ESP-WROVER-KIT V4.1 Getting Started Guide¶
This user guide shows how to get started with the ESP-WROVER-KIT V4.1 development board including description of its functionality and configuration options. For descriptions of other versions of the ESP-WROVER-KIT check ESP32 Hardware Reference.
If you would like to start using this board right now, go directly to the Start Application Development section.
What You Need¶
1 x Micro USB 2.0 Cable, Type A to Micro B
1 × PC loaded with Windows, Linux or Mac OS
Overview¶
The ESP-WROVER-KIT is a development board built around the ESP32 and produced by Espressif. This board is compatible with multiple ESP32 modules, including the ESP32-WROOM-32, ESP32-WROVER and ESP32-WROVER-B. The ESP-WROVER-KIT features support for an LCD and a MicroSD card. The I/O pins have been broken out from the ESP32 module for easy extension. The board carries an advanced multi-protocol USB bridge (the FTDI FT2232HL), enabling developers to use JTAG directly to debug the ESP32 through the USB interface. The development board makes secondary development easy and cost-effective.
Functionality Overview¶
The block diagram below illustrates the ESP-WROVER-KIT’s main components and their interconnections.
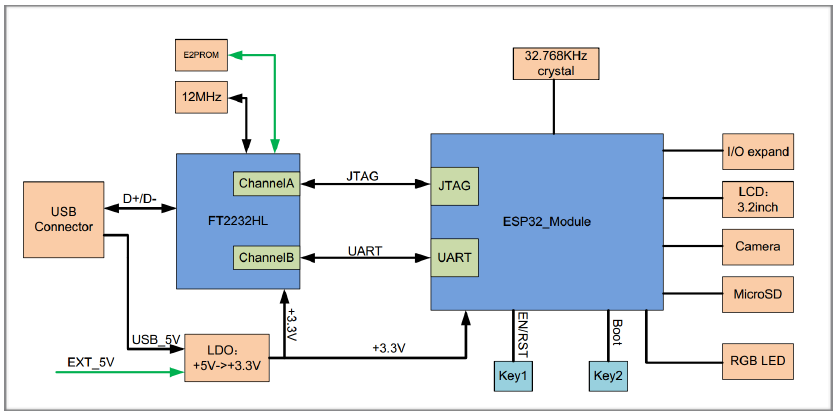
ESP-WROVER-KIT block diagram¶
Functional Description¶
The following lists and figures describe the key components, interfaces, and controls of ESP-WROVER-KIT board.
- 32.768 kHz
An external precision 32.768 kHz crystal oscillator provides a low-power consumption clock used during Deep-Sleep mode.
- FT2232
The FT2232 chip is a multi-protocol USB-to-serial bridge. Users can control and program the FT2232 chip through the USB interface to establish communication with ESP32. The FT2232 chip also features USB-to-JTAG interface. USB-to-JTAG is available on channel A of the FT2232, whilst USB-to-serial is on channel B. The embedded FT2232 chip is one of the distinguishing features of the ESP-WROVER-KIT. It enhances users’ convenience in terms of application development and debugging. In addition, users need not purchase a JTAG debugger separately, which reduces the development cost, see ESP-WROVER-KIT V4.1 schematic.
- 0R
A zero Ohm resistor intended as a placeholder for a current shunt. May be desoldered or replaced with a current shunt to facilitate measurement of current required by ESP32 module depending on power mode.
- ESP32-WROVER
This version of ESP-WROVER-KIT board has ESP-WROVER-B module installed that integrates 64-Mbit PSRAM for flexible extended storage and data processing capabilities. The board can accommodate other versions of ESP modules described under WROOM, SOLO and WROVER Modules.
Note
GPIO16 and GPIO17 are used as the CS and clock signal for PSRAM. To ensure reliable performance, the two GPIOs are not broken out.
- Diagnostic LEDs
Four red LEDs connected to GPIO pins of the FT2232 chip. Intended for future use.
- UART
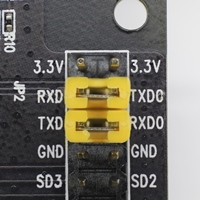
Serial port: the serial TX/RX signals on the FT2232HL and the ESP32 are broken out to each side of JP2. By default, the two signals are connected with jumpers. To use the ESP32 module serial interface only, the jumpers may be removed and the module can be connected to another external serial device.
- SPI
SPI interface used by ESP32 to access flash and PSRAM memories inside the module. Please note that the voltage level on this interface depends on the module used.
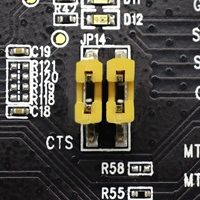
- CTS/RTS
Serial port flow control signals: the pins are not connected to the circuitry by default. To enable them, respective pins of JP14 must be shorted with jumpers.
- JTAG
JTAG interface: the JTAG signals on FT2232HL and ESP32 are broken out to the two sides of JP2. By default, the two signals are disconnected. To enable JTAG, shorting jumpers are required on the signals as shown in section Setup Options.
- USB Port
USB interface. It functions as the power supply for the board and the communication interface between PC and ESP32 module.
- EN Button
Reset button: pressing this button resets the system.
- Boot Button
Download button: holding down the Boot button and pressing the EN button initiates the firmware download mode. Then user can download firmware through the serial port.
- Power Switch
Power on/off button: toggling to the right powers the board on; toggling to the left powers the board off.
- Power Selector
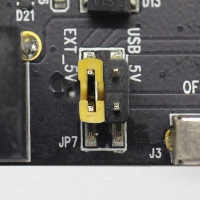
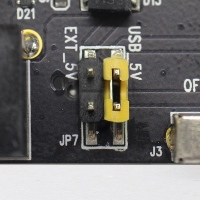
Power supply selection interface: the ESP-WROVER-KIT can be powered through the USB interface or the 5V Input interface. The user can select the power supply with a jumper. More details can be found in section Setup Options, jumper header JP7.
- 5V Input
The 5V power supply interface is used as a backup power supply in case of full-load operation.
- 5V Power On LED
This red LED indicates that a power supply (either from USB or 5V Input) is applied to the board.
- LDO
NCP1117(1A). 5V-to-3.3V LDO. (There is an alternative pin-compatible LDO — LM317DCY, with an output current of up to 1.5A). NCP1117 can provide a maximum current of 1A. The LDO solutions are available with both fixed output voltage and variable output voltage. For details please refer to ESP-WROVER-KIT V4.1 schematic.
- Camera Connector
Camera interface: a standard OV7670 camera module is supported.
- RGB LED
Red, green and blue (RGB) light emitting diodes (LEDs), which may be controlled by pulse width modulation (PWM).
- I/O Connector
All the pins on the ESP32 module are led out to the pin headers on the ESP-WROVER-KIT. Users can program ESP32 to enable multiple functions such as PWM, ADC, DAC, I2C, I2S, SPI, etc.
- Micro SD Card Slot
Develop applications that access Micro SD card for data storage and retrieval.
- LCD
ESP-WROVER-KIT supports mounting and interfacing a 3.2” SPI (standard 4-wire Serial Peripheral Interface) LCD, as shown on figure ESP-WROVER-KIT board layout - back.
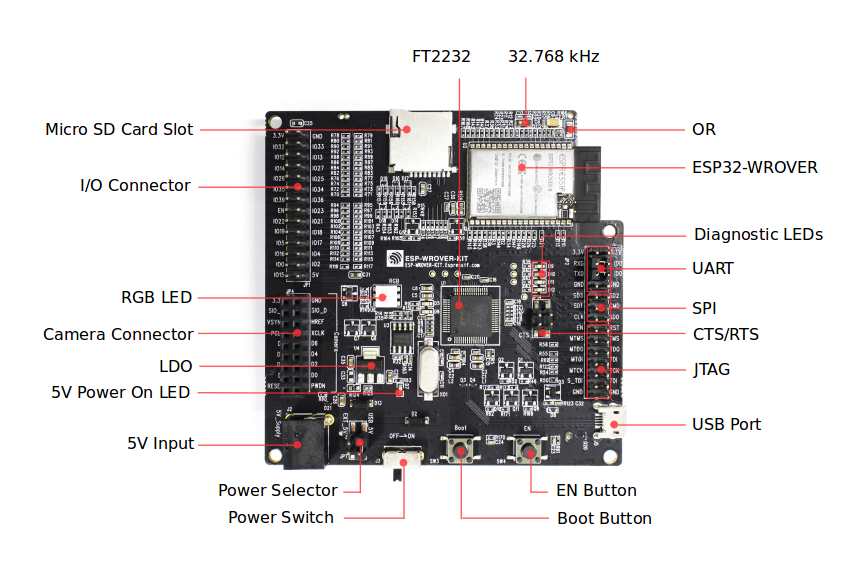
ESP-WROVER-KIT board layout - front¶
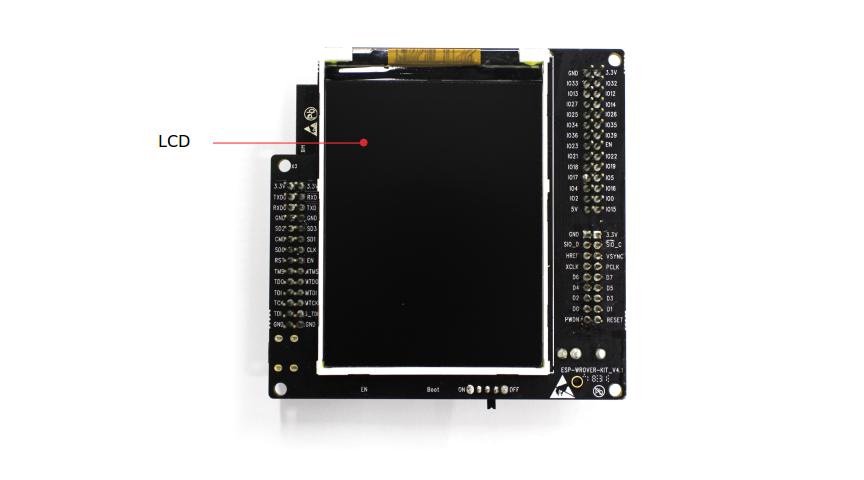
ESP-WROVER-KIT board layout - back¶
Setup Options¶
There are three jumper headers available to set up the board functionality. Typical options to select from are listed in table below.
Header |
Jumper Setting |
Description of Functionality |
|---|---|---|
JP7 |
|
Power ESP-WROVER-KIT board from an external power supply |
JP7 |
|
Power ESP-WROVER-KIT board from an USB port |
JP2 |
|
Enable JTAG functionality |
JP2 |
|
Enable UART communication |
JP14 |
|
Enable RTS/CTS flow control for serial communication |
Allocation of ESP32 Pins¶
Several pins / terminals of ESP32 module are allocated to the on board hardware. If certain hardware is not installed, e.g. nothing is plugged in to the Camera / JP4 header, then selected GPIOs may be used for other purposes.
Some of pins, like GPIO0 or GPIO2, have multiple functions and some of them are shared among on board and optional peripheral devices. Certain combinations of peripherals cannot work together. For example it is not possible to do JTAG debugging of an application that is using SD card, because several pins are shared by JTAG and the SD card slot.
In other cases peripherals can coexist under certain conditions. This is applicable to e.g. LCD screen and SD card that share only a single pin GPIO21. This pin is used to provide D/C (Data / Control) signal for the LCD and CD (Card Detect) signal read from the SD card slot. If the card detect functionality is not essential, then it may be disabled by removing R167, so both LCD and SD may operate together.
For more details what pins are shared among peripherals please refer to the table below.
Main I/O Connector / JP1¶
The JP1 connector is shown in two columns in the middle under “I/O” headers. The two columns “Shared With” outside, describe where else on the board certain GPIO is used.
Shared With |
I/O |
I/O |
Shared With |
|---|---|---|---|
NC/XTAL |
IO32 |
IO33 |
NC/XTAL |
JTAG, MicroSD |
IO12 |
IO13 |
JTAG, MicroSD |
JTAG, MicroSD |
IO14 |
IO27 |
Camera |
Camera |
IO26 |
IO25 |
Camera, LCD |
Camera |
IO35 |
IO34 |
Camera |
Camera |
IO39 |
IO36 |
Camera |
JTAG |
EN |
IO23 |
Camera, LCD |
Camera, LCD |
IO22 |
IO21 |
Camera, LCD, MicroSD |
Camera, LCD |
IO19 |
IO18 |
Camera, LCD |
Camera, LCD |
IO5 |
IO17 |
PSRAM |
PSRAM |
IO16 |
IO4 |
LED, Camera, MicroSD |
Camera, LED, Boot |
IO0 |
IO2 |
LED, MicroSD |
JTAG, MicroSD |
IO15 |
5V |
Legend:
NC/XTAL - 32.768 kHz Oscillator
JTAG - JTAG / JP8
Boot - Boot button / SW2
Camera - Camera / JP4
LED - RGB LED
MicroSD - MicroSD Card / J4
LCD - LCD / U5
PSRAM - ESP32-WROVER’s PSRAM, if ESP32-WROVER is installed
32.768 kHz Oscillator¶
. |
ESP32 Pin |
|---|---|
1 |
GPIO32 |
2 |
GPIO33 |
Note
As GPIO32 and GPIO33 are connected to the oscillator, they are not connected to JP1 I/O expansion connector to maintain signal integrity. This allocation may be changed from oscillator to JP1 by desoldering the 0R resistors from positions R11 / R23 and installing them in positions R12 / R24.
SPI Flash / JP2¶
. |
ESP32 Pin |
|---|---|
1 |
CLK / GPIO6 |
2 |
SD0 / GPIO7 |
3 |
SD1 / GPIO8 |
4 |
SD2 / GPIO9 |
5 |
SD3 / GPIO10 |
6 |
CMD / GPIO11 |
Important
The module’s flash bus is connected to the pin header JP2 through 0-Ohm resistors R140 ~ R145. If the flash frequency needs to operate at 80 MHz for reasons such as improving the integrity of bus signals, it is recommended that resistors R140 ~ R145 be desoldered. At this point, the module’s flash bus is disconnected with the pin header JP2.
JTAG / JP2¶
. |
ESP32 Pin |
JTAG Signal |
|---|---|---|
1 |
EN |
TRST_N |
2 |
MTMS / GPIO14 |
TMS |
3 |
MTDO / GPIO15 |
TDO |
4 |
MTDI / GPIO12 |
TDI |
5 |
MTCK / GPIO13 |
TCK |
Camera / JP4¶
. |
ESP32 Pin |
Camera Signal |
|---|---|---|
1 |
n/a |
3.3V |
2 |
n/a |
Ground |
3 |
GPIO27 |
SIO_C / SCCB Clock |
4 |
GPIO26 |
SIO_D / SCCB Data |
5 |
GPIO25 |
VSYNC / Vertical Sync |
6 |
GPIO23 |
HREF / Horizontal Reference |
7 |
GPIO22 |
PCLK / Pixel Clock |
8 |
GPIO21 |
XCLK / System Clock |
9 |
GPIO35 |
D7 / Pixel Data Bit 7 |
10 |
GPIO34 |
D6 / Pixel Data Bit 6 |
11 |
GPIO39 |
D5 / Pixel Data Bit 5 |
12 |
GPIO36 |
D4 / Pixel Data Bit 4 |
13 |
GPIO19 |
D3 / Pixel Data Bit 3 |
14 |
GPIO18 |
D2 / Pixel Data Bit 2 |
15 |
GPIO5 |
D1 / Pixel Data Bit 1 |
16 |
GPIO4 |
D0 / Pixel Data Bit 0 |
17 |
GPIO0 |
RESET / Camera Reset |
18 |
n/a |
PWDN / Camera Power Down |
Signals D0 .. D7 denote camera data bus
RGB LED¶
. |
ESP32 Pin |
RGB LED |
|---|---|---|
1 |
GPIO0 |
Red |
2 |
GPIO2 |
Green |
3 |
GPIO4 |
Blue |
MicroSD Card / J4¶
. |
ESP32 Pin |
MicroSD Signal |
|---|---|---|
1 |
MTDI / GPIO12 |
DATA2 |
2 |
MTCK / GPIO13 |
CD / DATA3 |
3 |
MTDO / GPIO15 |
CMD |
4 |
MTMS / GPIO14 |
CLK |
5 |
GPIO2 |
DATA0 |
6 |
GPIO4 |
DATA1 |
7 |
GPIO21 |
CD |
LCD / U5¶
. |
ESP32 Pin |
LCD Signal |
|---|---|---|
1 |
GPIO18 |
RESET |
2 |
GPIO19 |
SCL |
3 |
GPIO21 |
D/C |
4 |
GPIO22 |
CS |
5 |
GPIO23 |
SDA |
6 |
GPIO25 |
SDO |
7 |
GPIO5 |
Backlight |
Start Application Development¶
Before powering up the ESP-WROVER-KIT, please make sure that the board has been received in good condition with no obvious signs of damage.
Initial Setup¶
Select the source of power supply for the board by setting jumper JP7. The options are either USB port or an external 5V Input. For this application, the selection of the USB port is sufficient. Enable UART communication by installing jumpers on JP2. Both selections are shown in table below.
Power up from USB port |
Enable UART communication |
|---|---|
|
|
Do not install any other jumpers.
Turn the Power Switch on. The 5V Power On LED should turn on.
Now to Development¶
To start development of applications for ESP-WROVER-KIT, proceed to the Get Started section which will walk you through the following steps:
Setup Toolchain in your PC to develop applications for ESP32 in C language
Connect the module to the PC and verify if it is accessible
Build and Flash an example application to the ESP32
Monitor instantly what the application is doing