Ethernet
Overview
ESP-IDF provides a set of consistent and flexible APIs to support both internal Ethernet MAC (EMAC) controller and external SPI-Ethernet modules.
This programming guide is split into the following sections:
Basic Ethernet Concepts
Ethernet is an asynchronous Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detect (CSMA/CD) protocol/interface. It is generally not well suited for low-power applications. However, with ubiquitous deployment, internet connectivity, high data rates, and limitless-range expandability, Ethernet can accommodate nearly all wired communications.
Normal IEEE 802.3 compliant Ethernet frames are between 64 and 1518 bytes in length. They are made up of five or six different fields: a destination MAC address (DA), a source MAC address (SA), a type/length field, a data payload, an optional padding field and a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). Additionally, when transmitted on the Ethernet medium, a 7-byte preamble field and Start-of-Frame (SOF) delimiter byte are appended to the beginning of the Ethernet packet.
Thus the traffic on the twist-pair cabling appears as shown below:
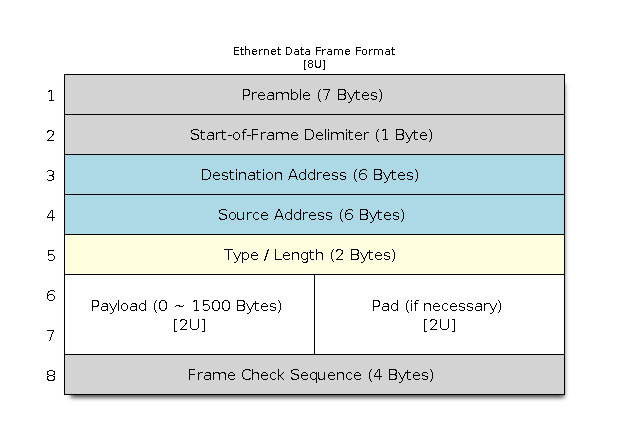
Ethernet Data Frame Format
Preamble and Start-of-Frame Delimiter
The preamble contains seven bytes of 55H. It allows the receiver to lock onto the stream of data before the actual frame arrives.
The Start-of-Frame Delimiter (SFD) is a binary sequence 10101011 (as seen on the physical medium). It is sometimes considered to be part of the preamble.
When transmitting and receiving data, the preamble and SFD bytes will be automatically generated or stripped from the packets.
Destination Address
The destination address field contains a 6-byte length MAC address of the device that the packet is directed to. If the Least Significant bit in the first byte of the MAC address is set, the address is a multicast destination. For example, 01-00-00-00-F0-00 and 33-45-67-89-AB-CD are multi-cast addresses, while 00-00-00-00-F0-00 and 32-45-67-89-AB-CD are not.
Packets with multi-cast destination addresses are designed to arrive and be important to a selected group of Ethernet nodes. If the destination address field is the reserved multicast address, i.e., FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF, the packet is a broadcast packet and it will be directed to everyone sharing the network. If the Least Significant bit in the first byte of the MAC address is clear, the address is a unicast address and will be designed for usage by only the addressed node.
Normally the EMAC controller incorporates receive filters which can be used to discard or accept packets with multi-cast, broadcast and/or unicast destination addresses. When transmitting packets, the host controller is responsible for writing the desired destination address into the transmit buffer.
Source Address
The source address field contains a 6-byte length MAC address of the node which created the Ethernet packet. Users of Ethernet must generate a unique MAC address for each controller used. MAC addresses consist of two portions. The first three bytes are known as the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI). OUIs are distributed by the IEEE. The last three bytes are address bytes at the discretion of the company that purchased the OUI. For more information about MAC Address used in ESP-IDF, please see MAC Address Allocation.
When transmitting packets, the assigned source MAC address must be written into the transmit buffer by the host controller.
Type/Length
The type/length field is a 2-byte field. If the value in this field is <= 1500 (decimal), it is considered a length field and it specifies the amount of non-padding data which follows in the data field. If the value is >= 1536, it represents the protocol the following packet data belongs to. The following are the most common type values:
IPv4 = 0800H
IPv6 = 86DDH
ARP = 0806H
Users implementing proprietary networks may choose to treat this field as a length field, while applications implementing protocols such as the Internet Protocol (IP) or Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), should program this field with the appropriate type defined by the protocol's specification when transmitting packets.
Payload
The payload field is a variable length field, anywhere from 0 to 1500 bytes. Larger data packets violates Ethernet standards and will be dropped by most Ethernet nodes.
This field contains the client data, such as an IP datagram.
Padding and FCS
The padding field is a variable length field added to meet the IEEE 802.3 specification requirements when small data payloads are used.
The DA, SA, type, payload, and padding of an Ethernet packet must be no smaller than 60 bytes in total. If the required 4-byte FCS field is added, packets must be no smaller than 64 bytes. If the payload field is less than 46-byte long, a padding field is required.
The FCS field is a 4-byte field that contains an industry-standard 32-bit CRC calculated with the data from the DA, SA, type, payload, and padding fields. Given the complexity of calculating a CRC, the hardware normally automatically generates a valid CRC and transmit it. Otherwise, the host controller must generate the CRC and place it in the transmit buffer.
Normally, the host controller does not need to concern itself with padding and the CRC which the hardware EMAC will also be able to automatically generate when transmitting and verify when receiving. However, the padding and CRC fields will be written into the receive buffer when packets arrive, so they may be evaluated by the host controller if needed.
Note
Besides the basic data frame described above, there are two other common frame types in 10/100 Mbps Ethernet: control frames and VLAN-tagged frames. They are not supported in ESP-IDF.
Configure MAC and PHY
The Ethernet driver is composed of two parts: MAC and PHY.
The communication between MAC and PHY can have diverse choices: MII (Media Independent Interface), RMII (Reduced Media Independent Interface), etc.
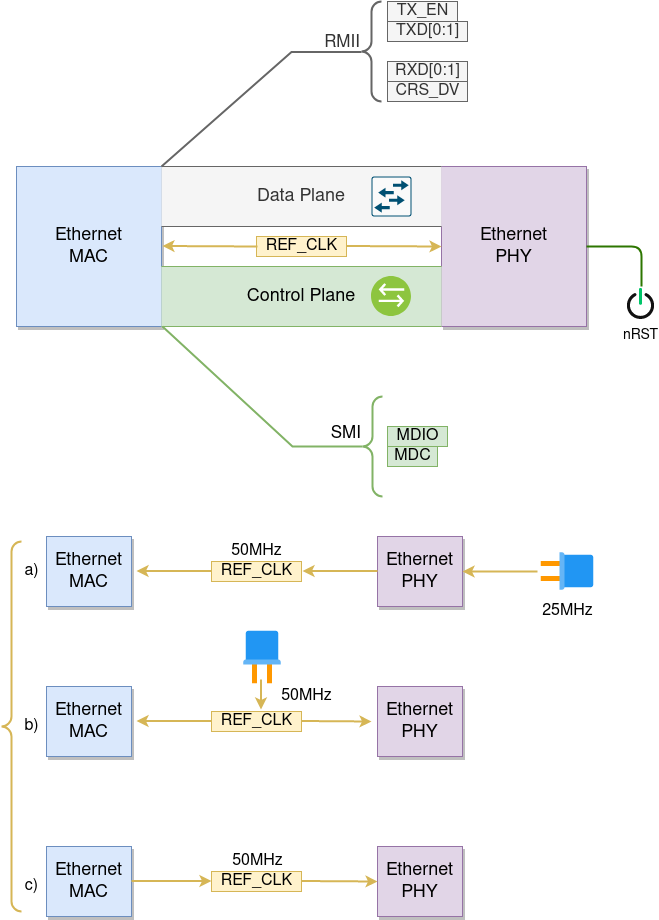
Ethernet RMII Interface
One of the obvious differences between MII and RMII is signal consumption. MII usually costs up to 18 signals, while the RMII interface can reduce the consumption to 9.
Note
ESP-IDF only supports the RMII interface. Therefore, always set eth_esp32_emac_config_t::interface to eth_data_interface_t::EMAC_DATA_INTERFACE_RMII.
In RMII mode, both the receiver and transmitter signals are referenced to the REF_CLK. REF_CLK must be stable during any access to PHY and MAC. Generally, there are three ways to generate the REF_CLK depending on the PHY device in your design:
Some PHY chips can derive the
REF_CLKfrom its externally connected 25 MHz crystal oscillator (as seen the option a in the picture). In this case, you should configureeth_mac_clock_config_t::clock_modeofeth_esp32_emac_config_t::clock_configtoemac_rmii_clock_mode_t::EMAC_CLK_EXT_IN.Some PHY chip uses an externally connected 50 MHz crystal oscillator or other clock sources, which can also be used as the
REF_CLKfor the MAC side (as seen the option b in the picture). In this case, you still need to configureeth_mac_clock_config_t::clock_modeofeth_esp32_emac_config_t::clock_configtoemac_rmii_clock_mode_t::EMAC_CLK_EXT_IN.Some EMAC controllers can generate the
REF_CLKusing an internal high-precision PLL (as seen the option c in the picture). In this case, you should configureeth_mac_clock_config_t::clock_modeofeth_esp32_emac_config_t::clock_configtoemac_rmii_clock_mode_t::EMAC_CLK_OUT.
Note
If the RMII clock mode is configured to emac_rmii_clock_mode_t::EMAC_CLK_OUT, GPIO23 and GPIO39 can be selected as output pin of the REF_CLK signal via IO_MUX.
If the RMII clock mode is configured to emac_rmii_clock_mode_t::EMAC_CLK_EXT_IN, GPIO32, GPIO44 and GPIO50 can be selected as input pin for the REF_CLK signal via IO_MUX.
Warning
If the RMII clock mode is configured to emac_rmii_clock_mode_t::EMAC_CLK_OUT, the REF_CLK output signal must be looped back to the EMAC externally. You have to configure eth_mac_clock_config_t::clock_mode of eth_esp32_emac_config_t::clock_config_out_in to emac_rmii_clock_mode_t::EMAC_CLK_EXT_IN and select GPIO number associated with REF_CLK input GPIO's (GPIO32, GPIO44 and GPIO50).

RMII REF_CKL Output Loopback
No matter which RMII clock mode you select, you really need to take care of the signal integrity of REF_CLK in your hardware design! Keep the trace as short as possible. Keep it away from RF devices and inductor elements.
Note
Signals used in the data plane can be configured to predefined set of GPIOs via IO_MUX for the RMII, see below table. The data plane GPIO configuration is performed by the driver based on content of eth_esp32_emac_config_t::emac_dataif_gpio. Signals used in the control plane can be routed to any free GPIOs via GPIO Matrix.
Pin Name |
GPIO Number |
|---|---|
TX_EN |
GPIO33, GPIO40 and GPIO49 |
TXD0 |
GPIO34 and GPIO41 |
TXD1 |
GPIO35 and GPIO42 |
CRS_DV |
GPIO28, GPIO45 and GPIO51 |
RXD0 |
GPIO29, GPIO46 and GPIO52 |
RXD1 |
GPIO30, GPIO47 and GPIO53 |
You need to set up the necessary parameters for MAC and PHY respectively based on your Ethernet board design, and then combine the two together to complete the driver installation.
Basic common configuration for MAC layer is described in eth_mac_config_t, including:
eth_mac_config_t::sw_reset_timeout_ms: software reset timeout value, in milliseconds. Typically, MAC reset should be finished within 100 ms.eth_mac_config_t::rx_task_stack_sizeandeth_mac_config_t::rx_task_prio: the MAC driver creates a dedicated task to process incoming packets. These two parameters are used to set the stack size and priority of the task.eth_mac_config_t::flags: specifying extra features that the MAC driver should have, it could be useful in some special situations. The value of this field can be OR'd with macros prefixed withETH_MAC_FLAG_. For example, if the MAC driver should work when the cache is disabled, then you should configure this field withETH_MAC_FLAG_WORK_WITH_CACHE_DISABLE.
Specific configuration for internal MAC module is described in eth_esp32_emac_config_t, including:
eth_esp32_emac_config_t::smi_mdc_gpio_numandeth_esp32_emac_config_t::smi_mdio_gpio_num: the GPIO number used to connect the SMI signals.eth_esp32_emac_config_t::interface: configuration of MAC Data interface to PHY (MII/RMII).eth_esp32_emac_config_t::clock_config: configuration of EMAC Interface clock (REF_CLKmode and GPIO number in case of RMII).eth_esp32_emac_config_t::intr_priority: sets the priority of the MAC interrupt. If it is set to0or a negative value, the driver will allocate an interrupt with a default priority. Otherwise, the driver will use the given priority. Note that Low and Medium interrupt priorities (1 to 3) can be set since these can be handled in C.eth_esp32_emac_config_t::emac_dataif_gpio: configuration of EMAC MII/RMII data plane GPIO numbers.eth_esp32_emac_config_t::clock_config_out_in: configuration of EMAC input interface clock whenREF_CLKsignal is generated internally and is looped back to the EMAC externally. The mode must be always configured toemac_rmii_clock_mode_t::EMAC_CLK_EXT_IN. This option is valid only when configuration ofeth_esp32_emac_config_t::clock_configis set toemac_rmii_clock_mode_t::EMAC_CLK_OUT.
Memory Considerations when Using Internal MAC
The internal MAC subsystem transfers data to and from the CPU domain via DMA using a linked list of descriptors. There are two types of descriptors: Transmit and Receive. Based on its type, a descriptor holds status information about the received or transmitted frame or provides controls for transmission. Each descriptor also contains pointers to the current data buffer and the next descriptor. As such, a single EMAC DMA descriptor has size of 32 bytes (64 bytes in fact due to the need for proper memory alignment) in DMA-capable memory.
The default configuration should cover most use cases. However, certain scenarios may require configuring the Ethernet DMA memory utilization to suit specific needs. Typical problems may arise in the following situations:
Short and frequent frames dominate network traffic: If your network traffic primarily consists of very short and frequently transmitted/received frames, you may observe issues such as lower-than-expected throughput (despite the rated 100 Mbps) and missed frames during reception. On transmission, the socket send API may return
errnoequal toENOMEM, accompanied by the insufficient TX buffer size message (if debug log level is enabled). This is because the default memory configuration is optimized for larger frames; CONFIG_ETH_DMA_BUFFER_SIZE is set to 512 bytes by default to ensure a better data buffer to descriptor size overhead ratio. The solution is to increase CONFIG_ETH_DMA_RX_BUFFER_NUM or CONFIG_ETH_DMA_TX_BUFFER_NUM. Additionally, consider decreasing CONFIG_ETH_DMA_BUFFER_SIZE to match the typical frame size in your network to maintain a reasonable memory footprint of the Ethernet driver.High throughput leads to buffer exhaustion: If the socket send API intermittently returns
errnoequal toENOMEM, accompanied by the insufficient TX buffer size message (if debug log level is enabled), and the throughput is close to the rated 100 Mbps, this likely indicates nearing hardware limitations. In such case, the hardware cannot keep up with the transmission requests. The solution is to increase CONFIG_ETH_DMA_TX_BUFFER_NUM to buffer more frames and mitigate temporary peaks in transmission requests. However, this will not help if the requested traffic consistently exceeds the rated throughput. In such situations, the only solution is to limit the bandwidth by software means at the application level.
Configuration for PHY is described in eth_phy_config_t, including:
eth_phy_config_t::phy_addr: multiple PHY devices can share the same SMI bus, so each PHY needs a unique address. Usually, this address is configured during hardware design by pulling up/down some PHY strapping pins. You can set the value from0to15based on your Ethernet board. Especially, if the SMI bus is shared by only one PHY device, setting this value to-1can enable the driver to detect the PHY address automatically.eth_phy_config_t::reset_timeout_ms: reset timeout value, in milliseconds. Typically, PHY reset should be finished within 100 ms.eth_phy_config_t::autonego_timeout_ms: auto-negotiation timeout value, in milliseconds. The Ethernet driver starts negotiation with the peer Ethernet node automatically, to determine to duplex and speed mode. This value usually depends on the ability of the PHY device on your board.eth_phy_config_t::reset_gpio_num: if your board also connects the PHY reset pin to one of the GPIO, then set it here. Otherwise, set this field to-1.eth_phy_config_t::hw_reset_assert_time_us: Time the PHY reset pin is asserted in usec. Set this field to0to use chip specific default timing.eth_phy_config_t::post_hw_reset_delay_ms: Time to wait after the PHY hardware reset is done in msec. Set this field to0to use chip specific default timing. Set this field to-1to not wait after the PHY hardware reset.
ESP-IDF provides a default configuration for MAC and PHY in macro ETH_MAC_DEFAULT_CONFIG and ETH_PHY_DEFAULT_CONFIG.
Create MAC and PHY Instance
The Ethernet driver is implemented in an Object-Oriented style. Any operation on MAC and PHY should be based on the instance of the two.
Internal EMAC + External PHY
eth_mac_config_t mac_config = ETH_MAC_DEFAULT_CONFIG(); // apply default common MAC configuration
eth_esp32_emac_config_t esp32_emac_config = ETH_ESP32_EMAC_DEFAULT_CONFIG(); // apply default vendor-specific MAC configuration
esp32_emac_config.smi_gpio.mdc_num = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_MDC_GPIO; // alter the GPIO used for MDC signal
esp32_emac_config.smi_gpio.mdio_num = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_MDIO_GPIO; // alter the GPIO used for MDIO signal
esp_eth_mac_t *mac = esp_eth_mac_new_esp32(&esp32_emac_config, &mac_config); // create MAC instance
eth_phy_config_t phy_config = ETH_PHY_DEFAULT_CONFIG(); // apply default PHY configuration
phy_config.phy_addr = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_PHY_ADDR; // alter the PHY address according to your board design
phy_config.reset_gpio_num = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_PHY_RST_GPIO; // alter the GPIO used for PHY reset
esp_eth_phy_t *phy = esp_eth_phy_new_generic(&phy_config); // create generic PHY instance
// ESP-IDF officially supports several different specific Ethernet PHY chip driver
// esp_eth_phy_t *phy = esp_eth_phy_new_ip101(&phy_config);
// esp_eth_phy_t *phy = esp_eth_phy_new_rtl8201(&phy_config);
// esp_eth_phy_t *phy = esp_eth_phy_new_lan8720(&phy_config);
// esp_eth_phy_t *phy = esp_eth_phy_new_dp83848(&phy_config);
Note
Any Ethernet PHY chip compliant with IEEE 802.3 can be used when creating new PHY instance with esp_eth_phy_new_generic(). However, while basic functionality should always work, some specific features might be limited, even if the PHY meets IEEE 802.3 standard. A typical example is loopback functionality, where certain PHYs may require setting a specific speed mode to operate correctly. If this is the concern and you need PHY driver specifically tailored to your chip needs, use drivers for PHY chips the ESP-IDF already officially supports or consult with Custom PHY Driver section to create a new custom driver.
Optional Runtime MAC Clock Configuration
EMAC REF_CLK can be optionally configured from the user application code.
eth_esp32_emac_config_t esp32_emac_config = ETH_ESP32_EMAC_DEFAULT_CONFIG(); // apply default vendor-specific MAC configuration
// ...
esp32_emac_config.interface = EMAC_DATA_INTERFACE_RMII; // alter EMAC Data Interface
esp32_emac_config.clock_config.rmii.clock_mode = EMAC_CLK_OUT; // select EMAC REF_CLK mode
esp32_emac_config.clock_config.rmii.clock_gpio = EMAC_CLK_OUT_GPIO; // select GPIO number used to input/output EMAC REF_CLK
esp_eth_mac_t *mac = esp_eth_mac_new_esp32(&esp32_emac_config, &mac_config); // create MAC instance
SPI-Ethernet Module
eth_mac_config_t mac_config = ETH_MAC_DEFAULT_CONFIG(); // apply default common MAC configuration
eth_phy_config_t phy_config = ETH_PHY_DEFAULT_CONFIG(); // apply default PHY configuration
phy_config.phy_addr = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_PHY_ADDR; // alter the PHY address according to your board design
phy_config.reset_gpio_num = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_PHY_RST_GPIO; // alter the GPIO used for PHY reset
// Install GPIO interrupt service (as the SPI-Ethernet module is interrupt-driven)
gpio_install_isr_service(0);
// SPI bus configuration
spi_device_handle_t spi_handle = NULL;
spi_bus_config_t buscfg = {
.miso_io_num = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_SPI_MISO_GPIO,
.mosi_io_num = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_SPI_MOSI_GPIO,
.sclk_io_num = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_SPI_SCLK_GPIO,
.quadwp_io_num = -1,
.quadhd_io_num = -1,
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(spi_bus_initialize(CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_SPI_HOST, &buscfg, 1));
// Configure SPI device
spi_device_interface_config_t spi_devcfg = {
.mode = 0,
.clock_speed_hz = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_SPI_CLOCK_MHZ * 1000 * 1000,
.spics_io_num = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_SPI_CS_GPIO,
.queue_size = 20
};
/* dm9051 ethernet driver is based on spi driver */
eth_dm9051_config_t dm9051_config = ETH_DM9051_DEFAULT_CONFIG(CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_SPI_HOST, &spi_devcfg);
dm9051_config.int_gpio_num = CONFIG_EXAMPLE_ETH_SPI_INT_GPIO;
esp_eth_mac_t *mac = esp_eth_mac_new_dm9051(&dm9051_config, &mac_config);
esp_eth_phy_t *phy = esp_eth_phy_new_dm9051(&phy_config);
Note
When creating MAC and PHY instances for SPI-Ethernet modules (e.g., DM9051), the constructor function must have the same suffix (e.g., esp_eth_mac_new_dm9051 and esp_eth_phy_new_dm9051). This is because we don not have other choices but the integrated PHY.
The SPI device configuration (i.e., spi_device_interface_config_t) may slightly differ for other Ethernet modules or to meet SPI timing on specific PCB. Please check out your module's specs and the examples in ESP-IDF.
Install Driver
To install the Ethernet driver, we need to combine the instance of MAC and PHY and set some additional high-level configurations (i.e., not specific to either MAC or PHY) in esp_eth_config_t:
esp_eth_config_t::mac: instance that created from MAC generator (e.g.,esp_eth_mac_new_esp32()).esp_eth_config_t::phy: instance that created from PHY generator (e.g.,esp_eth_phy_new_ip101()).esp_eth_config_t::check_link_period_ms: Ethernet driver starts an OS timer to check the link status periodically, this field is used to set the interval, in milliseconds.esp_eth_config_t::stack_inputoresp_eth_config_t::stack_input_info: In most Ethernet IoT applications, any Ethernet frame received by a driver should be passed to the upper layer (e.g., TCP/IP stack). This field is set to a function that is responsible to deal with the incoming frames. You can even update this field at runtime via functionesp_eth_update_input_path()after driver installation.esp_eth_config_t::on_lowlevel_init_doneandesp_eth_config_t::on_lowlevel_deinit_done: These two fields are used to specify the hooks which get invoked when low-level hardware has been initialized or de-initialized.
ESP-IDF provides a default configuration for driver installation in macro ETH_DEFAULT_CONFIG.
esp_eth_config_t config = ETH_DEFAULT_CONFIG(mac, phy); // apply default driver configuration
esp_eth_handle_t eth_handle = NULL; // after the driver is installed, we will get the handle of the driver
esp_eth_driver_install(&config, ð_handle); // install driver
The Ethernet driver also includes an event-driven model, which sends useful and important events to user space. We need to initialize the event loop before installing the Ethernet driver. For more information about event-driven programming, please refer to ESP Event.
/** Event handler for Ethernet events */
static void eth_event_handler(void *arg, esp_event_base_t event_base,
int32_t event_id, void *event_data)
{
uint8_t mac_addr[6] = {0};
/* we can get the ethernet driver handle from event data */
esp_eth_handle_t eth_handle = *(esp_eth_handle_t *)event_data;
switch (event_id) {
case ETHERNET_EVENT_CONNECTED:
esp_eth_ioctl(eth_handle, ETH_CMD_G_MAC_ADDR, mac_addr);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Ethernet Link Up");
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Ethernet HW Addr %02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",
mac_addr[0], mac_addr[1], mac_addr[2], mac_addr[3], mac_addr[4], mac_addr[5]);
break;
case ETHERNET_EVENT_DISCONNECTED:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Ethernet Link Down");
break;
case ETHERNET_EVENT_START:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Ethernet Started");
break;
case ETHERNET_EVENT_STOP:
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Ethernet Stopped");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
esp_event_loop_create_default(); // create a default event loop that runs in the background
esp_event_handler_register(ETH_EVENT, ESP_EVENT_ANY_ID, ð_event_handler, NULL); // register Ethernet event handler (to deal with user-specific stuff when events like link up/down happened)
Start Ethernet Driver
After driver installation, we can start Ethernet immediately.
esp_eth_start(eth_handle); // start Ethernet driver state machine
Connect Driver to TCP/IP Stack
Up until now, we have installed the Ethernet driver. From the view of OSI (Open System Interconnection), we are still on level 2 (i.e., Data Link Layer). While we can detect link up and down events and gain MAC address in user space, it is infeasible to obtain the IP address, let alone send an HTTP request. The TCP/IP stack used in ESP-IDF is called LwIP. For more information about it, please refer to LwIP.
To connect the Ethernet driver to TCP/IP stack, follow these three steps:
Create a network interface for the Ethernet driver
Attach the network interface to the Ethernet driver
Register IP event handlers
For more information about the network interface, please refer to Network Interface.
/** Event handler for IP_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP */
static void got_ip_event_handler(void *arg, esp_event_base_t event_base,
int32_t event_id, void *event_data)
{
ip_event_got_ip_t *event = (ip_event_got_ip_t *) event_data;
const esp_netif_ip_info_t *ip_info = &event->ip_info;
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Ethernet Got IP Address");
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "~~~~~~~~~~~");
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "ETHIP:" IPSTR, IP2STR(&ip_info->ip));
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "ETHMASK:" IPSTR, IP2STR(&ip_info->netmask));
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "ETHGW:" IPSTR, IP2STR(&ip_info->gw));
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "~~~~~~~~~~~");
}
esp_netif_init()); // Initialize TCP/IP network interface (should be called only once in application)
esp_netif_config_t cfg = ESP_NETIF_DEFAULT_ETH(); // apply default network interface configuration for Ethernet
esp_netif_t *eth_netif = esp_netif_new(&cfg); // create network interface for Ethernet driver
esp_netif_attach(eth_netif, esp_eth_new_netif_glue(eth_handle)); // attach Ethernet driver to TCP/IP stack
esp_event_handler_register(IP_EVENT, IP_EVENT_ETH_GOT_IP, &got_ip_event_handler, NULL); // register user defined IP event handlers
esp_eth_start(eth_handle); // start Ethernet driver state machine
Warning
It is recommended to fully initialize the Ethernet driver and network interface before registering the user's Ethernet/IP event handlers, i.e., register the event handlers as the last thing prior to starting the Ethernet driver. Such an approach ensures that Ethernet/IP events get executed first by the Ethernet driver or network interface so the system is in the expected state when executing the user's handlers.
Misc Control of Ethernet Driver
The following functions should only be invoked after the Ethernet driver has been installed.
Stop Ethernet driver:
esp_eth_stop()Update Ethernet data input path:
esp_eth_update_input_path()Misc get/set of Ethernet driver attributes:
esp_eth_ioctl()
/* get MAC address */
uint8_t mac_addr[6];
memset(mac_addr, 0, sizeof(mac_addr));
esp_eth_ioctl(eth_handle, ETH_CMD_G_MAC_ADDR, mac_addr);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Ethernet MAC Address: %02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x",
mac_addr[0], mac_addr[1], mac_addr[2], mac_addr[3], mac_addr[4], mac_addr[5]);
/* get PHY address */
int phy_addr = -1;
esp_eth_ioctl(eth_handle, ETH_CMD_G_PHY_ADDR, &phy_addr);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Ethernet PHY Address: %d", phy_addr);
EMAC Hardware Time Stamping
Time stamping in EMAC allows precise tracking of when Ethernet frames are transmitted or received. Hardware time stamping is crucial for applications like Precision Time Protocol (PTP) because it minimizes jitter and inaccuracies that can occur when relying on software time stamps. Embedded time stamps in hardware avoid delays introduced by software layers or processing overhead. Therefore, it ensures nanosecond-level precision.
Warning
Time stamp associated API is currently in "Experimental Feature" state so be aware it may change with future releases.
The basic way how to enable time stamping, get and set time in the EMAC is demonstrated below.
// Enable hardware time stamping
bool ptp_enable = true;
esp_eth_ioctl(eth_hndl, ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_PTP_ENABLE, &ptp_enable);
// Get current EMAC time
eth_mac_time_t ptp_time;
esp_eth_ioctl(eth_hndl, ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_G_PTP_TIME, &ptp_time);
// Set EMAC time
ptp_time = {
.seconds = 42,
.nanoseconds = 0
};
esp_eth_ioctl(eth_hndl, ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_S_PTP_TIME, &ptp_time);
You have an option to schedule event at precise point in time by registering callback function and configuring a target time when the event is supposed to be fired. Note that the callback function is then called from ISR context so it should be as brief as possible.
// Register the callback function
esp_eth_ioctl(eth_hndl, ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_S_TARGET_CB, ts_callback);
// Set time when event is triggered
eth_mac_time_t mac_target_time = {
.seconds = 42,
.nanoseconds = 0
};
esp_eth_ioctl(s_eth_hndl, ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_S_TARGET_TIME, &mac_target_time);
Time stamps for transmitted and received frames can be accessed via the last argument of the registered esp_eth_config_t::stack_input_info function for the receive path, and via the ctrl argument of the esp_eth_transmit_ctrl_vargs() function for the transmit path. However, a more user-friendly approach to retrieve time stamp information in user space is by utilizing the L2 TAP Extended Buffer mechanism.
Flow Control
Ethernet on MCU usually has a limitation in the number of frames it can handle during network congestion, because of the limitation in RAM size. A sending station might be transmitting data faster than the peer end can accept it. The ethernet flow control mechanism allows the receiving node to signal the sender requesting the suspension of transmissions until the receiver catches up. The magic behind that is the pause frame, which was defined in IEEE 802.3x.
Pause frame is a special Ethernet frame used to carry the pause command, whose EtherType field is 0x8808, with the Control opcode set to 0x0001. Only stations configured for full-duplex operation may send pause frames. When a station wishes to pause the other end of a link, it sends a pause frame to the 48-bit reserved multicast address of 01-80-C2-00-00-01. The pause frame also includes the period of pause time being requested, in the form of a two-byte integer, ranging from 0 to 65535.
After the Ethernet driver installation, the flow control feature is disabled by default. You can enable it by:
bool flow_ctrl_enable = true;
esp_eth_ioctl(eth_handle, ETH_CMD_S_FLOW_CTRL, &flow_ctrl_enable);
One thing that should be kept in mind is that the pause frame ability is advertised to the peer end by PHY during auto-negotiation. The Ethernet driver sends a pause frame only when both sides of the link support it.
Application Examples
ethernet/basic demonstrates how to use the Ethernet driver, covering driver installation, attaching it to esp_netif, sending DHCP requests, and obtaining a pingable IP address.
ethernet/iperf demonstrates how to use the Ethernet capabilities to measure the throughput/bandwidth using iPerf.
ethernet/ptp demonstrates the use of Precision Time Protocol (PTP) for time synchronization over Ethernet.
network/vlan_support demonstrates how to create virtual network interfaces over Ethernet, including VLAN and non-VLAN interfaces.
network/sta2eth demonstrates how to create a 1-to-1 bridge using a Wi-Fi station and a wired interface such as Ethernet or USB.
network/simple_sniffer demonstrates how to use Wi-Fi and Ethernet in sniffer mode to capture packets and save them in PCAP format.
network/eth2ap demonstrates how to implement a bridge that forwards packets between an Ethernet port and a Wi-Fi AP interface. It uses ESP32-P4 to create a 1-to-many connection between Ethernet and Wi-Fi without initializing the TCP/IP stack.
network/bridge demonstrates how to use the LwIP IEEE 802.1D bridge to forward Ethernet frames between multiple network segments based on MAC addresses.
Most protocol examples should also work for Ethernet: protocols.
Advanced Topics
Custom PHY Driver
There are multiple PHY manufacturers with wide portfolios of chips available. The ESP-IDF supports Generic PHY and also several specific PHY chips however one can easily get to a point where none of them satisfies the user's actual needs due to price, features, stock availability, etc.
Luckily, a management interface between EMAC and PHY is standardized by IEEE 802.3 in Section 22.2.4 Management Functions. It defines provisions of the so-called "MII Management Interface" to control the PHY and gather status from the PHY. A set of management registers is defined to control chip behavior, link properties, auto-negotiation configuration, etc. This basic management functionality is addressed by esp_eth/src/phy/esp_eth_phy_802_3.c in ESP-IDF and so it makes the creation of a new custom PHY chip driver quite a simple task.
Note
Always consult with PHY datasheet since some PHY chips may not comply with IEEE 802.3, Section 22.2.4. It does not mean you are not able to create a custom PHY driver, but it just requires more effort. You will have to define all PHY management functions.
The majority of PHY management functionality required by the ESP-IDF Ethernet driver is covered by the esp_eth/src/phy/esp_eth_phy_802_3.c. However, the following may require developing chip-specific management functions:
Link status which is almost always chip-specific
Chip initialization, even though not strictly required, should be customized to at least ensure that the expected chip is used
Chip-specific features configuration
Steps to create a custom PHY driver:
Define vendor-specific registry layout based on the PHY datasheet. See esp_eth/src/phy/esp_eth_phy_ip101.c as an example.
Prepare derived PHY management object info structure which:
must contain at least parent IEEE 802.3
phy_802_3_tobjectoptionally contain additional variables needed to support non-IEEE 802.3 or customized functionality. See esp_eth/src/phy/esp_eth_phy_ksz80xx.c as an example.
Define chip-specific management call-back functions.
Initialize parent IEEE 802.3 object and re-assign chip-specific management call-back functions.
Once you finish the new custom PHY driver implementation, consider sharing it among other users via ESP Component Registry.
API Reference
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "hal/eth_types.h"
Enumerations
-
enum eth_data_interface_t
Ethernet interface.
Values:
-
enumerator EMAC_DATA_INTERFACE_RMII
Reduced Media Independent Interface
-
enumerator EMAC_DATA_INTERFACE_MII
Media Independent Interface
-
enumerator EMAC_DATA_INTERFACE_RMII
-
enum eth_link_t
Ethernet link status.
Values:
-
enumerator ETH_LINK_UP
Ethernet link is up
-
enumerator ETH_LINK_DOWN
Ethernet link is down
-
enumerator ETH_LINK_UP
-
enum eth_speed_t
Ethernet speed.
Values:
-
enumerator ETH_SPEED_10M
Ethernet speed is 10Mbps
-
enumerator ETH_SPEED_100M
Ethernet speed is 100Mbps
-
enumerator ETH_SPEED_MAX
Max speed mode (for checking purpose)
-
enumerator ETH_SPEED_10M
-
enum eth_duplex_t
Ethernet duplex mode.
Values:
-
enumerator ETH_DUPLEX_HALF
Ethernet is in half duplex
-
enumerator ETH_DUPLEX_FULL
Ethernet is in full duplex
-
enumerator ETH_DUPLEX_HALF
-
enum eth_checksum_t
Ethernet Checksum.
Values:
-
enumerator ETH_CHECKSUM_SW
Ethernet checksum calculate by software
-
enumerator ETH_CHECKSUM_HW
Ethernet checksum calculate by hardware
-
enumerator ETH_CHECKSUM_SW
-
enum eth_mac_dma_burst_len_t
Internal ethernet EMAC's DMA available burst sizes.
Values:
-
enumerator ETH_DMA_BURST_LEN_32
-
enumerator ETH_DMA_BURST_LEN_16
-
enumerator ETH_DMA_BURST_LEN_8
-
enumerator ETH_DMA_BURST_LEN_4
-
enumerator ETH_DMA_BURST_LEN_2
-
enumerator ETH_DMA_BURST_LEN_1
-
enumerator ETH_DMA_BURST_LEN_32
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_eth.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_ethcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_eth, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_eth
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_eth
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_eth_driver.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_ethcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_eth, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_eth
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_eth
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_driver_install(const esp_eth_config_t *config, esp_eth_handle_t *out_hdl)
Install Ethernet driver.
- Parameters:
config -- [in] configuration of the Ethernet driver
out_hdl -- [out] handle of Ethernet driver
- Returns:
ESP_OK: install esp_eth driver successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: install esp_eth driver failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM: install esp_eth driver failed because there's no memory for driver
ESP_FAIL: install esp_eth driver failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_driver_uninstall(esp_eth_handle_t hdl)
Uninstall Ethernet driver.
Note
It's not recommended to uninstall Ethernet driver unless it won't get used any more in application code. To uninstall Ethernet driver, you have to make sure, all references to the driver are released. Ethernet driver can only be uninstalled successfully when reference counter equals to one.
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Returns:
ESP_OK: uninstall esp_eth driver successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: uninstall esp_eth driver failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: uninstall esp_eth driver failed because it has more than one reference
ESP_FAIL: uninstall esp_eth driver failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_start(esp_eth_handle_t hdl)
Start Ethernet driver ONLY in standalone mode (i.e. without TCP/IP stack)
Note
This API will start driver state machine and internal software timer (for checking link status).
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Returns:
ESP_OK: start esp_eth driver successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: start esp_eth driver failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: start esp_eth driver failed because driver has started already
ESP_FAIL: start esp_eth driver failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_stop(esp_eth_handle_t hdl)
Stop Ethernet driver.
Note
This function does the opposite operation of
esp_eth_start.- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Returns:
ESP_OK: stop esp_eth driver successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: stop esp_eth driver failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: stop esp_eth driver failed because driver has not started yet
ESP_FAIL: stop esp_eth driver failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_update_input_path(esp_eth_handle_t hdl, esp_err_t (*stack_input)(esp_eth_handle_t hdl, uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t length, void *priv), void *priv)
Update Ethernet data input path (i.e. specify where to pass the input buffer)
Note
After install driver, Ethernet still don't know where to deliver the input buffer. In fact, this API registers a callback function which get invoked when Ethernet received new packets.
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
stack_input -- [in] function pointer, which does the actual process on incoming packets
priv -- [in] private resource, which gets passed to
stack_inputcallback without any modification
- Returns:
ESP_OK: update input path successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: update input path failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: update input path failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_update_input_path_info(esp_eth_handle_t hdl, esp_err_t (*stack_input_info)(esp_eth_handle_t hdl, uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t length, void *priv, void *info), void *priv)
Update Ethernet data input path with input function which consumes extra info about received frame.
Note
Extra information may include but is not limited to such info like Time Stamp, CRC check offload result, etc. The MAC layer of the Ethernet driver of the particular device must provide extra information using
stack_input_info()function. Otherwise, input path function registered by this API is not invoked. If this is the case, registerstack_inputfunction byesp_eth_update_input_path()instead.Note
After install driver, Ethernet still don't know where to deliver the input buffer. In fact, this API registers a callback function which get invoked when Ethernet received new packets.
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
stack_input_info -- [in] function pointer, which does the actual process on incoming packets
priv -- [in] private resource, which gets passed to
stack_input_infocallback without any modification
- Returns:
ESP_OK: update input path successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: update input path failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: update input path failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_transmit(esp_eth_handle_t hdl, void *buf, size_t length)
General Transmit.
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
buf -- [in] buffer of the packet to transfer
length -- [in] length of the buffer to transfer
- Returns:
ESP_OK: transmit frame buffer successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: transmit frame buffer failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: invalid driver state (e.i., driver is not started)
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: transmit frame buffer failed because HW was not get available in predefined period
ESP_FAIL: transmit frame buffer failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_transmit_ctrl_vargs(esp_eth_handle_t hdl, void *ctrl, uint32_t argc, ...)
Extended Transmit with variable number of arguments.
Note
Typical intended use case of this function is to assemble Ethernet frame from multiple input buffers at lower layer of the driver (MAC layer) to avoid unnecessary buffer reallocation and copy.
- Parameters:
hdl -- handle of Ethernet driver
ctrl -- optional transmit control structure (MAC specific), set to NULL when not required
argc -- number variable arguments
... -- variable arguments
- Returns:
ESP_OK: transmit successful
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: invalid driver state (e.i., driver is not started)
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: transmit frame buffer failed because HW was not get available in predefined period
ESP_FAIL: transmit frame buffer failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_ioctl(esp_eth_handle_t hdl, esp_eth_io_cmd_t cmd, void *data)
Misc IO function of Ethernet driver.
The following common IO control commands are supported:
ETH_CMD_S_MAC_ADDRsets Ethernet interface MAC address.dataargument is pointer to MAC address buffer with expected size of 6 bytes.ETH_CMD_G_MAC_ADDRgets Ethernet interface MAC address.dataargument is pointer to a buffer to which MAC address is to be copied. The buffer size must be at least 6 bytes.ETH_CMD_S_PHY_ADDRsets PHY address in range of <0-31>.dataargument is pointer to memory of uint32_t datatype from where the configuration option is read.ETH_CMD_G_PHY_ADDRgets PHY address.dataargument is pointer to memory of uint32_t datatype to which the PHY address is to be stored.ETH_CMD_S_AUTONEGOenables or disables Ethernet link speed and duplex mode autonegotiation.dataargument is pointer to memory of bool datatype from which the configuration option is read. Preconditions: Ethernet driver needs to be stopped.ETH_CMD_G_AUTONEGOgets current configuration of the Ethernet link speed and duplex mode autonegotiation.dataargument is pointer to memory of bool datatype to which the current configuration is to be stored.ETH_CMD_S_SPEEDsets the Ethernet link speed.dataargument is pointer to memory of eth_speed_t datatype from which the configuration option is read. Preconditions: Ethernet driver needs to be stopped and auto-negotiation disabled.ETH_CMD_G_SPEEDgets current Ethernet link speed.dataargument is pointer to memory of eth_speed_t datatype to which the speed is to be stored.ETH_CMD_S_PROMISCUOUSsets/resets Ethernet interface promiscuous mode.dataargument is pointer to memory of bool datatype from which the configuration option is read.ETH_CMD_S_FLOW_CTRLsets/resets Ethernet interface flow control.dataargument is pointer to memory of bool datatype from which the configuration option is read.ETH_CMD_S_DUPLEX_MODEsets the Ethernet duplex mode.dataargument is pointer to memory of eth_duplex_t datatype from which the configuration option is read. Preconditions: Ethernet driver needs to be stopped and auto-negotiation disabled.ETH_CMD_G_DUPLEX_MODEgets current Ethernet link duplex mode.dataargument is pointer to memory of eth_duplex_t datatype to which the duplex mode is to be stored.ETH_CMD_S_PHY_LOOPBACKsets/resets PHY to/from loopback mode.dataargument is pointer to memory of bool datatype from which the configuration option is read.ETH_CMD_S_ALL_MULTICASTsets/resets Ethernet interface to/from receive all multicast mode.dataargument is pointer to memory of bool datatype from which the configuration option is read.ETH_CMD_ADD_MAC_FILTERadds a MAC address to the MAC filter.dataargument is pointer to MAC address buffer with expected size of 6 bytes.ETH_CMD_DEL_MAC_FILTERdeletes a MAC address from the MAC filter.dataargument is pointer to MAC address buffer with expected size of 6 bytes.
Note that additional control commands may be available for specific MAC or PHY chips. Please consult specific MAC or PHY documentation or driver code.
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
cmd -- [in] IO control command
data -- [inout] address of data for
setcommand or address where to store the data when used withgetcommand
- Returns:
ESP_OK: process io command successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: process io command failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: process io command failed because some other error occurred
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: requested feature is not supported
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_get_phy_instance(esp_eth_handle_t hdl, esp_eth_phy_t **phy)
Get PHY instance memory address.
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
phy -- [out] pointer to memory to store the instance
- Returns:
esp_err_t
ESP_OK: success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: failed because of some invalid argument
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_get_mac_instance(esp_eth_handle_t hdl, esp_eth_mac_t **mac)
Get MAC instance memory address.
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
mac -- [out] pointer to memory to store the instance
- Returns:
esp_err_t
ESP_OK: success
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: failed because of some invalid argument
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_increase_reference(esp_eth_handle_t hdl)
Increase Ethernet driver reference.
Note
Ethernet driver handle can be obtained by os timer, netif, etc. It's dangerous when thread A is using Ethernet but thread B uninstall the driver. Using reference counter can prevent such risk, but care should be taken, when you obtain Ethernet driver, this API must be invoked so that the driver won't be uninstalled during your using time.
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Returns:
ESP_OK: increase reference successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: increase reference failed because of some invalid argument
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_decrease_reference(esp_eth_handle_t hdl)
Decrease Ethernet driver reference.
- Parameters:
hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Returns:
ESP_OK: increase reference successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: increase reference failed because of some invalid argument
Structures
-
struct esp_eth_config_t
Configuration of Ethernet driver.
Public Members
-
esp_eth_mac_t *mac
Ethernet MAC object.
-
esp_eth_phy_t *phy
Ethernet PHY object.
-
uint32_t check_link_period_ms
Period time of checking Ethernet link status.
-
esp_err_t (*stack_input)(esp_eth_handle_t eth_handle, uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t length, void *priv)
Input frame buffer to user's stack.
- Param eth_handle:
[in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Param buffer:
[in] frame buffer that will get input to upper stack
- Param length:
[in] length of the frame buffer
- Param priv:
[in] pointer to private resource, defined when registering the input function
- Return:
ESP_OK: input frame buffer to upper stack successfully
ESP_FAIL: error occurred when inputting buffer to upper stack
-
esp_err_t (*stack_input_info)(esp_eth_handle_t eth_handle, uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t length, void *priv, void *info)
Input frame buffer to user's stack with additional information about received frame.
- Param eth_handle:
[in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Param buffer:
[in] frame buffer that will get input to upper stack
- Param length:
[in] length of the frame buffer
- Param priv:
[in] pointer to private resource, defined when registering the input function
- Param info:
[in] extra information about received Ethernet frame (may be timestamp, CRC offload check result, etc.)
- Return:
ESP_OK: input frame buffer to upper stack successfully
ESP_FAIL: error occurred when inputting buffer to upper stack
-
esp_err_t (*on_lowlevel_init_done)(esp_eth_handle_t eth_handle)
Callback function invoked when lowlevel initialization is finished.
- Param eth_handle:
[in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Return:
ESP_OK: process extra lowlevel initialization successfully
ESP_FAIL: error occurred when processing extra lowlevel initialization
-
esp_err_t (*on_lowlevel_deinit_done)(esp_eth_handle_t eth_handle)
Callback function invoked when lowlevel deinitialization is finished.
- Param eth_handle:
[in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Return:
ESP_OK: process extra lowlevel deinitialization successfully
ESP_FAIL: error occurred when processing extra lowlevel deinitialization
-
esp_err_t (*read_phy_reg)(esp_eth_handle_t eth_handle, uint32_t phy_addr, uint32_t phy_reg, uint32_t *reg_value)
Read PHY register.
Note
Usually the PHY register read/write function is provided by MAC (SMI interface), but if the PHY device is managed by other interface (e.g. I2C), then user needs to implement the corresponding read/write. Setting this to NULL means your PHY device is managed by MAC's SMI interface.
- Param eth_handle:
[in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Param phy_addr:
[in] PHY chip address (0~31)
- Param phy_reg:
[in] PHY register index code
- Param reg_value:
[out] PHY register value
- Return:
ESP_OK: read PHY register successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: read PHY register failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: read PHY register failed because of timeout
ESP_FAIL: read PHY register failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*write_phy_reg)(esp_eth_handle_t eth_handle, uint32_t phy_addr, uint32_t phy_reg, uint32_t reg_value)
Write PHY register.
Note
Usually the PHY register read/write function is provided by MAC (SMI interface), but if the PHY device is managed by other interface (e.g. I2C), then user needs to implement the corresponding read/write. Setting this to NULL means your PHY device is managed by MAC's SMI interface.
- Param eth_handle:
[in] handle of Ethernet driver
- Param phy_addr:
[in] PHY chip address (0~31)
- Param phy_reg:
[in] PHY register index code
- Param reg_value:
[in] PHY register value
- Return:
ESP_OK: write PHY register successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: read PHY register failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: write PHY register failed because of timeout
ESP_FAIL: write PHY register failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_eth_mac_t *mac
-
struct esp_eth_phy_reg_rw_data_t
Data structure to Read/Write PHY register via ioctl API.
Macros
-
ETH_DEFAULT_CONFIG(emac, ephy)
Default configuration for Ethernet driver.
-
esp_eth_transmit_vargs(eth_hdl, argc, ...)
Wrapper over Extended Transmit function to ensure backward compatibility.
Note
For new implementations, it is recommended to use
esp_eth_transmit_ctrl_vargs()directly.- Parameters:
eth_hdl -- [in] handle of Ethernet driver
argc -- [in] number variable arguments
... -- variable arguments
- Returns:
ESP_OK: transmit successful
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: invalid driver state (e.i., driver is not started)
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: transmit frame buffer failed because HW was not get available in predefined period
ESP_FAIL: transmit frame buffer failed because some other error occurred
Type Definitions
-
typedef void *esp_eth_handle_t
Handle of Ethernet driver.
Enumerations
-
enum esp_eth_io_cmd_t
Command list for ioctl API.
Values:
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_G_MAC_ADDR
Get MAC address
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_S_MAC_ADDR
Set MAC address
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_G_PHY_ADDR
Get PHY address
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_S_PHY_ADDR
Set PHY address
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_G_AUTONEGO
Get PHY Auto Negotiation
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_S_AUTONEGO
Set PHY Auto Negotiation
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_G_SPEED
Get Speed
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_S_SPEED
Set Speed
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_S_PROMISCUOUS
Set promiscuous mode
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_S_FLOW_CTRL
Set flow control
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_G_DUPLEX_MODE
Get Duplex mode
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_S_DUPLEX_MODE
Set Duplex mode
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_S_PHY_LOOPBACK
Set PHY loopback
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_READ_PHY_REG
Read PHY register
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_WRITE_PHY_REG
Write PHY register
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_S_ALL_MULTICAST
Set receive all multicast
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_ADD_MAC_FILTER
Add MAC filter
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_DEL_MAC_FILTER
Delete MAC filter
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_CUSTOM_MAC_CMDS
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_CUSTOM_PHY_CMDS
-
enumerator ETH_CMD_G_MAC_ADDR
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_eth_com.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_ethcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_eth, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_eth
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_eth
Structures
-
struct esp_eth_mediator_s
Ethernet mediator.
Public Members
-
esp_err_t (*phy_reg_read)(esp_eth_mediator_t *eth, uint32_t phy_addr, uint32_t phy_reg, uint32_t *reg_value)
Read PHY register.
- Param eth:
[in] mediator of Ethernet driver
- Param phy_addr:
[in] PHY Chip address (0~31)
- Param phy_reg:
[in] PHY register index code
- Param reg_value:
[out] PHY register value
- Return:
ESP_OK: read PHY register successfully
ESP_FAIL: read PHY register failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*phy_reg_write)(esp_eth_mediator_t *eth, uint32_t phy_addr, uint32_t phy_reg, uint32_t reg_value)
Write PHY register.
- Param eth:
[in] mediator of Ethernet driver
- Param phy_addr:
[in] PHY Chip address (0~31)
- Param phy_reg:
[in] PHY register index code
- Param reg_value:
[in] PHY register value
- Return:
ESP_OK: write PHY register successfully
ESP_FAIL: write PHY register failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*stack_input)(esp_eth_mediator_t *eth, uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t length)
Deliver packet to upper stack.
- Param eth:
[in] mediator of Ethernet driver
- Param buffer:
[in] packet buffer
- Param length:
[in] length of the packet
- Return:
ESP_OK: deliver packet to upper stack successfully
ESP_FAIL: deliver packet failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*stack_input_info)(esp_eth_mediator_t *eth, uint8_t *buffer, uint32_t length, void *info)
Deliver packet to upper stack with additional information about reception.
- Param eth:
[in] mediator of Ethernet driver
- Param buffer:
[in] packet buffer
- Param length:
[in] length of the packet
- Param info:
[in] info associated with reception (e.g. time stamp)
- Return:
ESP_OK: deliver packet to upper stack successfully
ESP_FAIL: deliver packet failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*on_state_changed)(esp_eth_mediator_t *eth, esp_eth_state_t state, void *args)
Callback on Ethernet state changed.
- Param eth:
[in] mediator of Ethernet driver
- Param state:
[in] new state
- Param args:
[in] optional argument for the new state
- Return:
ESP_OK: process the new state successfully
ESP_FAIL: process the new state failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*phy_reg_read)(esp_eth_mediator_t *eth, uint32_t phy_addr, uint32_t phy_reg, uint32_t *reg_value)
Macros
-
ETH_CMD_CUSTOM_MAC_CMDS_OFFSET
Offset for start of MAC custom ioctl commands.
-
ETH_CMD_CUSTOM_PHY_CMDS_OFFSET
Offset for start of PHY custom ioctl commands.
Type Definitions
-
typedef struct esp_eth_mediator_s esp_eth_mediator_t
Ethernet mediator.
Enumerations
-
enum esp_eth_state_t
Ethernet driver state.
Values:
-
enumerator ETH_STATE_LLINIT
Lowlevel init done
-
enumerator ETH_STATE_DEINIT
Deinit done
-
enumerator ETH_STATE_LINK
Link status changed
-
enumerator ETH_STATE_SPEED
Speed updated
-
enumerator ETH_STATE_DUPLEX
Duplex updated
-
enumerator ETH_STATE_PAUSE
Pause ability updated
-
enumerator ETH_STATE_LLINIT
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_eth_mac.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_ethcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_eth, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_eth
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_eth
Structures
-
struct esp_eth_mac_s
Ethernet MAC.
Public Members
-
esp_err_t (*set_mediator)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, esp_eth_mediator_t *eth)
Set mediator for Ethernet MAC.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param eth:
[in] Ethernet mediator
- Return:
ESP_OK: set mediator for Ethernet MAC successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: set mediator for Ethernet MAC failed because of invalid argument
-
esp_err_t (*init)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac)
Initialize Ethernet MAC.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: initialize Ethernet MAC successfully
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: initialize Ethernet MAC failed because of timeout
ESP_FAIL: initialize Ethernet MAC failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*deinit)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac)
Deinitialize Ethernet MAC.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: deinitialize Ethernet MAC successfully
ESP_FAIL: deinitialize Ethernet MAC failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*start)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac)
Start Ethernet MAC.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: start Ethernet MAC successfully
ESP_FAIL: start Ethernet MAC failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*stop)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac)
Stop Ethernet MAC.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: stop Ethernet MAC successfully
ESP_FAIL: stop Ethernet MAC failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*transmit)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint8_t *buf, uint32_t length)
Transmit packet from Ethernet MAC.
Note
Returned error codes may differ for each specific MAC chip.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param buf:
[in] packet buffer to transmit
- Param length:
[in] length of packet
- Return:
ESP_OK: transmit packet successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE: number of actually sent bytes differs to expected
ESP_FAIL: transmit packet failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*transmit_ctrl_vargs)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, void *ctrl, uint32_t argc, va_list args)
Transmit packet with extended control from Ethernet MAC and constructed with special parameters at Layer2.
Note
Typical intended use case is to make possible to construct a frame from multiple higher layer buffers without a need of buffer reallocations. However, other use cases are not limited.
Note
Returned error codes may differ for each specific MAC chip.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param ctrl:
[in] optional transmit control structure (chip specific), set to NULL when not required
- Param argc:
[in] number variable arguments
- Param args:
[in] variable arguments
- Return:
ESP_OK: transmit packet successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE: number of actually sent bytes differs to expected
ESP_FAIL: transmit packet failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*transmit_vargs)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint32_t argc, va_list args)
Transmit packet from Ethernet MAC constructed with special parameters at Layer2.
Note
Typical intended use case is to make possible to construct a frame from multiple higher layer buffers without a need of buffer reallocations. However, other use cases are not limited.
Note
Returned error codes may differ for each specific MAC chip.
Warning
Deprecated, use
transmit_ctrl_vargs()function instead.- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param argc:
[in] number variable arguments
- Param args:
[in] variable arguments
- Return:
ESP_OK: transmit packet successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE: number of actually sent bytes differs to expected
ESP_FAIL: transmit packet failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*receive)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint8_t *buf, uint32_t *length)
Receive packet from Ethernet MAC.
Note
Memory of buf is allocated in the Layer2, make sure it get free after process.
Note
Before this function got invoked, the value of "length" should set by user, equals the size of buffer. After the function returned, the value of "length" means the real length of received data.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param buf:
[out] packet buffer which will preserve the received frame
- Param length:
[out] length of the received packet
- Return:
ESP_OK: receive packet successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: receive packet failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_SIZE: input buffer size is not enough to hold the incoming data. in this case, value of returned "length" indicates the real size of incoming data.
ESP_FAIL: receive packet failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*read_phy_reg)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint32_t phy_addr, uint32_t phy_reg, uint32_t *reg_value)
Read PHY register.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param phy_addr:
[in] PHY chip address (0~31)
- Param phy_reg:
[in] PHY register index code
- Param reg_value:
[out] PHY register value
- Return:
ESP_OK: read PHY register successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: read PHY register failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: read PHY register failed because of wrong state of MAC
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: read PHY register failed because of timeout
ESP_FAIL: read PHY register failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*write_phy_reg)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint32_t phy_addr, uint32_t phy_reg, uint32_t reg_value)
Write PHY register.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param phy_addr:
[in] PHY chip address (0~31)
- Param phy_reg:
[in] PHY register index code
- Param reg_value:
[in] PHY register value
- Return:
ESP_OK: write PHY register successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: write PHY register failed because of wrong state of MAC
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: write PHY register failed because of timeout
ESP_FAIL: write PHY register failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_addr)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint8_t *addr)
Set MAC address.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param addr:
[in] MAC address
- Return:
ESP_OK: set MAC address successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: set MAC address failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: set MAC address failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*get_addr)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint8_t *addr)
Get MAC address.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param addr:
[out] MAC address
- Return:
ESP_OK: get MAC address successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: get MAC address failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: get MAC address failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*add_mac_filter)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint8_t *addr)
Add Destination address MAC filter.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param addr:
[in] MAC address
- Return:
ESP_OK: add MAC filter successfully
ESP_FAIL: add MAC filter failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*rm_mac_filter)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint8_t *addr)
Remove Destination address MAC filter.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param addr:
[in] MAC address
- Return:
ESP_OK: remove MAC filter successfully
ESP_FAIL: remove MAC filter failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_speed)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, eth_speed_t speed)
Set speed of MAC.
- Param ma:c:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param speed:
[in] MAC speed
- Return:
ESP_OK: set MAC speed successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: set MAC speed failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: set MAC speed failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_duplex)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, eth_duplex_t duplex)
Set duplex mode of MAC.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param duplex:
[in] MAC duplex
- Return:
ESP_OK: set MAC duplex mode successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: set MAC duplex failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: set MAC duplex failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_link)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, eth_link_t link)
Set link status of MAC.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param link:
[in] Link status
- Return:
ESP_OK: set link status successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: set link status failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: set link status failed because some other error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_promiscuous)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, bool enable)
Set promiscuous of MAC.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param enable:
[in] set true to enable promiscuous mode; set false to disable promiscuous mode
- Return:
ESP_OK: set promiscuous mode successfully
ESP_FAIL: set promiscuous mode failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_all_multicast)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, bool enable)
Set receive all multicast.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param enable:
[in] set true to enable receive all multicast; set false to disable receive all multicast
- Return:
ESP_OK: set receive all multicast successfully
ESP_FAIL: set receive all multicast failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*enable_flow_ctrl)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, bool enable)
Enable flow control on MAC layer or not.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param enable:
[in] set true to enable flow control; set false to disable flow control
- Return:
ESP_OK: set flow control successfully
ESP_FAIL: set flow control failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_peer_pause_ability)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, uint32_t ability)
Set the PAUSE ability of peer node.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param ability:
[in] zero indicates that pause function is supported by link partner; non-zero indicates that pause function is not supported by link partner
- Return:
ESP_OK: set peer pause ability successfully
ESP_FAIL: set peer pause ability failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*custom_ioctl)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, int cmd, void *data)
Custom IO function of MAC driver. This function is intended to extend common options of esp_eth_ioctl to cover specifics of MAC chip.
Note
This function may not be assigned when the MAC chip supports only most common set of configuration options.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Param cmd:
[in] IO control command
- Param data:
[inout] address of data for
setcommand or address where to store the data when used withgetcommand- Return:
ESP_OK: process io command successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: process io command failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: process io command failed because some other error occurred
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: requested feature is not supported
-
esp_err_t (*del)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac)
Free memory of Ethernet MAC.
- Param mac:
[in] Ethernet MAC instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: free Ethernet MAC instance successfully
ESP_FAIL: free Ethernet MAC instance failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_mediator)(esp_eth_mac_t *mac, esp_eth_mediator_t *eth)
-
struct eth_mac_time_t
Ethernet MAC Time Stamp.
-
struct eth_mac_config_t
Configuration of Ethernet MAC object.
Macros
-
ETH_MAC_FLAG_WORK_WITH_CACHE_DISABLE
MAC driver can work when cache is disabled
-
ETH_MAC_FLAG_PIN_TO_CORE
Pin MAC task to the CPU core where driver installation happened
-
ETH_MAC_DEFAULT_CONFIG()
Default configuration for Ethernet MAC object.
Type Definitions
-
typedef struct esp_eth_mac_s esp_eth_mac_t
Ethernet MAC.
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_eth_mac_esp.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_ethcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_eth, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_eth
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_eth
Functions
-
esp_eth_mac_t *esp_eth_mac_new_esp32(const eth_esp32_emac_config_t *esp32_config, const eth_mac_config_t *config)
Create ESP32 Ethernet MAC instance.
- Parameters:
esp32_config -- EMAC specific configuration
config -- Ethernet MAC configuration
- Returns:
instance: create MAC instance successfully
NULL: create MAC instance failed because some error occurred
Unions
-
union eth_mac_clock_config_t
- #include <esp_eth_mac_esp.h>
Ethernet MAC Clock Configuration.
Public Members
-
struct eth_mac_clock_config_t mii
EMAC MII Clock Configuration
-
emac_rmii_clock_mode_t clock_mode
RMII Clock Mode Configuration
-
emac_rmii_clock_gpio_t clock_gpio
RMII Clock GPIO Configuration
-
struct eth_mac_clock_config_t rmii
EMAC RMII Clock Configuration
-
struct eth_mac_clock_config_t mii
-
union eth_mac_dataif_gpio_config_t
- #include <esp_eth_mac_esp.h>
Ethernet MAC MII/RMII data plane GPIO configuration.
Public Members
-
eth_mac_mii_gpio_config_t mii
EMAC MII Data GPIO Configuration
-
eth_mac_rmii_gpio_config_t rmii
EMAC RMII Data GPIO Configuration
-
eth_mac_mii_gpio_config_t mii
Structures
-
struct emac_esp_smi_gpio_config_t
EMAC SMI GPIO configuration.
-
struct eth_mac_mii_gpio_config_t
EMAC MII data interface GPIO configuration.
Public Members
-
int tx_clk_num
TX_CLK GPIO number
-
int tx_en_num
TX_EN GPIO number
-
int txd0_num
TXD0 GPIO number
-
int txd1_num
TXD1 GPIO number
-
int txd2_num
TXD2 GPIO number
-
int txd3_num
TXD3 GPIO number
-
int rx_clk_num
RX_CLK GPIO number
-
int rx_dv_num
RX_DV GPIO number
-
int rxd0_num
RXD0 GPIO number
-
int rxd1_num
RXD1 GPIO number
-
int rxd2_num
RXD2 GPIO number
-
int rxd3_num
RXD3 GPIO number
-
int col_in_num
COL_IN GPIO number
-
int crs_in_num
CRS_IN GPIO number
-
int tx_er_num
TX_ER GPIO number
-
int rx_er_num
RX_ER GPIO number
-
int tx_clk_num
-
struct eth_mac_rmii_gpio_config_t
EMAC RMII data interface GPIO configuration.
-
struct eth_esp32_emac_config_t
EMAC specific configuration.
Public Members
-
emac_esp_smi_gpio_config_t smi_gpio
SMI GPIO numbers
-
int smi_mdc_gpio_num
SMI MDC GPIO number, set to -1 could bypass the SMI GPIO configuration
-
int smi_mdio_gpio_num
SMI MDIO GPIO number, set to -1 could bypass the SMI GPIO configuration
-
eth_data_interface_t interface
EMAC Data interface to PHY (MII/RMII)
-
eth_mac_clock_config_t clock_config
EMAC Interface clock configuration
-
eth_mac_dma_burst_len_t dma_burst_len
EMAC DMA burst length for both Tx and Rx
-
int intr_priority
EMAC interrupt priority, if set to 0 or a negative value, the driver will try to allocate an interrupt with a default priority
-
eth_mac_dataif_gpio_config_t emac_dataif_gpio
EMAC MII/RMII data plane GPIO configuration
-
eth_mac_clock_config_t clock_config_out_in
EMAC input clock configuration for internally generated output clock (when output clock is looped back externally)
-
int32_t mdc_freq_hz
EMAC MDC frequency range limit, if set to 0 or a negative value, the driver will set the CSR clock range up to 2.5 MHz
-
emac_esp_smi_gpio_config_t smi_gpio
Macros
-
ETH_ESP32_EMAC_DEFAULT_CONFIG()
Default ESP32's EMAC specific configuration.
Type Definitions
-
typedef int emac_rmii_clock_gpio_t
RMII Clock GPIO number.
-
typedef bool (*ts_target_exceed_cb_from_isr_t)(esp_eth_mediator_t *eth, void *user_args)
Type of callback function invoked under Time Stamp target time exceeded interrupt.
Warning
Time stamping is currently Experimental Feature! Be aware that API may change.
- Param eth:
mediator of Ethernet driver
- Param user_args:
user specific arguments (placeholder - IDF-11429)
- Return:
TRUE when high priority task has been woken by this function
FALSE no high priority task was woken by this function
Enumerations
-
enum emac_rmii_clock_mode_t
RMII Clock Mode Options.
Values:
-
enumerator EMAC_CLK_DEFAULT
Default values configured using Kconfig are going to be used when "Default" selected.
Warning
Deprecated option. Clock configuration using Kconfig is limitedly supported only for ESP32 SoC via
ETH_ESP32_EMAC_DEFAULT_CONFIGand is going to be reevaluated in the next major release. Clock mode and clock GPIO number is supposed to be defined inEMAC specific configurationstructure from user's code.
-
enumerator EMAC_CLK_EXT_IN
Input RMII Clock from external. EMAC Clock GPIO number needs to be configured when this option is selected.
Note
MAC will get RMII clock from outside. Note that ESP32 only supports GPIO0 to input the RMII clock.
-
enumerator EMAC_CLK_OUT
Output RMII Clock from internal (A/M)PLL Clock. EMAC Clock GPIO number needs to be configured when this option is selected.
-
enumerator EMAC_CLK_DEFAULT
-
enum eth_mac_esp_io_cmd_t
List of ESP EMAC specific commands for ioctl API.
Values:
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_SET_TDES0_CFG_BITS
Set Transmit Descriptor Word 0 control bit mask (debug option)
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_CLEAR_TDES0_CFG_BITS
Clear Transmit Descriptor Word 0 control bit mask (debug option)
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_PTP_ENABLE
Enable IEEE1588 Time stamping
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_S_PTP_TIME
Set PTP time in the module
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_G_PTP_TIME
Get PTP time from the module
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_ADJ_PTP_FREQ
Adjust current PTP time frequency increment by scale factor
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_ADJ_PTP_TIME
Adjust base PTP time frequency increment by PPS
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_S_TARGET_TIME
Set Target Time at which interrupt is invoked when PTP time exceeds this value
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_S_TARGET_CB
Set pointer to a callback function invoked when PTP time exceeds Target Time
-
enumerator ETH_MAC_ESP_CMD_SET_TDES0_CFG_BITS
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_eth_mac_spi.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_ethcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_eth, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_eth
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_eth
Structures
-
struct eth_spi_custom_driver_config_t
Custom SPI Driver Configuration. This structure declares configuration and callback functions to access Ethernet SPI module via user's custom SPI driver.
Public Members
-
void *config
Custom driver specific configuration data used by
init()function.Note
Type and its content is fully under user's control
-
void *(*init)(const void *spi_config)
Custom driver SPI Initialization.
Note
return type and its content is fully under user's control
- Param spi_config:
[in] Custom driver specific configuration
- Return:
spi_ctx: when initialization is successful, a pointer to context structure holding all variables needed for subsequent SPI access operations (e.g. SPI bus identification, mutexes, etc.)
NULL: driver initialization failed
-
esp_err_t (*deinit)(void *spi_ctx)
Custom driver De-initialization.
- Param spi_ctx:
[in] a pointer to driver specific context structure
- Return:
ESP_OK: driver de-initialization was successful
ESP_FAIL: driver de-initialization failed
any other failure codes are allowed to be used to provide failure isolation
-
esp_err_t (*read)(void *spi_ctx, uint32_t cmd, uint32_t addr, void *data, uint32_t data_len)
Custom driver SPI read.
Note
The read function is responsible to construct command, address and data fields of the SPI frame in format expected by particular SPI Ethernet module
- Param spi_ctx:
[in] a pointer to driver specific context structure
- Param cmd:
[in] command
- Param addr:
[in] register address
- Param data:
[out] read data
- Param data_len:
[in] read data length in bytes
- Return:
ESP_OK: read was successful
ESP_FAIL: read failed
any other failure codes are allowed to be used to provide failure isolation
-
esp_err_t (*write)(void *spi_ctx, uint32_t cmd, uint32_t addr, const void *data, uint32_t data_len)
Custom driver SPI write.
Note
The write function is responsible to construct command, address and data fields of the SPI frame in format expected by particular SPI Ethernet module
- Param spi_ctx:
[in] a pointer to driver specific context structure
- Param cmd:
[in] command
- Param addr:
[in] register address
- Param data:
[in] data to write
- Param data_len:
[in] length of data to write in bytes
- Return:
ESP_OK: write was successful
ESP_FAIL: write failed
any other failure codes are allowed to be used to provide failure isolation
-
void *config
Macros
-
ETH_DEFAULT_SPI
Default configuration of the custom SPI driver. Internal ESP-IDF SPI Master driver is used by default.
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_eth_phy.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_ethcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_eth, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_eth
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_eth
Functions
-
esp_eth_phy_t *esp_eth_phy_new_generic(const eth_phy_config_t *config)
Create a PHY instance of generic chip which conforms with IEEE 802.3.
Note
Default reset timing configuration is set conservatively(
DEFAULT_PHY_RESET_ASSERTION_TIME_US). If you need faster response and your chip supports it, configure it viaconfigparameter.Warning
While basic functionality should always work, some specific features might be limited, even if the PHY meets IEEE 802.3 standard. A typical example is loopback functionality, where certain PHYs may require setting a specific speed mode to operate correctly.
- Parameters:
config -- [in] configuration of PHY
- Returns:
instance: create PHY instance successfully
NULL: create PHY instance failed because some error occurred
-
esp_eth_phy_t *esp_eth_phy_new_ip101(const eth_phy_config_t *config)
Create a PHY instance of IP101.
- Parameters:
config -- [in] configuration of PHY
- Returns:
instance: create PHY instance successfully
NULL: create PHY instance failed because some error occurred
-
esp_eth_phy_t *esp_eth_phy_new_rtl8201(const eth_phy_config_t *config)
Create a PHY instance of RTL8201.
- Parameters:
config -- [in] configuration of PHY
- Returns:
instance: create PHY instance successfully
NULL: create PHY instance failed because some error occurred
-
esp_eth_phy_t *esp_eth_phy_new_lan87xx(const eth_phy_config_t *config)
Create a PHY instance of LAN87xx.
- Parameters:
config -- [in] configuration of PHY
- Returns:
instance: create PHY instance successfully
NULL: create PHY instance failed because some error occurred
-
esp_eth_phy_t *esp_eth_phy_new_dp83848(const eth_phy_config_t *config)
Create a PHY instance of DP83848.
- Parameters:
config -- [in] configuration of PHY
- Returns:
instance: create PHY instance successfully
NULL: create PHY instance failed because some error occurred
-
esp_eth_phy_t *esp_eth_phy_new_ksz80xx(const eth_phy_config_t *config)
Create a PHY instance of KSZ80xx.
The phy model from the KSZ80xx series is detected automatically. If the driver is unable to detect a supported model,
NULLis returned.Currently, the following models are supported: KSZ8001, KSZ8021, KSZ8031, KSZ8041, KSZ8051, KSZ8061, KSZ8081, KSZ8091
- Parameters:
config -- [in] configuration of PHY
- Returns:
instance: create PHY instance successfully
NULL: create PHY instance failed because some error occurred
Structures
-
struct esp_eth_phy_s
Ethernet PHY.
Public Members
-
esp_err_t (*set_mediator)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, esp_eth_mediator_t *mediator)
Set mediator for PHY.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param mediator:
[in] mediator of Ethernet driver
- Return:
ESP_OK: set mediator for Ethernet PHY instance successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: set mediator for Ethernet PHY instance failed because of some invalid arguments
-
esp_err_t (*reset)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy)
Software Reset Ethernet PHY.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: reset Ethernet PHY successfully
ESP_FAIL: reset Ethernet PHY failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*reset_hw)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy)
Hardware Reset Ethernet PHY.
Note
Hardware reset is mostly done by pull down and up PHY's nRST pin
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: reset Ethernet PHY successfully
ESP_FAIL: reset Ethernet PHY failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*init)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy)
Initialize Ethernet PHY.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: initialize Ethernet PHY successfully
ESP_FAIL: initialize Ethernet PHY failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*deinit)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy)
Deinitialize Ethernet PHY.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: deinitialize Ethernet PHY successfully
ESP_FAIL: deinitialize Ethernet PHY failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*autonego_ctrl)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, eth_phy_autoneg_cmd_t cmd, bool *autonego_en_stat)
Configure auto negotiation.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param cmd:
[in] Configuration command, it is possible to Enable (restart), Disable or get current status of PHY auto negotiation
- Param autonego_en_stat:
[out] Address where to store current status of auto negotiation configuration
- Return:
ESP_OK: restart auto negotiation successfully
ESP_FAIL: restart auto negotiation failed because some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: invalid command
-
esp_err_t (*get_link)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy)
Get Ethernet PHY link status.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: get Ethernet PHY link status successfully
ESP_FAIL: get Ethernet PHY link status failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_link)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, eth_link_t link)
Set Ethernet PHY link status.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param link:
[in] new link status
- Return:
ESP_OK: set Ethernet PHY link status successfully
ESP_FAIL: set Ethernet PHY link status failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*pwrctl)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, bool enable)
Power control of Ethernet PHY.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param enable:
[in] set true to power on Ethernet PHY; ser false to power off Ethernet PHY
- Return:
ESP_OK: control Ethernet PHY power successfully
ESP_FAIL: control Ethernet PHY power failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_addr)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, uint32_t addr)
Set PHY chip address.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param addr:
[in] PHY chip address
- Return:
ESP_OK: set Ethernet PHY address successfully
ESP_FAIL: set Ethernet PHY address failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*get_addr)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, uint32_t *addr)
Get PHY chip address.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param addr:
[out] PHY chip address
- Return:
ESP_OK: get Ethernet PHY address successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: get Ethernet PHY address failed because of invalid argument
-
esp_err_t (*advertise_pause_ability)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, uint32_t ability)
Advertise pause function supported by MAC layer.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param addr:
[out] Pause ability
- Return:
ESP_OK: Advertise pause ability successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Advertise pause ability failed because of invalid argument
-
esp_err_t (*loopback)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, bool enable)
Sets the PHY to loopback mode.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param enable:
[in] enables or disables PHY loopback
- Return:
ESP_OK: PHY instance loopback mode has been configured successfully
ESP_FAIL: PHY instance loopback configuration failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_speed)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, eth_speed_t speed)
Sets PHY speed mode.
Note
Autonegotiation feature needs to be disabled prior to calling this function for the new setting to be applied
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param speed:
[in] Speed mode to be set
- Return:
ESP_OK: PHY instance speed mode has been configured successfully
ESP_FAIL: PHY instance speed mode configuration failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_duplex)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, eth_duplex_t duplex)
Sets PHY duplex mode.
Note
Autonegotiation feature needs to be disabled prior to calling this function for the new setting to be applied
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param duplex:
[in] Duplex mode to be set
- Return:
ESP_OK: PHY instance duplex mode has been configured successfully
ESP_FAIL: PHY instance duplex mode configuration failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*custom_ioctl)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, int cmd, void *data)
Custom IO function of PHY driver. This function is intended to extend common options of esp_eth_ioctl to cover specifics of PHY chip.
Note
This function may not be assigned when the PHY chip supports only most common set of configuration options.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Param cmd:
[in] IO control command
- Param data:
[inout] address of data for
setcommand or address where to store the data when used withgetcommand- Return:
ESP_OK: process io command successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: process io command failed because of some invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: process io command failed because some other error occurred
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: requested feature is not supported
-
esp_err_t (*del)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy)
Free memory of Ethernet PHY instance.
- Param phy:
[in] Ethernet PHY instance
- Return:
ESP_OK: free PHY instance successfully
ESP_FAIL: free PHY instance failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t (*set_mediator)(esp_eth_phy_t *phy, esp_eth_mediator_t *mediator)
-
struct eth_phy_config_t
Ethernet PHY configuration.
Public Members
-
int32_t phy_addr
PHY address, set -1 to enable PHY address detection at initialization stage
-
uint32_t reset_timeout_ms
Reset timeout value (Unit: ms)
-
uint32_t autonego_timeout_ms
Auto-negotiation timeout value (Unit: ms)
-
int reset_gpio_num
Reset GPIO number, -1 means no hardware reset
-
int32_t hw_reset_assert_time_us
Time the reset pin is asserted (Unit: us), 0 to use chip specific default
-
int32_t post_hw_reset_delay_ms
Time to wait after the HW reset (Unit: ms), 0 to use chip specific default, -1 means no wait
-
int32_t phy_addr
Macros
-
ESP_ETH_PHY_ADDR_AUTO
-
ESP_ETH_NO_POST_HW_RESET_DELAY
-
ETH_PHY_DEFAULT_CONFIG()
Default configuration for Ethernet PHY object.
Type Definitions
-
typedef struct esp_eth_phy_s esp_eth_phy_t
Ethernet PHY.
Enumerations
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_eth_phy_802_3.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_ethcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_eth, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_eth
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_eth
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_set_mediator(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, esp_eth_mediator_t *eth)
Set Ethernet mediator.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
eth -- Ethernet mediator pointer
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethermet mediator set successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: if
ethisNULL
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_reset(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3)
Reset PHY.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY reset successfully
ESP_FAIL: reset Ethernet PHY failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_autonego_ctrl(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, eth_phy_autoneg_cmd_t cmd, bool *autonego_en_stat)
Control autonegotiation mode of Ethernet PHY.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
cmd -- autonegotiation command enumeration
autonego_en_stat -- [out] autonegotiation enabled flag
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY autonegotiation configured successfully
ESP_FAIL: Ethernet PHY autonegotiation configuration fail because some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: invalid value of
cmd
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_updt_link_dup_spd(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3)
Retrieve link status and propagate the status to higher layers if the status changed.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY link status retrieved successfully
ESP_FAIL: Error occurred during reading registry
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_pwrctl(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, bool enable)
Power control of Ethernet PHY.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
enable -- set true to power ON Ethernet PHY; set false to power OFF Ethernet PHY
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY power down mode set successfully
ESP_FAIL: Ethernet PHY power up or power down failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_set_addr(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint32_t addr)
Set Ethernet PHY address.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
addr -- new PHY address
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY address set
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_get_addr(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint32_t *addr)
Get Ethernet PHY address.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
addr -- [out] Ethernet PHY address
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY address read successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG:
addrpointer isNULL
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_advertise_pause_ability(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint32_t ability)
Advertise pause function ability.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
ability -- enable or disable pause ability
- Returns:
ESP_OK: pause ability set successfully
ESP_FAIL: Advertise pause function ability failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_loopback(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, bool enable)
Set Ethernet PHY loopback mode.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
enable -- set true to enable loopback; set false to disable loopback
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY loopback mode set successfully
ESP_FAIL: Ethernet PHY loopback configuration failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_set_speed(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, eth_speed_t speed)
Set Ethernet PHY speed.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
speed -- new speed of Ethernet PHY link
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY speed set successfully
ESP_FAIL: Set Ethernet PHY speed failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_set_duplex(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, eth_duplex_t duplex)
Set Ethernet PHY duplex mode.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
duplex -- new duplex mode for Ethernet PHY link
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY duplex mode set successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: unable to set duplex mode to Half if loopback is enabled
ESP_FAIL: Set Ethernet PHY duplex mode failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_set_link(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, eth_link_t link)
Set Ethernet PHY link status.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
link -- new link status
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY link set successfully
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_init(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3)
Initialize Ethernet PHY.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY initialized successfully
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_deinit(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3)
Power off Eternet PHY.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY powered off successfully
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_del(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3)
Delete Ethernet PHY infostructure.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Ethernet PHY infostructure deleted
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_reset_hw(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint32_t reset_assert_us)
Performs hardware reset with specific reset pin assertion time.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
reset_assert_us -- Hardware reset pin assertion time
- Returns:
ESP_OK: reset Ethernet PHY successfully
ESP_ERR_NOT_ALLOWED: reset GPIO not defined
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_detect_phy_addr(esp_eth_mediator_t *eth, int *detected_addr)
Detect PHY address.
- Parameters:
eth -- Mediator of Ethernet driver
detected_addr -- [out] a valid address after detection
- Returns:
ESP_OK: detect phy address successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: invalid parameter
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: can't detect any PHY device
ESP_FAIL: detect phy address failed because some error occurred
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_basic_phy_init(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3)
Performs basic PHY chip initialization.
Note
It should be called as the first function in PHY specific driver instance
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
- Returns:
ESP_OK: initialized Ethernet PHY successfully
ESP_FAIL: initialization of Ethernet PHY failed because some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: invalid argument
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: PHY device not detected
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: MII Management read/write operation timeout
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: PHY is in invalid state to perform requested operation
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_basic_phy_deinit(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3)
Performs basic PHY chip de-initialization.
Note
It should be called as the last function in PHY specific driver instance
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
- Returns:
ESP_OK: de-initialized Ethernet PHY successfully
ESP_FAIL: de-initialization of Ethernet PHY failed because some error occurred
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: MII Management read/write operation timeout
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: PHY is in invalid state to perform requested operation
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_read_oui(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint32_t *oui)
Reads raw content of OUI field.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
oui -- [out] OUI value
- Returns:
ESP_OK: OUI field read successfully
ESP_FAIL: OUI field read failed because some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: invalid
ouiargumentESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: MII Management read/write operation timeout
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: PHY is in invalid state to perform requested operation
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_read_manufac_info(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint8_t *model, uint8_t *rev)
Reads manufacturer’s model and revision number.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
model -- [out] Manufacturer’s model number (can be NULL when not required)
rev -- [out] Manufacturer’s revision number (can be NULL when not required)
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Manufacturer’s info read successfully
ESP_FAIL: Manufacturer’s info read failed because some error occurred
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: MII Management read/write operation timeout
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: PHY is in invalid state to perform requested operation
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_get_mmd_addr(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint8_t devaddr, uint16_t *mmd_addr)
Reads MDIO device's internal address register.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
devaddr -- Address of MDIO device
mmd_addr -- [out] Current address stored in device's register
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Address register read successfully
ESP_FAIL: Address register read failed because of some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Device address provided is out of range (hardware limits device address to 5 bits)
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_set_mmd_addr(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint8_t devaddr, uint16_t mmd_addr)
Write to DIO device's internal address register.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
devaddr -- Address of MDIO device
mmd_addr -- [out] New value of MDIO device's address register value
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Address register written to successfully
ESP_FAIL: Address register write failed because of some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Device address provided is out of range (hardware limits device address to 5 bits)
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_read_mmd_data(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint8_t devaddr, esp_eth_phy_802_3_mmd_func_t function, uint32_t *data)
Read data of MDIO device's memory at address register.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
devaddr -- Address of MDIO device
function -- MMD function
data -- [out] Data read from the device's memory
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Memory read successfully
ESP_FAIL: Memory read failed because of some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Device address provided is out of range (hardware limits device address to 5 bits) or MMD access function is invalid
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_write_mmd_data(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint8_t devaddr, esp_eth_phy_802_3_mmd_func_t function, uint32_t data)
Write data to MDIO device's memory at address register.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
devaddr -- Address of MDIO device
function -- MMD function
data -- [out] Data to write to the device's memory
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Memory written successfully
ESP_FAIL: Memory write failed because of some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Device address provided is out of range (hardware limits device address to 5 bits) or MMD access function is invalid
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_read_mmd_register(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint8_t devaddr, uint16_t mmd_addr, uint32_t *data)
Set MMD address to mmd_addr with function MMD_FUNC_NOINCR and read contents to *data.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
devaddr -- Address of MDIO device
mmd_addr -- Address of MDIO device register
data -- [out] Data read from the device's memory
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Memory read successfully
ESP_FAIL: Memory read failed because of some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Device address provided is out of range (hardware limits device address to 5 bits)
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_write_mmd_register(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, uint8_t devaddr, uint16_t mmd_addr, uint32_t data)
Set MMD address to mmd_addr with function MMD_FUNC_NOINCR and write data.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
devaddr -- Address of MDIO device
mmd_addr -- Address of MDIO device register
data -- [out] Data to write to the device's memory
- Returns:
ESP_OK: Memory written to successfully
ESP_FAIL: Memory write failed because of some error occurred
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Device address provided is out of range (hardware limits device address to 5 bits)
-
inline phy_802_3_t *esp_eth_phy_into_phy_802_3(esp_eth_phy_t *phy)
Returns address to parent IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure.
- Parameters:
phy -- Ethernet PHY instance
- Returns:
phy_802_3_t*
address to parent IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_phy_802_3_obj_config_init(phy_802_3_t *phy_802_3, const eth_phy_config_t *config)
Initializes configuration of parent IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure.
- Parameters:
phy_802_3 -- Address to IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure
config -- Configuration of the IEEE 802.3 PHY object
- Returns:
ESP_OK: configuration initialized successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: invalid
configargument
Structures
-
struct phy_802_3_t
IEEE 802.3 PHY object infostructure.
Public Members
-
esp_eth_phy_t parent
Parent Ethernet PHY instance
-
esp_eth_mediator_t *eth
Mediator of Ethernet driver
-
int addr
PHY address
-
uint32_t reset_timeout_ms
Reset timeout value (Unit: ms)
-
uint32_t autonego_timeout_ms
Auto-negotiation timeout value (Unit: ms)
-
eth_link_t link_status
Current Link status
-
int reset_gpio_num
Reset GPIO number, -1 means no hardware reset
-
int32_t hw_reset_assert_time_us
Time the reset pin is asserted (Unit: us)
-
int32_t post_hw_reset_delay_ms
Time to wait after the HW reset (Unit: ms)
-
esp_eth_phy_t parent
Enumerations
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_eth_netif_glue.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_ethcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_eth, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_eth
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_eth
Functions
-
esp_eth_netif_glue_handle_t esp_eth_new_netif_glue(esp_eth_handle_t eth_hdl)
Create a netif glue for Ethernet driver.
Note
netif glue is used to attach io driver to TCP/IP netif
- Parameters:
eth_hdl -- Ethernet driver handle
- Returns:
glue object, which inherits esp_netif_driver_base_t
-
esp_err_t esp_eth_del_netif_glue(esp_eth_netif_glue_handle_t eth_netif_glue)
Delete netif glue of Ethernet driver.
- Parameters:
eth_netif_glue -- netif glue
- Returns:
-ESP_OK: delete netif glue successfully
Type Definitions
-
typedef struct esp_eth_netif_glue_t *esp_eth_netif_glue_handle_t
Handle of netif glue - an intermediate layer between netif and Ethernet driver.