BluFi¶
Overview¶
The BluFi for ESP32 is a Wi-Fi network configuration function via Bluetooth channel. It provides a secure protocol to pass Wi-Fi configuration and credentials to the ESP32. Using this information ESP32 can then e.g. connect to an AP or establish a SoftAP.
Fragmenting, data encryption, checksum verification in the BluFi layer are the key elements of this process.
You can customize symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption and checksum support customization. Here we use the DH algorithm for key negotiation, 128-AES algorithm for data encryption, and CRC16 algorithm for checksum verification.
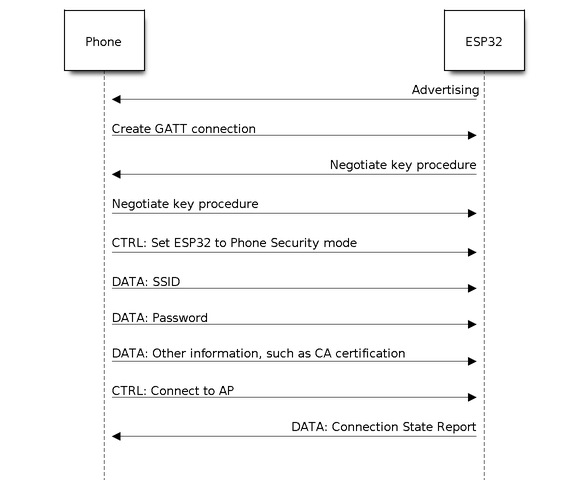
The BluFi Flow¶
The BluFi networking flow includes the configuration of the SoftAP and Station.
The following uses Station as an example to illustrate the core parts of the procedure, including broadcast, connection, service discovery, negotiation of the shared key, data transmission, connection status backhaul.
Set the ESP32 into GATT Server mode and then it will send broadcasts with specific advertising data. You can customize this broadcast as needed, which is not a part of the BluFi Profile.
Use the App installed on the mobile phone to search for this particular broadcast. The mobile phone will connect to ESP32 as the GATT Client once the broadcast is confirmed. The App used during this part is up to you.
After the GATT connection is successfully established, the mobile phone will send a data frame for key negotiation to ESP32 (see the section The Frame Formats Defined in BluFi for details).
After ESP32 receives the data frame of key negotiation, it will parse the content according to the user-defined negotiation method.
The mobile phone works with ESP32 for key negotiation using the encryption algorithms such as DH, RSA or ECC.
After the negotiation process is completed, the mobile phone will send a control frame for security-mode setup to ESP32.
When receiving this control frame, ESP32 will be able to encrypt and decrypt the communication data using the shared key and the security configuration.
The mobile phone sends the data frame defined in the section of The Frame Formats Defined in BluFi,with the Wi-Fi configuration information to ESP32, including SSID, password, etc.
The mobile phone sends a control frame of Wi-Fi connection request to ESP32. When receiving this control frame, ESP32 will regard the communication of essential information as done and get ready to connect to the Wi-Fi.
After connecting to the Wi-Fi, ESP32 will send a control frame of Wi-Fi connection status report to the mobile phone,to report the connection status. At this point the networking procedure is completed.
Note
After ESP32 receives the control frame of security-mode configuration, it will execute the operations in accordance with the defined security mode.
The data lengths before and after symmetric encryption/decryption must stay the same. It also supports in-place encryption and decryption.
The Frame Formats Defined in BluFi¶
The frame formats for the communication between the mobile phone App and ESP32 are defined as follows:
The frame format with no fragment (8 bit):
Description |
Value |
|---|---|
LSB - Type |
1 |
Frame Control |
1 |
Sequence Number |
1 |
Data Length |
1 |
Data |
${Data Length} |
MSB - CheckSum |
2 |
If the Frame Ctrl bit is enabled, the Total length bit indicates the length of remaining part of the frame. It can tell the remote how much memory needs to be alloced.
The frame format with fragments(8 bit):
Description |
Value |
|
|---|---|---|
LSB - Type |
1 |
|
FrameControl(Frag) |
1 |
|
SequenceNumber |
1 |
|
DataLength |
1 |
|
Data |
Total Content Length |
2 |
Content |
${Data Length} - 2 |
|
MSB - CheckSum |
2 |
|
Normally, the control frame does not contain data bits, except for Ack Frame.
The format of Ack Frame(8 bit):
Description |
Value |
|
LSB - Type (Ack) |
1 |
|
Frame Control |
1 |
|
SequenceNumber |
1 |
|
DataLength |
1 |
|
Data |
Acked Sequence Number |
2 |
MSB - CheckSum |
2 |
|
Type
The Type field, taking 1 byte, is divided into Type and Subtype, that Type uses the lower 2 bits and Subtype uses the upper 6 bits.
The control frame is not encrypted for the time being and supports to be verified;
The data frame supports to be encrypted and verified.
1.1 Control Frame (0x0 b’00)
Control Frame (Binary)
Implication
Explanation
Note
0x0 (b’000000)
Ack
The data field of the Ack frame uses the same sequence value of the frame to reply to.
The data field consumes a byte and its value is the same as the sequence field of the frame to reply to.
0x1 (b’000001)
Set ESP32 to the security mode.
To inform ESP32 of the security mode to use when sending data, which is allowed to be reset multiple times during the process. Each setting affects the subsequent security mode used. If it is not set, ESP32 will send the control frame and data frame with no checksum and encryption by default. The data transmission from the mobile phone to ESP32 is controlled by this control frame.
The data field consumes a byte. The higher 4 bits are for the security mode setting of the control frame, and the lower 4 bits are for the security mode setting of the data frame.
b’0000: no checksum and no encryption;
b’0001: with checksum but no encryption;
b’0010: no checksum but with encryption;
b’0011: with both checksum and encryption.
0x2 (b’000010)
Set the opmode of Wi-Fi.
The frame contains opmode settings for configuring for the Wi-Fi mode of ESP32.
data[0] is for opmode settings, including:
0x00: NULL;
0x01: STA;
0x02: SoftAP;
0x03: SoftAP&STA.
Please set the SSID/Password/Max Connection Number of the AP mode in the first place if an AP gets involved.
0x3 (b’000011)
Connect ESP32 to the AP.
To notify ESP32 that the essential information has been sent and it is allowed to connect to the AP.
No data field is contained.
0x4 (b’000100)
Disconnect ESP32 from the AP.
No data field is contained.
0x5 (b’000101)
To get the information of ESP32’s Wi-Fi mode and its status.
No data field is contained. When receiving this control frame, ESP32 will send back a follow-up frame of Wi-Fi connection state report to the mobile phone with the information of the current opmode, connection status, SSID and so on. The types of information sent to the mobile phone is defined by the application installed on the phone.
0x6 (b’000110)
Disconnect the STA device from the SoftAP (in SoftAP mode).
Date[0~5] is taken as the MAC address for the STA device. If there is a second STA device, then it uses data[6-11] and the rest can be done in the same manner.
0x7 (b’000111)
Get the version information.
0x8 (b’001000)
Disconnect the BLE GATT link.
ESP32 will disconnect the BLE GATT link after receives this command.
0x9 (b’001001)
Get the Wi-Fi list.
To get ESP32 to scan the Wi-Fi access points around.
No data field is contained. When receiving this control frame, ESP32 will send back a follow-up frame of Wi-Fi list report to the mobile phone.
1.2 Data Frame (0x1 b’01)
Data Frame(Binary)
Implication
Explanation
Note
0x0 (b’000000)
Send the negotiation data.
The negotiation data will be sent to the callback function registered in the application layer.
The length of the data depends on the length field.
0x1 (b’000001)
Send the BSSID for STA mode.
To send the BSSID of the AP for the STA device to connect under the condition that the SSID is hidden.
The length of the data depends on the length field. When the transmission direction is ESP32 to the mobile phone, it means to provide the mobile phone with the needed information.
0x2 (b’000010)
Send the SSID for STA mode.
To send the SSID of the AP for the STA device to connect.
The length of the data depends on the length field. When the transmission direction is ESP32 to the mobile phone, it means to provide the mobile phone with the needed information.
0x3 (b’000011)
Send the password for STA mode.
To send the password of the AP for the STA device to connect.
The length of the data depends on the length field. When the transmission direction is ESP32 to the mobile phone, it means to provide the mobile phone with the needed information.
0x4 (b’000100)
Send the SSID for SoftAP mode.
The length of the data depends on the length field. When the transmission direction is ESP32 to the mobile phone, it means to provide the mobile phone with the needed information.
0x5 (b’000101)
Send the password for SoftAPmode.
The length of the data depends on the length field. When the transmission direction is ESP32 to the mobile phone, it means to provide the mobile phone with the needed information.
0x6 (b’000110)
Set the maximum connection number for SoftAP mode.
data[0] represents the value of the connection number, ranging from 1 to 4. When the transmission direction is ESP32 to the mobile phone, it means to provide the mobile phone with the needed information.
0x7 (b’000111)
Set the authentication mode for the SoftAP.
data[0]:
0x00: OPEN
0x01: WEP
0x02: WPA_PSK
0x03: WPA2_PSK
0x04: WPA_WPA2_PSK
When the transmission direction is ESP32 to the mobile phone, it means to provide the mobile phone with the needed information.
0x8 (b’001000)
Set the channel amount for SoftAP mode.
data[0] represents the quantity of the supported channels, ranging from 1 to 14. When the transmission direction is ESP32 to the mobile phone, it means to provide the mobile phone with the needed information.
0x9 (b’001001)
Username
It provides the username of the GATT client when using encryption of enterprise level.
The length of the data depends on the length field.
0xa (b’001010)
CA Certification
It provides the CA Certification when using encryption of enterprise level.
The length of the data depends on the length field. The frame supports to be fragmented if the data length is not enough.
0xb (b’001011)
Client Certification
It provides the client certification when using encryption of enterprise level. Whether the private key is contained or not depends on the content of the certification.
The length of the data depends on the length field. The frame supports to be fragmented if the data length is not enough.
0xc (b’001100)
Server Certification
It provides the sever certification when using encryption of enterprise level. Whether the private key is contained or not depends on the content of the certification.
The length of the data depends on the length field. The frame supports to be fragmented if the data length is not enough.
0xd (b’001101)
ClientPrivate Key
It provides the private key of the client when using encryption of enterprise level.
The length of the data depends on the length field. The frame supports to be fragmented if the data length is not enough.
0xe (b’001110)
ServerPrivate Key
It provides the private key of the sever when using encryption of enterprise level.
The length of the data depends on the length field. The frame supports to be fragmented if the data length is not enough.
0xf (b’001111)
Wi-Fi Connection State Report
To notify the phone of the ESP32’s Wi-Fi status, including STA status and SoftAP status. It is for the STA device to connect to the mobile phone or the SoftAP. However, when the mobile phone receives the Wi-Fi status, it can reply to other frames in addition to this frame.
data[0] represents opmode, including:
0x00: NULL
0x01: STA
0x02: SoftAP
0x03: SoftAP&STA
data[1]:the connection state of the STA device, 0x0 indicates a connection state, and others represent a disconnected state;
data[2]:the connection state of the SoftAP, that is, how many STA devices have been connected.
data[3] and the subsequent is in accordance with the format of SSID/BSSID information.
0x10 (b’010000)
Version
data[0]= great versiondata[1]= sub version
0x11 (b’010001)
Wi-Fi List
To send the Wi-Fi list to ESP32.
The format of the data frame is length + RSSI + SSID and it supports to be sent into fragments if the data length is too long.
0x12 (b’010010)
Report Error
To notify the mobile phone that there is an error with BluFi.
0x00: sequence error
0x01: checksum error
0x02: decrypt error
0x03: encrypt error
0x04: init security error
0x05: dh malloc error
0x06: dh param error
0x07: read param error
0x08: make public error
0x13 (b’010011)
Custom Data
To send or receive custom data.
The data frame supports to be sent into fragments if the data length is too long.
Frame Control
Control field, takes 1 byte and each bit has a different meaning.
Bit
Meaning
0x01
Indicates whether the frame is encrypted.
1 means encryption, and 0 means unencrypted.
The encrypted part of the frame includes the full clear data before the DATA field is encrypted (no checksum).
Control frame is not encrypted, so this bit is 0.
0x02
The data field that indicates whether a frame contains a checksum (such as SHA1,MD5,CRC, etc.) for the end of the frame data field includes SEQUCNE + data length + clear text. Both the control frame and the data frame can contain a check bit or not.
0x04
Represents the data direction.
0 means the mobile phone to ESP32;
1 means ESP32 to the mobile phone.
0x08
Indicates whether the other person is required to reply to an ACK.
0 indicates no requirement;
1 indicates to reply Ack.
0x10
Indicates whether there are subsequent data fragments.
0 indicates that there are no subsequent data fragments for this frame;
1 indicates that there are subsequent data fragments and used to transmit longer data.
In the case of a frag frame, the total length of the current content section + subsequent content section is given, in the first 2 bytes of the data field (that is, the content data of the maximum support 64K).
0x10~0x80 reserved
Sequence Control
Sequence control field. When a frame is sent,the value of sequence fied is automatically incremented by 1 regardless of the type of frame, which prevents Replay Attack. The sequence is cleared after each reconnection.
Length
The length of the data field that does not include CheckSum.
Data
The instruction of the data field is different according to various values of Type or Subtype. Please refer to the table above.
CheckSum
This field takes 2 bytes that is used to check “sequence + data length + clear text data”.
The Security Implementation of ESP32¶
Securing data
To ensure that the transmission of the Wi-Fi SSID and password is secure, the message needs to be encrypted using symmetric encryption algorithms, such as AES, DES and so on. Before using symmetric encryption algorithms, the devices are required to negotiate (or generate) a shared key using an asymmetric encryption algorithm (DH, RSA, ECC, etc).
Ensuring data integrity
To ensure data integrity, you need to add a checksum algorithm, such as SHA1, MD5, CRC, etc.
Securing identity (signature)
Algorithm like RSA can be used to secure identity. But for DH, it needs other algorithms as an companion for signature.
Replay attack prevention
It is added to the Sequence field and used during the checksum verification.
For the coding of ESP32, you can determine and develop the security processing, such as key negotiation. The mobile application sends the negotiation data to ESP32 and then the data will be sent to the application layer for processing. If the application layer does not process it, you can use the DH encryption algorithm provided by BluFi to negotiate the key.
The application layer needs to register several security-related functions to BluFi:
typedef void (*esp_blufi_negotiate_data_handler_t)(uint8_t *data, int len, uint8_t **output_data, int *output_len, bool *need_free)
This function is for ESP32 to receive normal data during negotiation, and after processing is completed, the data will be transmitted using Output_data and Output_len.
BluFi will send output_data from Negotiate_data_handler after Negotiate_data_handler is called.
Here are two “*”, because the length of the data to be emitted is unknown that requires the function to allocate itself (malloc) or point to the global variable, and to inform whether the memory needs to be freed by NEED_FREE.
typedef int (* esp_blufi_encrypt_func_t)(uint8_t iv8, uint8_t *crypt_data, int cyprt_len)
The data to be encrypted and decrypted must use the same length. The IV8 is a 8 bit sequence value of frames, which can be used as a 8 bit of IV.
typedef int (* esp_blufi_decrypt_func_t)(uint8_t iv8, uint8_t *crypt_data, int crypt_len)
The data to be encrypted and decrypted must use the same length. The IV8 is a 8 bit sequence value of frames, which can be used as a 8 bit of IV.
typedef uint16_t (*esp_blufi_checksum_func_t)(uint8_t iv8, uint8_t *data, int len)
This function is used to compute CheckSum and return a value of CheckSum. BluFi uses the returned value to compare the CheckSum of the frame.