ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board v1.5.2
The older version: ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board v1.4
Note
If you are using ESP32-P4X-Function-EV-Board with chip revision v3.x, please refer to this user guide.
The version number v1.5.2 refers to the board hardware version. To identify the embedded chip revision, refer to ESP32-P4 Series SoC Errata > Chip Revision Identification.
This user guide will help you get started with ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board and will also provide more in-depth information.
ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board is a multimedia development board based on the ESP32-P4 chip. ESP32-P4 chip features a dual-core RISC-V processor and supports up to 32 MB PSRAM. In addition, ESP32-P4 supports USB 2.0 specification, MIPI-CSI/DSI, H264 Encoder, and various other peripherals. With all of its outstanding features, the board is an ideal choice for developing low-cost, high-performance, low-power network-connected audio and video products.
The 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi 6 & Bluetooth 5 (LE) module ESP32-C6-MINI-1 serves as the Wi-Fi and Bluetooth module of the board. The board also includes a 7-inch capacitive touch screen with a resolution of 1024 x 600 and a 2MP camera with MIPI CSI, enriching the user interaction experience. The development board is suitable for prototyping a wide range of products, including visual doorbells, network cameras, smart home central control screens, LCD electronic price tags, two-wheel vehicle dashboards, etc.
Most of the I/O pins are broken out to the pin headers for easy interfacing. Developers can connect peripherals with jumper wires.
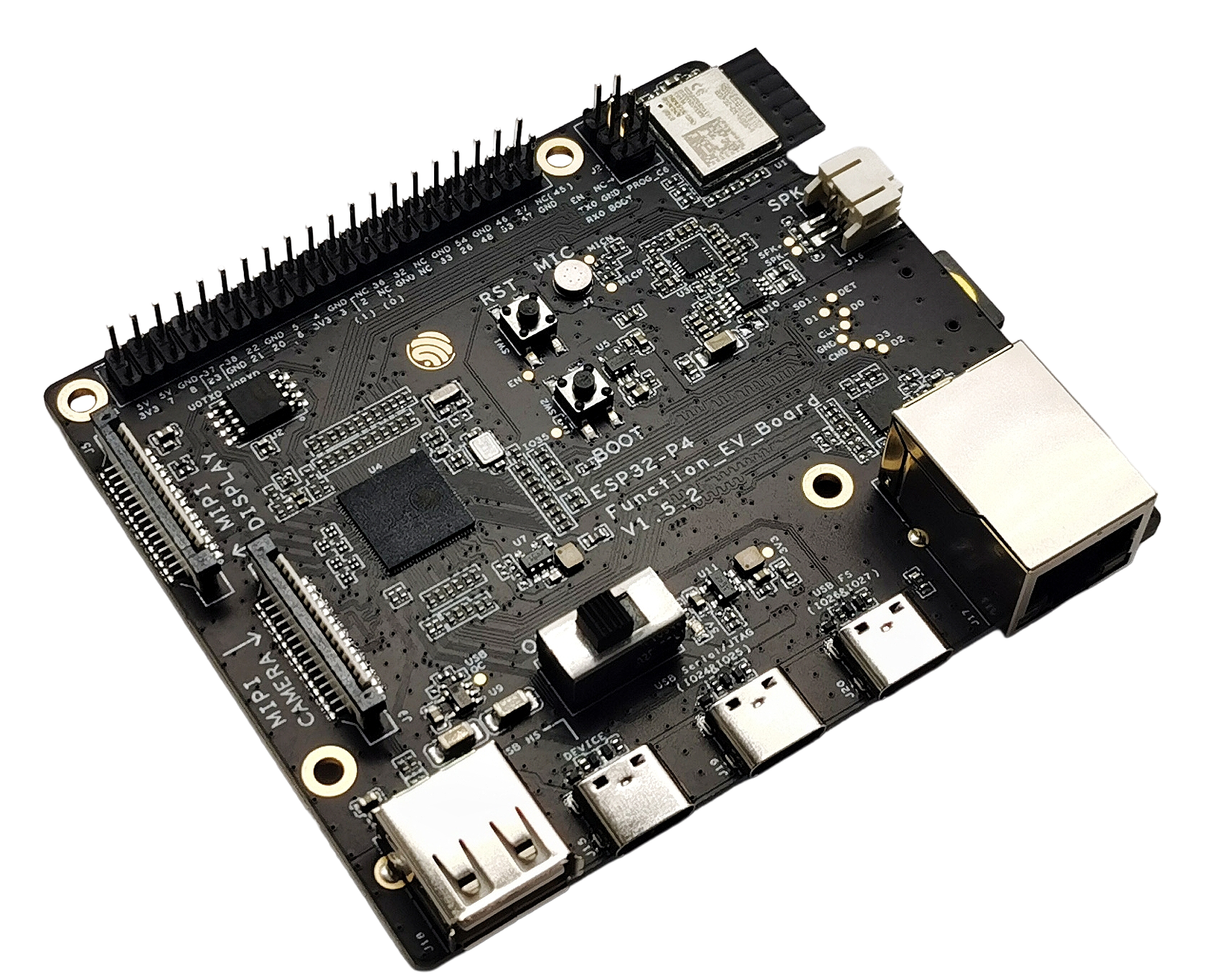
ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board
The document consists of the following major sections:
Getting Started: Overview of ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board and hardware/software setup instructions to get started.
Hardware Reference: More detailed information about the ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board’s hardware.
Hardware Revision Details: Revision history, known issues, and links to user guides for previous versions (if any) of ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board.
Related Documents: Links to related documentation.
Getting Started
This section provides a brief introduction to ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board, instructions on how to do the initial hardware setup and how to flash firmware onto it.
Description of Components
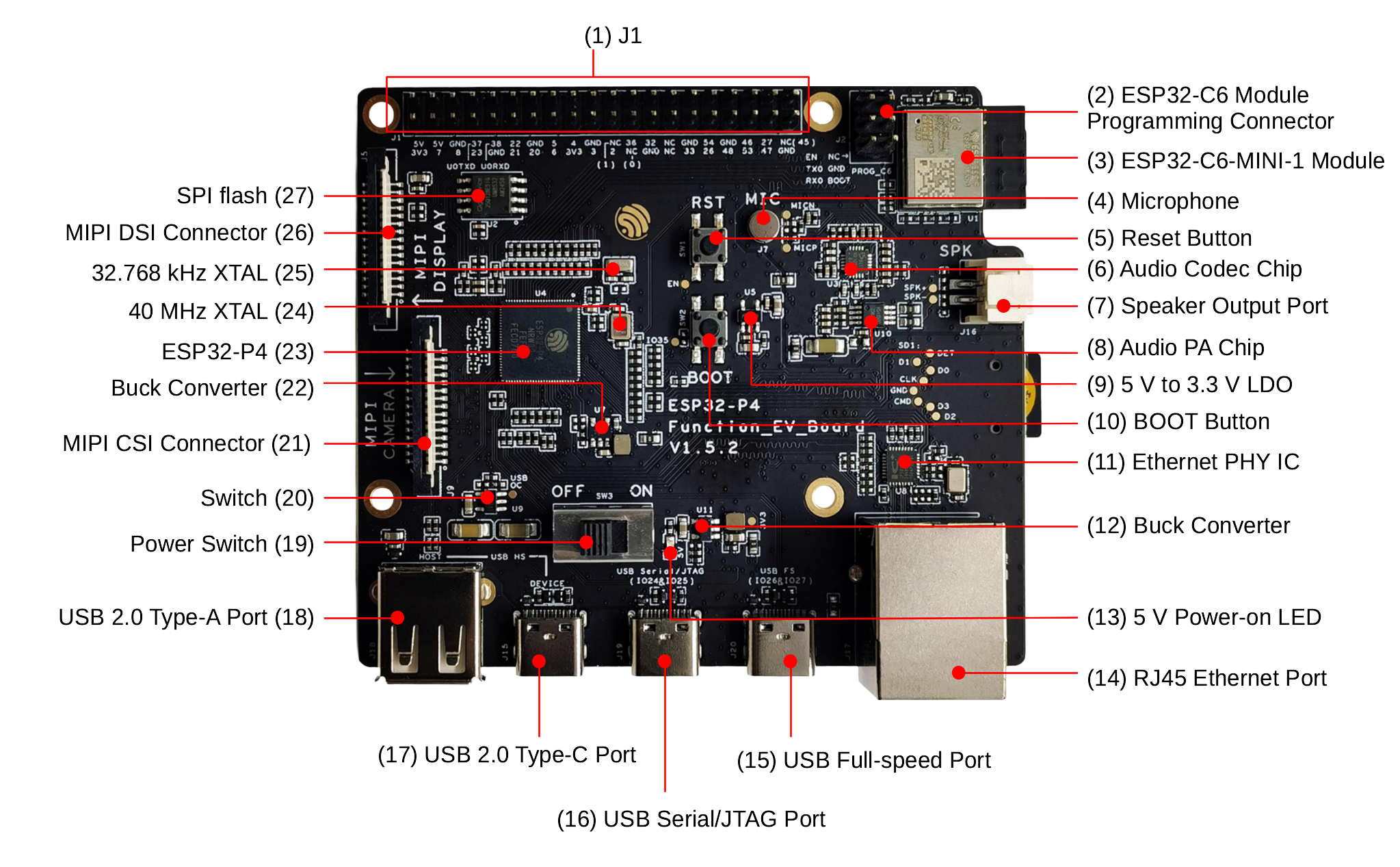
ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board - front (click to enlarge)
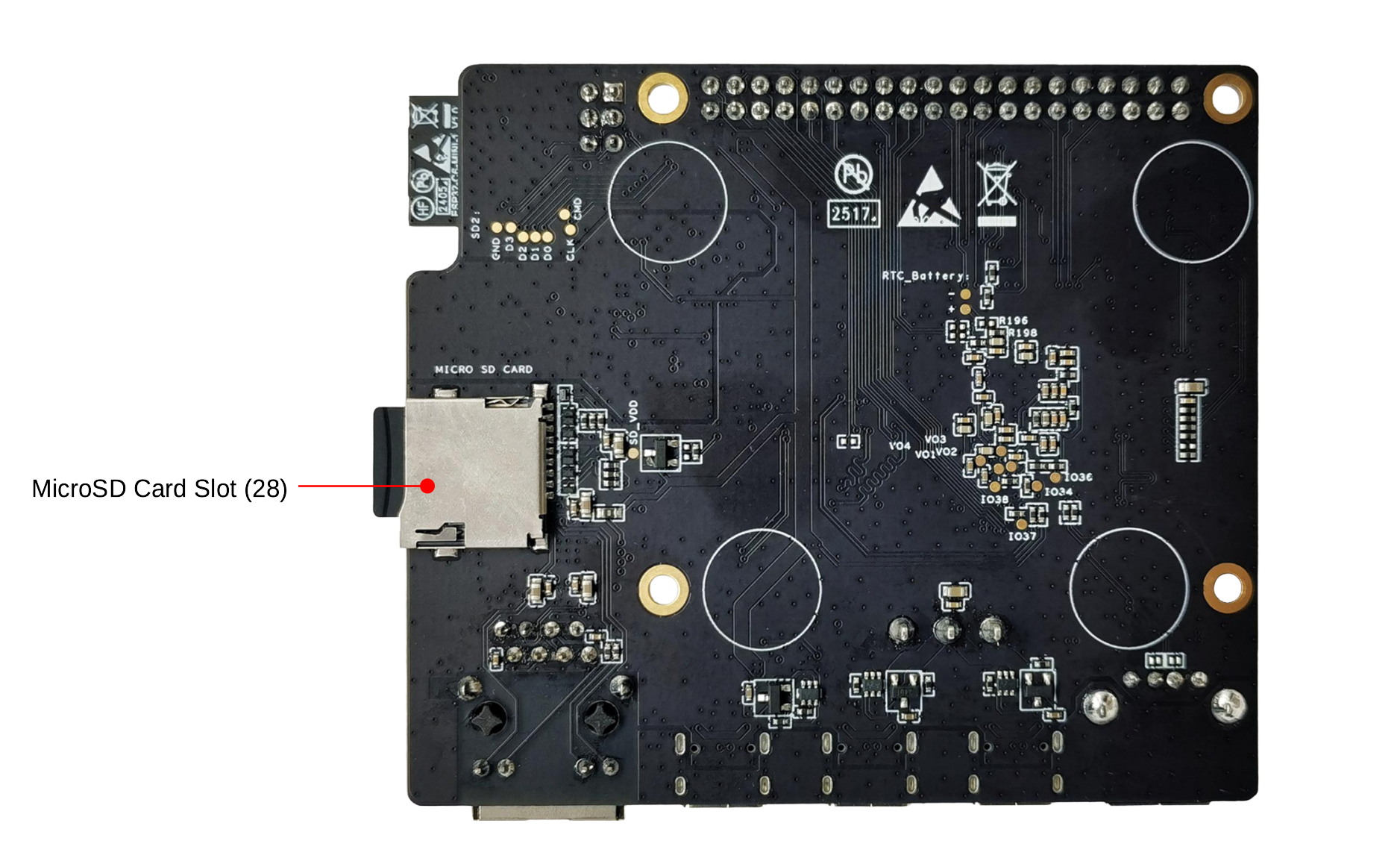
ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board - back (click to enlarge)
The key components of the board are described from front view to back view, starting from the J1, in a clockwise direction.
No. |
Key Component |
Description |
|---|---|---|
1 |
J1 |
All available GPIO pins are broken out to the header block J1 for easy interfacing. For more details, see Header Block. |
2 |
ESP32-C6 Module Programming Connector |
The connector can be used with ESP-Prog or other UART tools to flash firmware onto the ESP32-C6 module. |
3 |
ESP32-C6-MINI-1 Module |
This module serves as the Wi-Fi and Bluetooth communication module for the board. |
4 |
Microphone |
Onboard microphone connected to the interface of Audio Codec Chip. |
5 |
Reset Button |
Resets the board. |
6 |
Audio Codec Chip |
ES8311 is a low-power mono audio codec chip. It includes a single-channel ADC, a single-channel DAC, a low-noise pre-amplifier, a headphone driver, digital sound effects, analog mixing, and gain functions. It interfaces with the ESP32-P4 chip over I2S and I2C buses to provide hardware audio processing independent of the audio application. |
7 |
Speaker Output Port |
This port is used to connect a speaker. The maximum output power can drive a 4 Ω, 3 W speaker. The pin spacing is 2.00 mm (0.08”). |
8 |
Audio PA Chip |
NS4150B is an EMI-compliant, 3 W mono Class D audio power amplifier that amplifies audio signals from the audio codec chip to drive speakers. |
9 |
5 V to 3.3 V LDO |
A power regulator that converts a 5 V supply to a 3.3 V output. |
10 |
BOOT Button |
The boot mode control button. Press the Reset Button while holding down the Boot Button to reset ESP32-P4 and enter firmware download mode. Firmware can then be downloaded to SPI flash via the USB-to-UART Port. |
11 |
Ethernet PHY IC |
Ethernet PHY chip connected to the ESP32-P4 EMAC RMII interface and RJ45 Ethernet Port. |
12 |
Buck Converter |
A buck DC-DC converter for the 3.3 V power supply. |
13 |
5 V Power-on LED |
This LED lights up when the board is powered through any USB Type-C port. |
14 |
RJ45 Ethernet Port |
An Ethernet Port supporting 10/100 Mbps adaptive. |
No. |
Key Component |
Description |
|---|---|---|
15 |
USB Full-speed Port |
USB Type-C port that supports USB 2.0 Full-speed data rate. It can be used as the power supply interface for the development board and as a communication interface. |
16 |
USB Serial/JTAG Port |
USB Type-C port that supports USB 2.0 Full-speed data rate. It can be used to flash firmware to the ESP32-P4 chip, communicate with the chip via the USB protocol, and perform JTAG debugging. |
17 |
USB 2.0 Type-C Port |
The USB 2.0 Type-C Port is connected to the USB 2.0 OTG High-Speed interface of ESP32-P4, compliant with the USB 2.0 specification. When communicating with other devices via this port, ESP32-P4 acts as a USB device connecting to a USB host. Please note that USB 2.0 Type-C Port and USB 2.0 Type-A Port cannot be used simultaneously. USB 2.0 Type-C Port can also be used for powering the board. |
18 |
USB 2.0 Type-A Port |
The USB 2.0 Type-A Port is connected to the USB 2.0 OTG High-Speed interface of ESP32-P4, compliant with the USB 2.0 specification. When communicating with other devices via this port, ESP32-P4 acts as a USB host, providing up to 500 mA of current. Please note that USB 2.0 Type-C Port and USB 2.0 Type-A Port cannot be used simultaneously. |
19 |
Power Switch |
Power On/Off Switch. Toggling toward the ON sign powers the board on (5 V), toggling away from the ON sign powers the board off. |
20 |
Switch |
TPS2051C is a USB power switch that provides a 500 mA output current limit. |
21 |
MIPI CSI Connector |
The FPC connector 1.0K-GT-15PB is used for connecting external camera modules to enable image transmission. For details, please refer to 1.0K-GT-15PB specification in Related Documents. FPC specifications: 1.0 mm pitch, 0.7 mm pin width, 0.3 mm thickness, 15 pins. |
22 |
Buck Converter |
A buck DC-DC converter for VDD_HP power supply of ESP32-P4. |
23 |
ESP32-P4 |
A high-performance MCU with large internal memory and powerful image and voice processing capabilities. |
24 |
40 MHz XTAL |
An external precision 40 MHz crystal oscillator that serves as a clock for the system. |
25 |
32.768 kHz XTAL |
An external precision 32.768 kHz crystal oscillator that serves as a low-power clock while the chip is in deep-sleep mode. |
26 |
MIPI DSI Connector |
The FPC connector 1.0K-GT-15PB is used for connecting displays. For details, please refer to 1.0K-GT-15PB Specification in Related Documents. FPC specifications: 1.0 mm pitch, 0.7 mm pin width, 0.3 mm thickness, 15 pins. |
27 |
SPI flash |
The 16 MB flash is connected to the chip via the SPI interface. |
28 |
MicroSD Card Slot |
The development board supports a MicroSD card in 4-bit mode and can store or play audio files from the MicroSD card. |
Accessories
Optionally, the following accessories are included in the package:
LCD and its accessories (optional)
7-inch capacitive touch screen with a resolution of 1024 x 600
LCD adapter board
Accessories bag, including DuPont wires, ribbon cable for LCD, long standoffs (20 mm in length), and short standoffs (8 mm in length)
Camera and its accessories (optional)
2MP camera with MIPI CSI
Camera adapter board
Ribbon cable for camera
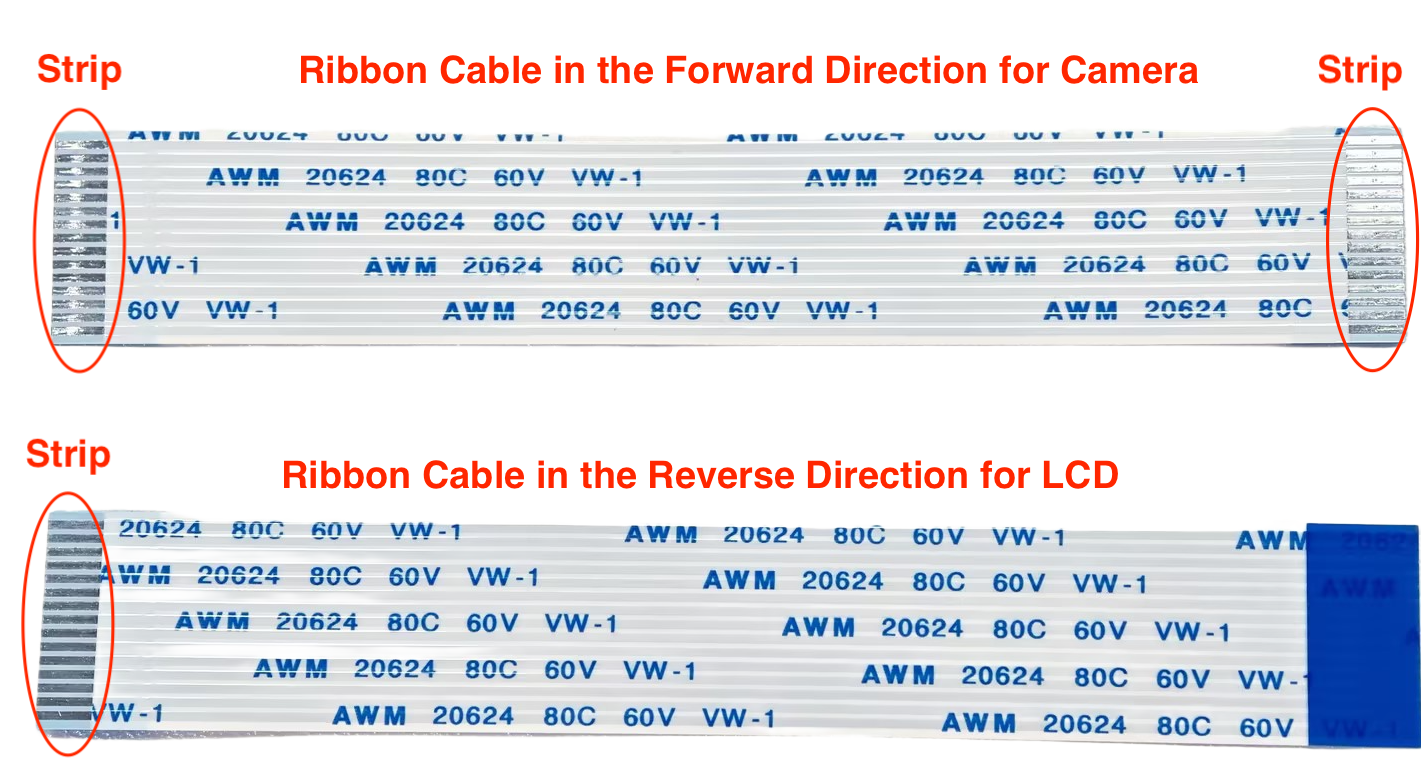
Ribbon Cables in Forward and Reverse Directions
Note
Please note that the ribbon cable in the forward direction, whose strips at the two ends are on the same side, should be used for the camera; the ribbon cable in the reverse direction, whose strips at the two ends are on different sides, should be used for the LCD.
Application Examples
The following application examples are available for ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board v1.5.2:
ESP_Brookesia Phone - Demonstrates an Android-like interface with multiple applications using ESP_Brookesia, utilizing MIPI-DSI, MIPI-CSI, ESP32-C6, SD card, and audio interfaces on a development board, providing a basis for efficient multimedia application development.
LVGL Demo v8 - Demonstrates how to port LVGL v8 and conduct performance testing using LVGL’s built-in demos on an ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board with a 7-inch LCD screen, serving as a foundation for developing applications based on LVGL v8.
LVGL Demo v9 - Demonstrates how to port LVGL v9 and conduct performance testing using LVGL’s built-in demos on an ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board, serving as a basis for developing applications based on LVGL v9.
For more examples and the latest updates, please refer to the examples folder.
To explore the application examples or to develop your own, please follow the steps outlined in the Start Application Development section.
Start Application Development
Before powering up your ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board, please make sure that it is in good condition with no obvious signs of damage.
Required Hardware
ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board
USB cables
Computer running Windows, Linux, or macOS
Note
Be sure to use a good quality USB cable. Some cables are for charging only and do not provide the needed data lines nor work for programming the boards.
Optional Hardware
MicroSD card
Hardware Setup
Connect the ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board to your computer using a USB cable. The board can be powered through any of the USB Type-C ports. The USB-to-UART Port is recommended for flashing firmware and debugging.
To connect the LCD, follow these steps:
Secure the development board to the LCD adapter board by attaching the short copper standoffs (8 mm in length) to the four standoff posts at the center of the LCD adapter board.
Connect the J3 header of the LCD adapter board to the MIPI DSI connector on the ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board using the LCD ribbon cable (reverse direction). Note that the LCD adapter board is already connected to the LCD.
Use a DuPont wire to connect the RST_LCD pin of the J6 header of the LCD adapter board to the GPIO27 pin of the J1 header on the ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board. The RST_LCD pin can be configured via software, with GPIO27 set as the default.
Use a DuPont wire to connect the PWM pin of the J6 header of the LCD adapter board to the GPIO26 pin of the J1 header on the ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board. The PWM pin can be configured via software, with GPIO26 set as the default.
It is recommended to power the LCD by connecting a USB cable to the J1 header of the LCD adapter board. If this is not feasible, connect the 5V and GND pins of the LCD adapter board to corresponding pins on the J1 header of the ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board, provided that the development board has sufficient power supply.
Attach the long copper standoffs (20 mm in length) to the four standoff posts on the periphery of the LCD adapter board to allow the LCD to stand upright.
In summary, the LCD adapter board and ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board are connected via the following pins:
LCD Adapter Board |
ESP32-P4-Function-EV |
|---|---|
J3 header |
MIPI DSI connector |
RST_LCD pin of J6 header |
GPIO27 pin of J1 header |
PWM pin of J6 header |
GPIO26 pin of J1 header |
5V pin of J6 header |
5V pin of J1 header |
GND pin of J6 header |
GND pin of J1 header |
Note
If you power the LCD adapter board by connecting a USB cable to its J1 header, you do not need to connect its 5V and GND pins to the corresponding pins on the development board.
To use the camera, connect the camera adapter board to the MIPI CSI connector on the development board using the camera ribbon cable (forward direction).
Software Setup
To set up your development environment and flash an application example onto your board, please follow the instructions in ESP-IDF Get Started.
Hardware Reference
Block Diagram
The block diagram below shows the components of ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board and their interconnections.
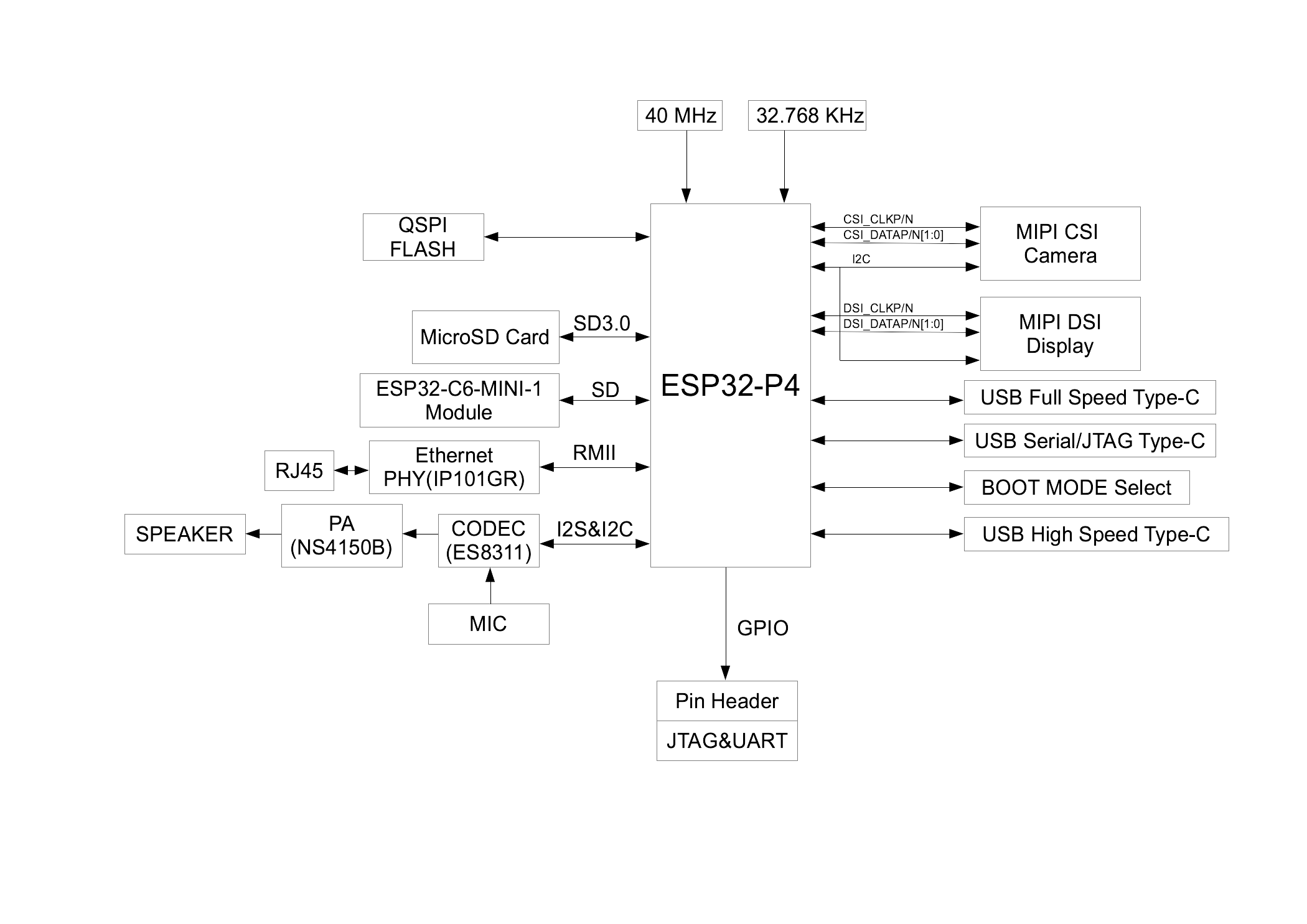
ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board Block Diagram (click to enlarge)
Power Supply Options
Power can be supplied through any of the following ports:
USB 2.0 Type-C Port
USB Full-speed Port
USB Serial/JTAG Port
If the USB cable used for debugging cannot provide enough current, you can connect the board to a power adapter via any available USB Type-C port.
Header Block
The tables below provide the Name and Function of the pin header J1 of the board. The pin header names are shown in Figure ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board - front (click to enlarge). The numbering is the same as in the ESP32-P4-Function-EV-Board Schematic.
J1
No. |
Name |
Type 1 |
Function |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
3V3 |
P |
3.3 V power supply |
2 |
5V |
P |
5 V power supply |
3 |
7 |
I/O/T |
GPIO7 |
4 |
5V |
P |
5 V power supply |
5 |
8 |
I/O/T |
GPIO8 |
6 |
GND |
GND |
Ground |
7 |
23 |
I/O/T |
GPIO23 |
8 |
37 |
I/O/T |
U0TXD, GPIO37 |
9 |
GND |
GND |
Ground |
10 |
38 |
I/O/T |
U0RXD, GPIO38 |
11 |
21 |
I/O/T |
GPIO21 |
12 |
22 |
I/O/T |
GPIO22 |
13 |
20 |
I/O/T |
GPIO20 |
14 |
GND |
GND |
Ground |
15 |
6 |
I/O/T |
GPIO6 |
16 |
5 |
I/O/T |
GPIO5 |
17 |
3V3 |
P |
3.3 V power supply |
18 |
4 |
I/O/T |
GPIO4 |
19 |
3 |
I/O/T |
GPIO3 |
20 |
GND |
GND |
Ground |
21 |
2 |
I/O/T |
GPIO2 |
22 |
NC(1) |
I/O/T |
GPIO1 2 |
23 |
NC(0) |
I/O/T |
GPIO0 2 |
24 |
36 |
I/O/T |
GPIO36 |
25 |
GND |
GND |
Ground |
26 |
32 |
I/O/T |
GPIO32 |
27 |
24 |
I/O/T |
GPIO24 |
28 |
25 |
I/O/T |
GPIO25 |
29 |
33 |
I/O/T |
GPIO33 |
30 |
GND |
GND |
Ground |
31 |
26 |
I/O/T |
GPIO26 |
32 |
54 |
I/O/T |
GPIO54 |
33 |
48 |
I/O/T |
GPIO48 |
34 |
GND |
GND |
Ground |
35 |
53 |
I/O/T |
GPIO53 |
36 |
46 |
I/O/T |
GPIO46 |
37 |
47 |
I/O/T |
GPIO47 |
38 |
27 |
I/O/T |
GPIO27 |
39 |
GND |
GND |
Ground |
40 |
NC(45) |
I/O/T |
GPIO45 3 |
- 1
P: Power supply; I: Input; O: Output; T: High impedance.
- 2(1,2)
GPIO0 and GPIO1 can be enabled by disabling the XTAL_32K function, which can be achieved by moving R61 and R59 to R199 and R197, respectively.
- 3
GPIO45 can be enabled by disabling the SD_PWRn function, which can be achieved by moving R231 to R100.
Hardware Revision Details
Note
The main improvements in development board version v1.52 compared to v1.4 include: replacing the USB-to-UART Type-C port used for debugging with the ESP32-P4 chip’s built-in USB Serial/JTAG port, and adding a Full-speed USB OTG breakout to a Type-C port.