, default 1
-
uint32_t color_hue
The color hue value, based on the color wheel. 0 degrees represents red, 120 degrees represents green, and 240 degrees represents blue. 360 degrees overlaps with 0 degrees Range 0 ~ 360, default 0.
-
int color_brightness
The color brightness value. Range -128 ~ 127, default 0. Negative range (-128 to -1): Decreases brightness, the smaller the value, the darker the image. Zero (0): Maintains the original brightness, without adjusting the image's brightness. Positive range (1 to 127): Increases brightness, the larger the value, the brighter the image.
-
isp_color_contrast_t color_contrast