Adding the Link-check Function
Links play an important role in documentation with the function of directing users to supplementary information. However, broken links can not lead the user to where the author intended, which will harm reading experience and leave a bad impression on users.
Considering the great amount of time and labor to conduct manual check on link function throughout hundreds or even thousands of pages, a helpful tool is provided to automatically check links in the process of building the document. It helps identify and locate broken links.
This document describes how to integrate the link-check tool to your project pipeline and how to suppress falsely reported links.
How to Integrate the Link-check Function
To integrate the link-check function to your project, add a CI/CD job to the GitLab YAML file of your project. It can be
.gitlab-ci.ymlor.docs.yml. Here is an example for your reference.check_doc_links: extends: - .build_docs_template only: - master stage: post_deploy tags: - build artifacts: when: always paths: - docs/_build/*/*/*.txt - docs/_build/*/*/linkcheck/*.txt expire_in: 1 week allow_failure: true script: - cd docs - build-docs -l $DOCLANG linkcheck parallel: matrix: - DOCLANG: ["en", "zh_CN"]extends: This command is to include the configuration from a predefined template in the.ymlfile. It helps reusing common configurations across multiple jobs. If you mention this template here, make sure you have defined it first. The following code provides an example on how to define the template:.build_docs_template: image: $ESP_IDF_DOC_ENV_IMAGE stage: build_doc tags: - build_docs dependencies: []only: In this case, the link-check function will only run on the master branch. Note that this is not a must for projects without any links to GitHub Files.stage: Specifies the stage of the pipeline where this job belongs. It is up to you which stage to do the link check.post_deployis just one possible stage. Note that if the docs contain links to GitHub files then link-check should be done in the stage after the code is deployed to GitHub. Otherwise all GitHub links will be broken.tags: Specifies the runner tags that this job should be picked up by. In this case, the job requires a runner with the tag build.artifacts: Defines the artifacts to be collected from the job after it completes.when: always means that the artifacts are collected regardless of whether the job succeeds or fails.
paths: specifies which files and directories to collect as artifacts.
expire_in: 1 week sets the expiration time for these artifacts, meaning they will be automatically deleted after one week.
allow_failure: true: Link-check might fail due circumstances outside of our control, e.g. a website being temporarily down or network outage. We use allow_failure so as not to mark a pipeline as failed just because the link-check failed.scripts:cd docs: changes the working directory to docs.
build-docs -l $DOCLANG linkcheck: runs a command to check links within the documentation. The -l $DOCLANG flag specifies the language for the documentation, with $DOCLANG being an environment variable set by the parallel matrix.
parallel: Defines a matrix of job configurations to run in parallel. In this case, it specifies that the build_docs command should be run twice: once for each value of DOCLANG (i.e., en for English and zh_CN for Simplified Chinese).image: to define the Docker image or environment used for running jobs or pipelines.
After automatic check, a report will be generated in
.txtfile.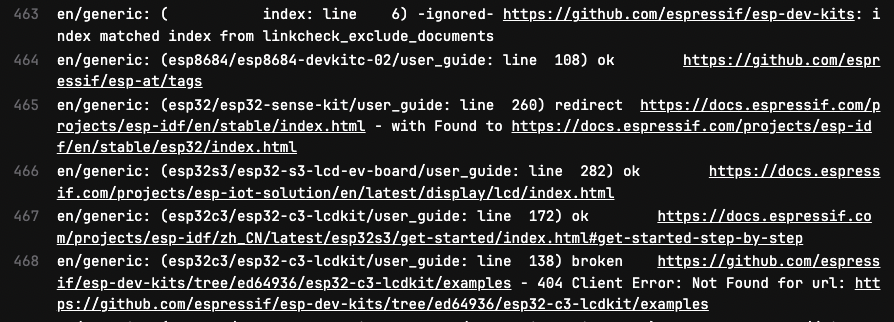
Link-check Report
Similar to the image above, the report file will generate detailed information, including the path of file that goes through link-check, the location of the link, link-check result and the complete link.
The result of the link-check can be classified in to 4 status:
ok: the link passes the check.
redirect: the broken link has been modified.
broken: the link is identified as invalid.
ignored: the link is excluded from check.
Note
It is possible that some links are reported as broken but when you open these links in the browser, they function well. These cases are called false positives. Common false positives are listed below. To exclude certain links from the scan, add the following code in conf_common.py file of your project.
Links in index documents
linkcheck_exclude_documents = ['index', # several false positives due to the way we link to different sections]
Links in documents located in a specific subdirectory (take the subdirectory named ‘wifi_provisioning’ as an example)
linkcheck_exclude_documents = ['api-reference/provisioning/wifi_provisioning', # Fails due to `https://<mdns-hostname>.local`]
Github links with anchors
Disable checking automatically generated anchors on github.com, such as anchors in reST/Markdown documents.
linkcheck_anchors = False
Links requesting too many times from github
If certain links are consistently reported as broken due to rate limiting but are valid, you might need to handle them manually. You can exclude them from the scan by referring to previous instructions.
Links to unpublished documents (take ESP32-C2 Datasheet as an example)
linkcheck_ignore = ['https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp32-c2_datasheet_en.pdf', # Not published]