红外遥控 (RMT)
简介
红外遥控 (RMT) 外设是一个红外发射和接收控制器。其数据格式灵活,可进一步扩展为多功能的通用收发器,发送或接收多种类型的信号。就网络分层而言,RMT 硬件包含物理层和数据链路层。物理层定义通信介质和比特信号的表示方式,数据链路层定义 RMT 帧的格式。RMT 帧的最小数据单元称为 RMT 符号,在驱动程序中以 rmt_symbol_word_t 表示。
ESP32-C6 的 RMT 外设存在多个通道 1,每个通道都可以独立配置为发射器或接收器。
RMT 外设通常支持以下场景:
发送或接收红外信号,支持所有红外线协议,如 NEC 协议
生成通用序列
有限或无限次地在硬件控制的循环中发送信号
多通道同时发送
将载波调制到输出信号或从输入信号解调载波
RMT 符号的内存布局
RMT 硬件定义了自己的数据模式,称为 RMT 符号。下图展示了一个 RMT 符号的位字段:每个符号由两对两个值组成,每对中的第一个值是一个 15 位的值,表示信号持续时间,以 RMT 滴答计。每对中的第二个值是一个 1 位的值,表示信号的逻辑电平,即高电平或低电平。
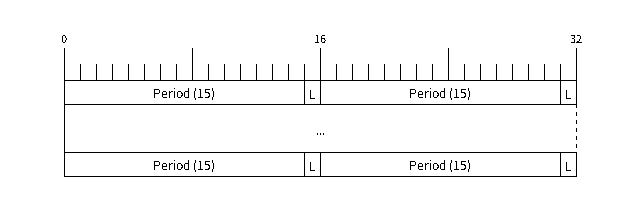
RMT 符号结构(L - 信号电平)
RMT 发射器概述
RMT 发送通道 (TX Channel) 的数据路径和控制路径如下图所示:
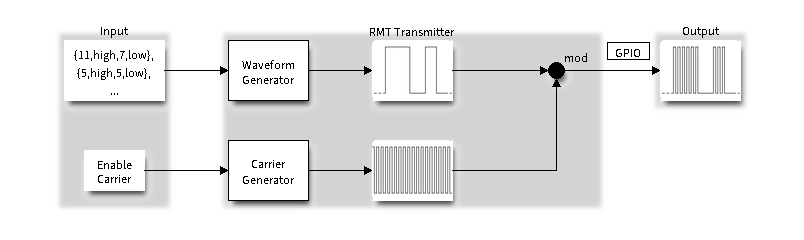
RMT 发射器概述
驱动程序将用户数据编码为 RMT 数据格式,随后由 RMT 发射器根据编码生成波形。在将波形发送到 GPIO 管脚前,还可以调制高频载波信号。
RMT 接收器概述
RMT 接收通道 (RX Channel) 的数据路径和控制路径如下图所示:
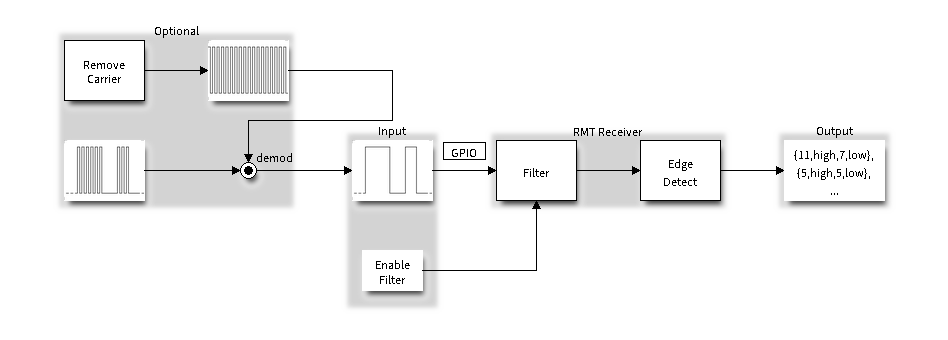
RMT 接收器概述
RMT 接收器可以对输入信号采样,将其转换为 RMT 数据格式,并将数据存储在内存中。还可以向接收器提供输入信号的基本特征,使其识别信号停止条件,并过滤掉信号干扰和噪声。RMT 外设还支持从基准信号中解调出高频载波信号。
功能概述
下文将分节概述 RMT 的功能:
资源分配 - 介绍如何分配和正确配置 RMT 通道,以及如何回收闲置信道及其他资源。
载波调制与解调 - 介绍如何调制和解调用于 TX 和 RX 通道的载波信号。
注册事件回调 - 介绍如何注册用户提供的事件回调函数以接收 RMT 通道事件。
启用及禁用通道 - 介绍如何启用和禁用 RMT 通道。
发起 TX 事务 - 介绍发起 TX 通道事务的步骤。
发起 RX 事务 - 介绍发起 RX 通道事务的步骤。
多通道同时发送 - 介绍如何将多个通道收集到一个同步组中,以便同时启动发送。
RMT 编码器 - 介绍如何通过组合驱动程序提供的多个基本编码器来编写自定义编码器。
电源管理 - 介绍不同时钟源对功耗的影响。
IRAM 安全 - 介绍禁用 cache 对 RMT 驱动程序的影响,并提供应对方案。
线程安全 - 介绍由驱动程序认证为线程安全的 API。
Kconfig 选项 - 介绍 RMT 驱动程序支持的各种 Kconfig 选项。
资源分配
驱动程序中,rmt_channel_handle_t 用于表示 RMT 的 TX 和 RX 通道。驱动程序在内部管理可用的通道,并在收到请求时提供空闲通道。
安装 RMT TX 通道
要安装 RMT TX 通道,应预先提供配置结构体 rmt_tx_channel_config_t。以下列表介绍了配置结构体中的各个部分。
rmt_tx_channel_config_t::gpio_num设置发射器使用的 GPIO 编号。rmt_tx_channel_config_t::clk_src选择 RMT 通道的时钟源。rmt_clock_source_t中列出了可用的时钟源。注意,其他信道将使用同一所选时钟源,因此,应确保分配的任意 TX 或 RX 通道都享有相同的配置。有关不同时钟源对功耗的影响,请参阅 电源管理。rmt_tx_channel_config_t::resolution_hz设置内部滴答计数器的分辨率。基于此 滴答,可以计算 RMT 信号的定时参数。在启用 DMA 后端和未启用 DMA 后端的情况下,
rmt_tx_channel_config_t::mem_block_symbols字段含义稍有不同。若通过
rmt_tx_channel_config_t::with_dma启用 DMA,则该字段可以控制内部 DMA 缓冲区大小。为实现更好的吞吐量、减少 CPU 开销,建议为字段设置一个较大的值,如1024。如果未启用 DMA,则该字段控制通道专用内存块大小,至少为 48。
rmt_tx_channel_config_t::trans_queue_depth设置内部事务队列深度。队列越深,在待处理队列中可以准备的事务越多。rmt_tx_channel_config_t::invert_out决定是否在将 RMT 信号发送到 GPIO 管脚前反转 RMT 信号。rmt_tx_channel_config_t::with_dma为通道启用 DMA 后端。启用 DMA 后端可以释放 CPU 上的大部分通道工作负载,显著减轻 CPU 负担。但并非所有 ESP 芯片都支持 DMA 后端,在启用此选项前,请参阅 [TRM]。若所选芯片不支持 DMA 后端,可能会报告ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED错误。rmt_tx_channel_config_t::io_loop_back启用通道所分配的 GPIO 上的输入和输出功能,将发送通道和接收通道绑定到同一个 GPIO 上,从而实现回环功能。rmt_tx_channel_config_t::io_od_mode配置通道分配的 GPIO 为开漏模式 (open-drain)。当与rmt_tx_channel_config_t::io_loop_back结合使用时,可以实现双向总线,如 1-wire。rmt_tx_channel_config_t::intr_priority设置中断的优先级。如果设置为0,驱动将会使用一个中低优先级的中断(优先级可能为1,2或3),否则会使用rmt_tx_channel_config_t::intr_priority指定的优先级。请使用优先级序号(1,2,3),而不是bitmask的形式((1<<1),(1<<2),(1<<3))。请注意,中断优先级一旦设置,在rmt_del_channel()被调用之前不可再次修改。
将必要参数填充到结构体 rmt_tx_channel_config_t 后,可以调用 rmt_new_tx_channel() 来分配和初始化 TX 通道。如果函数运行正确,会返回 RMT 通道句柄;如果 RMT 资源池内缺少空闲通道,会返回 ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND 错误;如果硬件不支持 DMA 后端等部分功能,则返回 ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED 错误。
rmt_channel_handle_t tx_chan = NULL;
rmt_tx_channel_config_t tx_chan_config = {
.clk_src = RMT_CLK_SRC_DEFAULT, // 选择时钟源
.gpio_num = 0, // GPIO 编号
.mem_block_symbols = 64, // 内存块大小,即 64 * 4 = 256 字节
.resolution_hz = 1 * 1000 * 1000, // 1 MHz 滴答分辨率,即 1 滴答 = 1 µs
.trans_queue_depth = 4, // 设置后台等待处理的事务数量
.flags.invert_out = false, // 不反转输出信号
.flags.with_dma = false, // 不需要 DMA 后端
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_new_tx_channel(&tx_chan_config, &tx_chan));
安装 RMT RX 通道
要安装 RMT RX 通道,应预先提供配置结构体 rmt_rx_channel_config_t。以下列表介绍了配置结构体中的各个部分。
rmt_rx_channel_config_t::gpio_num设置接收器使用的 GPIO 编号。rmt_rx_channel_config_t::clk_src选择 RMT 通道的时钟源。rmt_clock_source_t中列出了可用的时钟源。注意,其他信道将使用同一所选时钟源,因此,应确保分配的任意 TX 或 RX 通道都享有相同的配置。有关不同时钟源对功耗的影响,请参阅 电源管理。rmt_rx_channel_config_t::resolution_hz设置内部滴答计数器的分辨率。基于此 滴答,可以计算 RMT 信号的定时参数。在启用 DMA 后端和未启用 DMA 后端的情况下,
rmt_rx_channel_config_t::mem_block_symbols字段含义稍有不同。若通过
rmt_rx_channel_config_t::with_dma启用 DMA,则该字段可以最大化控制内部 DMA 缓冲区大小。如果未启用 DMA,则该字段控制通道专用内存块大小,至少为 48。
rmt_rx_channel_config_t::invert_in在输入信号传递到 RMT 接收器前对其进行反转。该反转由 GPIO 交换矩阵完成,而非 RMT 外设。rmt_rx_channel_config_t::with_dma为通道启用 DMA 后端。启用 DMA 后端可以释放 CPU 上的大部分通道工作负载,显著减轻 CPU 负担。但并非所有 ESP 芯片都支持 DMA 后端,在启用此选项前,请参阅 [TRM]。若所选芯片不支持 DMA 后端,可能会报告ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED错误。rmt_rx_channel_config_t::io_loop_back启用通道所分配的 GPIO 上的输入和输出功能,将发送通道和接收通道绑定到同一个 GPIO 上,从而实现回环功能。rmt_rx_channel_config_t::intr_priority设置中断的优先级。如果设置为0,驱动将会使用一个中低优先级的中断(优先级可能为1,2或3),否则会使用rmt_rx_channel_config_t::intr_priority指定的优先级。请使用优先级序号(1,2,3),而不是bitmask的形式((1<<1),(1<<2),(1<<3))。请注意,中断优先级一旦设置,在rmt_del_channel()被调用之前不可再次修改。
将必要参数填充到结构体 rmt_rx_channel_config_t 后,可以调用 rmt_new_rx_channel() 来分配和初始化 RX 通道。如果函数运行正确,会返回 RMT 通道句柄;如果 RMT 资源池内缺少空闲通道,会返回 ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND 错误;如果硬件不支持 DMA 后端等部分功能,则返回 ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED 错误。
rmt_channel_handle_t rx_chan = NULL;
rmt_rx_channel_config_t rx_chan_config = {
.clk_src = RMT_CLK_SRC_DEFAULT, // 选择时钟源
.resolution_hz = 1 * 1000 * 1000, // 1 MHz 滴答分辨率,即 1 滴答 = 1 µs
.mem_block_symbols = 64, // 内存块大小,即 64 * 4 = 256 字节
.gpio_num = 2, // GPIO 编号
.flags.invert_in = false, // 不反转输入信号
.flags.with_dma = false, // 不需要 DMA 后端
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_new_rx_channel(&rx_chan_config, &rx_chan));
备注
由于 GPIO 驱动程序中的软件限制,当 TX 和 RX 通道都绑定到同一 GPIO 时,请确保在 TX 通道之前初始化 RX 通道。如果先设置 TX 通道,那么在 RX 通道设置期间,GPIO 控制信号将覆盖先前的 RMT TX 通道信号。
卸载 RMT 通道
如果不再需要之前安装的 RMT 通道,建议调用 rmt_del_channel() 回收资源,使底层软件与硬件重新用于其他功能。
载波调制与解调
RMT 发射器可以生成载波信号,并将其调制到消息信号上。载波信号的频率远高于消息信号。此外,仅支持配置载波信号的频率和占空比。RMT 接收器可以从输入信号中解调出载波信号。注意,并非所有 ESP 芯片都支持载波调制和解调功能,在配置载波前,请参阅 [TRM]。若所选芯片不支持载波调制和解调功能,可能会报告 ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED 错误。
载波相关配置位于 rmt_carrier_config_t 中,该配置中的各部分详情如下:
rmt_carrier_config_t::frequency_hz设置载波频率,单位为 Hz。rmt_carrier_config_t::duty_cycle设置载波占空比。rmt_carrier_config_t::polarity_active_low设置载波极性,即应用载波的电平。rmt_carrier_config_t::always_on设置是否在数据发送完成后仍输出载波,该配置仅适用于 TX 通道。
备注
RX 通道的载波频率不应设置为理论值,建议为载波频率留出一定的容差。例如,以下代码片段的载波频率设置为 25 KHz,而非 TX 侧配置的 38 KHz。因为信号在空气中传播时会发生反射和折射,导致接收端接收的频率失真。
rmt_carrier_config_t tx_carrier_cfg = {
.duty_cycle = 0.33, // 载波占空比为 33%
.frequency_hz = 38000, // 38 KHz
.flags.polarity_active_low = false, // 载波应调制到高电平
};
// 将载波调制到 TX 通道
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_apply_carrier(tx_chan, &tx_carrier_cfg));
rmt_carrier_config_t rx_carrier_cfg = {
.duty_cycle = 0.33, // 载波占空比为 33%
.frequency_hz = 25000, // 载波频率为 25 KHz,应小于发射器的载波频率
.flags.polarity_active_low = false, // 载波调制到高电平
};
// 从 RX 通道解调载波
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_apply_carrier(rx_chan, &rx_carrier_cfg));
注册事件回调
当 RMT 信道生成发送或接收完成等事件时,会通过中断告知 CPU。如果需要在发生特定事件时调用函数,可以为 TX 和 RX 信道分别调用 rmt_tx_register_event_callbacks() 和 rmt_rx_register_event_callbacks(),向 RMT 驱动程序的中断服务程序 (ISR) 注册事件回调。由于上述回调函数是在 ISR 中调用的,因此,这些函数不应涉及 block 操作。可以检查调用 API 的后缀,确保在函数中只调用了后缀为 ISR 的 FreeRTOS API。回调函数具有布尔返回值,指示回调是否解除了更高优先级任务的阻塞状态。
有关 TX 通道支持的事件回调,请参阅 rmt_tx_event_callbacks_t:
rmt_tx_event_callbacks_t::on_trans_done为“发送完成”的事件设置回调函数,函数原型声明为rmt_tx_done_callback_t。
有关 RX 通道支持的事件回调,请参阅 rmt_rx_event_callbacks_t:
rmt_rx_event_callbacks_t::on_recv_done为“接收完成”的事件设置回调函数,函数原型声明为rmt_rx_done_callback_t。
也可使用参数 user_data,在 rmt_tx_register_event_callbacks() 和 rmt_rx_register_event_callbacks() 中保存自定义上下文。用户数据将直接传递给每个回调函数。
在回调函数中可以获取驱动程序在 edata 中填充的特定事件数据。注意,edata 指针仅在回调的持续时间内有效。
有关 TX 完成事件数据的定义,请参阅 rmt_tx_done_event_data_t:
rmt_tx_done_event_data_t::num_symbols表示已发送的 RMT 符号数量,也反映了编码数据大小。注意,该值还考虑了由驱动程序附加的EOF符号,该符号标志着一次事务的结束。
有关 RX 完成事件数据的定义,请参阅 rmt_rx_done_event_data_t:
rmt_rx_done_event_data_t::received_symbols指向接收到的 RMT 符号,这些符号存储在rmt_receive()函数的buffer参数中,在回调函数返回前不应释放此接收缓冲区。rmt_rx_done_event_data_t::num_symbols表示接收到的 RMT 符号数量,该值不会超过rmt_receive()函数的buffer_size参数。如果buffer_size不足以容纳所有接收到的 RMT 符号,驱动程序将只保存缓冲区能够容纳的最大数量的符号,并丢弃或忽略多余的符号。
启用及禁用通道
在发送或接收 RMT 符号前,应预先调用 rmt_enable()。启用 TX 通道会启用特定中断,并使硬件准备发送事务。启用 RX 通道也会启用中断,但由于传入信号的特性尚不明确,接收器不会在此时启动,而是在 rmt_receive() 中启动。
相反,rmt_disable() 会禁用中断并清除队列中的中断,同时禁用发射器和接收器。
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_enable(tx_chan));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_enable(rx_chan));
发起 TX 事务
RMT 是一种特殊的通信外设,无法像 SPI 和 I2C 那样发送原始字节流,只能以 rmt_symbol_word_t 格式发送数据。然而,硬件无法将用户数据转换为 RMT 符号,该转换只能通过 RMT 编码器在软件中完成。编码器将用户数据编码为 RMT 符号,随后写入 RMT 内存块或 DMA 缓冲区。有关创建 RMT 编码器的详细信息,请参阅 RMT 编码器。
获取编码器后,调用 rmt_transmit() 启动 TX 事务,该函数会接收少数位置参数,如通道句柄、编码器句柄和有效负载缓冲区。此外,还需要在 rmt_transmit_config_t 中提供专用于发送的配置,具体如下:
rmt_transmit_config_t::loop_count设置发送的循环次数。在发射器完成一轮发送后,如果该值未设置为零,则再次启动相同的发送程序。由于循环由硬件控制,RMT 通道可以在几乎不需要 CPU 干预的情况下,生成许多周期性序列。将
rmt_transmit_config_t::loop_count设置为-1,会启用无限循环发送机制,此时,除非手动调用rmt_disable(),否则通道不会停止,也不会生成“完成发送”事件。将
rmt_transmit_config_t::loop_count设置为正数,意味着迭代次数有限。此时,“完成发送”事件在指定的迭代次数完成后发生。
备注
注意,不是所有 ESP 芯片都支持 循环发送 功能,在配置此选项前,请参阅 [TRM]。若所选芯片不支持配置此选项,可能会报告
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED错误。rmt_transmit_config_t::eot_level设置发射器完成工作时的输出电平,该设置同时适用于调用rmt_disable()停止发射器工作时的输出电平。rmt_transmit_config_t::queue_nonblocking设置当传输队列满的时候该函数是否需要等待。如果该值设置为true那么当遇到队列满的时候,该函数会立即返回错误代码ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE。否则,函数会阻塞当前线程,直到传输队列有空档。
备注
如果将 rmt_transmit_config_t::loop_count 设置为非零值,即启用循环功能,则传输的大小将受到限制。编码器返回的符号总量不能超过 SOC_RMT_MEM_WORDS_PER_CHANNEL,否则会出现类似 encoding artifacts can't exceed hw memory block for loop transmission 的报错信息。如需通过循环启动大型事务,请尝试以下任一方法:
增加
rmt_tx_channel_config_t::mem_block_symbols。若此时启用了 DMA 后端,该方法将失效。自定义编码器,并在编码函数中构造一个无限循环,详情请参阅 RMT 编码器。
rmt_transmit() 会在其内部构建一个事务描述符,并将其发送到作业队列中,该队列将在 ISR 中调度。因此,在 rmt_transmit() 返回时,事务可能尚未启动。为确保完成所有挂起的事务,请调用 rmt_tx_wait_all_done()。
多通道同时发送
在一些实时控制应用程序中,启动多个 TX 通道(例如使两个器械臂同时移动)时,应避免出现任何时间漂移。为此,RMT 驱动程序可以创建 同步管理器 帮助管理该过程。在驱动程序中,同步管理器为 rmt_sync_manager_handle_t。RMT 同步发送过程如下图所示:
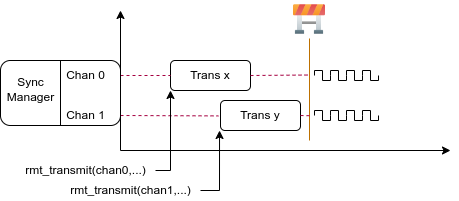
RMT TX 同步发送
安装 RMT 同步管理器
要创建同步管理器,应预先在 rmt_sync_manager_config_t 中指定要管理的通道:
rmt_sync_manager_config_t::tx_channel_array指向要管理的 TX 通道数组。rmt_sync_manager_config_t::array_size设置要管理的通道数量。
成功调用 rmt_new_sync_manager() 函数将返回管理器句柄,该函数也可能因为无效参数等错误而无法调用。在已经安装了同步管理器,且缺少硬件资源来创建另一个管理器时,该函数将报告 ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND 错误。此外,如果硬件不支持同步管理器,将报告 ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED 错误。在使用同步管理器功能之前,请参阅 [TRM]。
发起同时发送
在调用 rmt_sync_manager_config_t::tx_channel_array 中所有通道上的 rmt_transmit() 前,任何受管理的 TX 通道都不会启动发送机制,而是处于待命状态。由于各通道事务不同,TX 通道通常会在不同的时间完成相应事务,这可能导致无法同步。因此,在重新启动同时发送程序之前,应调用 rmt_sync_reset() 函数重新同步所有通道。
调用 rmt_del_sync_manager() 函数可以回收同步管理器,并使通道可以在将来独立启动发送程序。
rmt_channel_handle_t tx_channels[2] = {NULL}; // 声明两个通道
int tx_gpio_number[2] = {0, 2};
// 依次安装通道
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
rmt_tx_channel_config_t tx_chan_config = {
.clk_src = RMT_CLK_SRC_DEFAULT, // 选择时钟源
.gpio_num = tx_gpio_number[i], // GPIO 编号
.mem_block_symbols = 64, // 内存块大小,即 64 * 4 = 256 字节
.resolution_hz = 1 * 1000 * 1000, // 1 MHz 分辨率
.trans_queue_depth = 1, // 设置可以在后台挂起的事务数量
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_new_tx_channel(&tx_chan_config, &tx_channels[i]));
}
// 安装同步管理器
rmt_sync_manager_handle_t synchro = NULL;
rmt_sync_manager_config_t synchro_config = {
.tx_channel_array = tx_channels,
.array_size = sizeof(tx_channels) / sizeof(tx_channels[0]),
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_new_sync_manager(&synchro_config, &synchro));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_transmit(tx_channels[0], led_strip_encoders[0], led_data, led_num * 3, &transmit_config));
// 只有在调用 tx_channels[1] 的 rmt_transmit() 函数返回后,tx_channels[0] 才会开始发送数据。
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_transmit(tx_channels[1], led_strip_encoders[1], led_data, led_num * 3, &transmit_config));
发起 RX 事务
如 启用及禁用通道 一节所述,仅调用 rmt_enable() 时,RX 信道无法接收 RMT 符号。为此,应在 rmt_receive_config_t 中指明传入信号的基本特征:
rmt_receive_config_t::signal_range_min_ns指定高电平或低电平有效脉冲的最小持续时间。如果脉冲宽度小于指定值,硬件会将其视作干扰信号并忽略。rmt_receive_config_t::signal_range_max_ns指定高电平或低电平有效脉冲的最大持续时间。如果脉冲宽度大于指定值,接收器会将其视作 停止信号,并立即生成接收完成事件。
根据以上配置调用 rmt_receive() 后,RMT 接收器会启动 RX 机制。注意,以上配置均针对特定事务存在,也就是说,要开启新一轮的接收时,需要再次设置 rmt_receive_config_t 选项。接收器会将传入信号以 rmt_symbol_word_t 的格式保存在内部内存块或 DMA 缓冲区中。
由于内存块大小有限,RMT 接收器会交替提醒驱动程序将累积的符号复制到外部处理。
应在 rmt_receive() 函数的 buffer 参数中提供复制目标。如果由于缓冲区大小不足而导致缓冲区溢出,接收器仍可继续工作,但会丢弃溢出的符号,并报告此错误信息:user buffer too small, received symbols truncated。请注意 buffer 参数的生命周期,确保在接收器完成或停止工作前不会回收缓冲区。
当接收器完成工作,即接收到持续时间大于 rmt_receive_config_t::signal_range_max_ns 的信号时,驱动程序将停止接收器。如有需要,应再次调用 rmt_receive() 重新启动接收器。在 rmt_rx_event_callbacks_t::on_recv_done 的回调中可以获取接收到的数据。要获取更多有关详情,请参阅 注册事件回调。
static bool example_rmt_rx_done_callback(rmt_channel_handle_t channel, const rmt_rx_done_event_data_t *edata, void *user_data)
{
BaseType_t high_task_wakeup = pdFALSE;
QueueHandle_t receive_queue = (QueueHandle_t)user_data;
// 将接收到的 RMT 符号发送到解析任务的消息队列中
xQueueSendFromISR(receive_queue, edata, &high_task_wakeup);
// 返回是否唤醒了任何任务
return high_task_wakeup == pdTRUE;
}
QueueHandle_t receive_queue = xQueueCreate(1, sizeof(rmt_rx_done_event_data_t));
rmt_rx_event_callbacks_t cbs = {
.on_recv_done = example_rmt_rx_done_callback,
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_rx_register_event_callbacks(rx_channel, &cbs, receive_queue));
// 以下时间要求均基于 NEC 协议
rmt_receive_config_t receive_config = {
.signal_range_min_ns = 1250, // NEC 信号的最短持续时间为 560 µs,由于 1250 ns < 560 µs,有效信号不会视为噪声
.signal_range_max_ns = 12000000, // NEC 信号的最长持续时间为 9000 µs,由于 12000000 ns > 9000 µs,接收不会提前停止
};
rmt_symbol_word_t raw_symbols[64]; // 64 个符号应足够存储一个标准 NEC 帧的数据
// 准备开始接收
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_receive(rx_channel, raw_symbols, sizeof(raw_symbols), &receive_config));
// 等待 RX 完成信号
rmt_rx_done_event_data_t rx_data;
xQueueReceive(receive_queue, &rx_data, portMAX_DELAY);
// 解析接收到的符号数据
example_parse_nec_frame(rx_data.received_symbols, rx_data.num_symbols);
RMT 编码器
RMT 编码器是 RMT TX 事务的一部分,用于在特定时间生成正确的 RMT 符号,并将其写入硬件内存或 DMA 缓冲区。对于编码函数,存在以下特殊限制条件:
由于目标 RMT 内存块无法一次性容纳所有数据,在单个事务中,须多次调用编码函数。为突破这一限制,可以采用 交替 方式,将编码会话分成多个部分。为此,编码器需要 记录其状态,以便从上一部分编码结束之处继续编码。
编码函数在 ISR 上下文中运行。为加快编码会话,建议将编码函数放入 IRAM,这也有助于避免在编码过程中出现 cache 失效的情况。
为帮助用户更快速地上手 RMT 驱动程序,该程序默认提供了一些常用编码器,可以单独使用,也可以链式组合成新的编码器,有关原理请参阅 组合模式。驱动程序在 rmt_encoder_t 中定义了编码器接口,包含以下函数:
rmt_encoder_t::encode是编码器的基本函数,编码会话即在此处进行。在单个事务中,可能会多次调用
rmt_encoder_t::encode函数,该函数会返回当前编码会话的状态。可能出现的编码状态已在
rmt_encode_state_t列出。如果返回结果中包含RMT_ENCODING_COMPLETE,表示当前编码器已完成编码。如果返回结果中包含
RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL,表示保存编码数据的空间不足,需要从当前会话中退出。
rmt_encoder_t::reset会将编码器重置为初始状态(编码器有其特定状态)。如果在未重置 RMT 发射器对应编码器的情况下,手动停止 RMT 发射器,随后的编码会话将报错。
该函数也会在
rmt_disable()中隐式调用。
rmt_encoder_t::del可以释放编码器分配的资源。
拷贝编码器
调用 rmt_new_copy_encoder() 可以创建拷贝编码器,将 RMT 符号从用户空间复制到驱动程序层。拷贝编码器通常用于编码 const 数据,即初始化后在运行时不会发生更改的数据,如红外协议中的前导码。
调用 rmt_new_copy_encoder() 前,应预先提供配置结构体 rmt_copy_encoder_config_t。目前,该配置保留用作未来的扩展功能,暂无具体用途或设置项。
字节编码器
调用 rmt_new_bytes_encoder() 可以创建字节编码器,将用户空间的字节流动态转化成 RMT 符号。字节编码区通常用于编码动态数据,如红外协议中的地址和命令字段。
调用 rmt_new_bytes_encoder() 前,应预先提供配置结构体 rmt_bytes_encoder_config_t,具体配置如下:
rmt_bytes_encoder_config_t::bit0和rmt_bytes_encoder_config_t::bit1为必要项,用于告知编码器如何以rmt_symbol_word_t格式表示零位和一位。rmt_bytes_encoder_config_t::msb_first设置各字节的位编码。如果设置为真,编码器将首先编码 最高有效位,否则将首先编码 最低有效位。
除驱动程序提供的原始编码器外,也可以将现有编码器链式组合成自定义编码器。常见编码器链如下图所示:
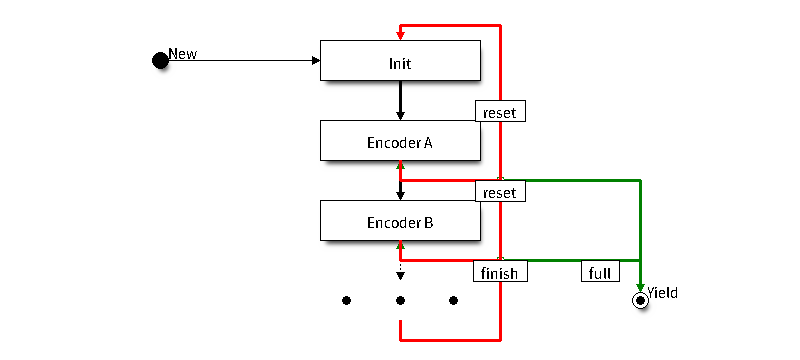
RMT 编码器链
自定义 NEC 协议的 RMT 编码器
本节将演示编写 NEC 编码器的流程。NEC 红外协议使用脉冲距离编码来发送消息位,每个脉冲突发的持续时间为 562.5 µs,逻辑位发送详见下文。注意,各字节的最低有效位会优先发送。
逻辑
0:562.5 µs的脉冲突发后有562.5 µs的空闲时间,总发送时间为1.125 ms逻辑
1:562.5 µs的脉冲突发后有1.6875 ms的空闲时间,总发送时间为2.25 ms
在遥控器上按下某个按键时,将按以下顺序发送有关信号:
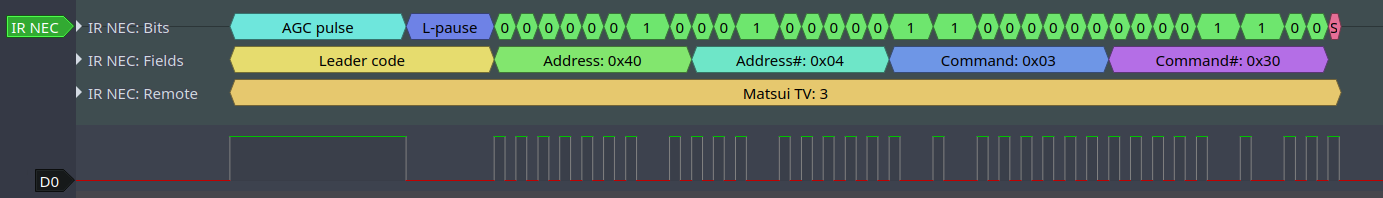
红外 NEC 帧
9 ms的引导脉冲发射,也称为 AGC 脉冲4.5 ms的空闲时间接收设备的 8 位地址
地址的 8 位逻辑反码
8 位命令
命令的 8 位逻辑反码
最后的
562.5 µs脉冲突发,表示消息发送结束
随后可以按相同顺序构建 NEC rmt_encoder_t::encode 函数,例如
// 红外 NEC 扫码表示法
typedef struct {
uint16_t address;
uint16_t command;
} ir_nec_scan_code_t;
// 通过组合原始编码器构建编码器
typedef struct {
rmt_encoder_t base; // 基础类 "class" 声明了标准编码器接口
rmt_encoder_t *copy_encoder; // 使用拷贝编码器来编码前导码和结束码
rmt_encoder_t *bytes_encoder; // 使用字节编码器来编码地址和命令数据
rmt_symbol_word_t nec_leading_symbol; // 使用 RMT 表示的 NEC 前导码
rmt_symbol_word_t nec_ending_symbol; // 使用 RMT 表示的 NEC 结束码
int state; // 记录当前编码状态,即所处编码阶段
} rmt_ir_nec_encoder_t;
static size_t rmt_encode_ir_nec(rmt_encoder_t *encoder, rmt_channel_handle_t channel, const void *primary_data, size_t data_size, rmt_encode_state_t *ret_state)
{
rmt_ir_nec_encoder_t *nec_encoder = __containerof(encoder, rmt_ir_nec_encoder_t, base);
rmt_encode_state_t session_state = RMT_ENCODING_RESET;
rmt_encode_state_t state = RMT_ENCODING_RESET;
size_t encoded_symbols = 0;
ir_nec_scan_code_t *scan_code = (ir_nec_scan_code_t *)primary_data;
rmt_encoder_handle_t copy_encoder = nec_encoder->copy_encoder;
rmt_encoder_handle_t bytes_encoder = nec_encoder->bytes_encoder;
switch (nec_encoder->state) {
case 0: // 发送前导码
encoded_symbols += copy_encoder->encode(copy_encoder, channel, &nec_encoder->nec_leading_symbol,
sizeof(rmt_symbol_word_t), &session_state);
if (session_state & RMT_ENCODING_COMPLETE) {
nec_encoder->state = 1; // 只有在当前编码器完成工作时才能切换到下一个状态
}
if (session_state & RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL) {
state |= RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL;
goto out; // 如果没有足够的空间来存放其他编码相关的数据,程序会暂停当前操作,并跳转到指定位置继续执行。
}
// 继续执行
case 1: // 发送地址
encoded_symbols += bytes_encoder->encode(bytes_encoder, channel, &scan_code->address, sizeof(uint16_t), &session_state);
if (session_state & RMT_ENCODING_COMPLETE) {
nec_encoder->state = 2; // 只有在当前编码器完成工作时才能切换到下一个状态
}
if (session_state & RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL) {
state |= RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL;
goto out; // 如果没有足够的空间来存放其他编码相关的数据,程序会暂停当前操作,并跳转到指定位置继续执行。
}
// 继续执行
case 2: // 发送命令
encoded_symbols += bytes_encoder->encode(bytes_encoder, channel, &scan_code->command, sizeof(uint16_t), &session_state);
if (session_state & RMT_ENCODING_COMPLETE) {
nec_encoder->state = 3; // 只有在当前编码器完成工作时才能切换到下一个状态
}
if (session_state & RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL) {
state |= RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL;
goto out; // 如果没有足够的空间来存放其他编码相关的数据,程序会暂停当前操作,并跳转到指定位置继续执行。
}
// 继续执行
case 3: // 发送结束码
encoded_symbols += copy_encoder->encode(copy_encoder, channel, &nec_encoder->nec_ending_symbol,
sizeof(rmt_symbol_word_t), &session_state);
if (session_state & RMT_ENCODING_COMPLETE) {
nec_encoder->state = RMT_ENCODING_RESET; // 返回初始编码会话
state |= RMT_ENCODING_COMPLETE; // 告知调用者 NEC 编码已完成
}
if (session_state & RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL) {
state |= RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL;
goto out; // 如果没有足够的空间来存放其他编码相关的数据,程序会暂停当前操作,并跳转到指定位置继续执行。
}
}
out:
*ret_state = state;
return encoded_symbols;
}
完整示例代码存放在 peripherals/rmt/ir_nec_transceiver 目录下。以上代码片段使用了 switch-case 和一些 goto 语句实现了一个 有限状态机,借助此模式可构建更复杂的红外协议。
电源管理
通过 CONFIG_PM_ENABLE 选项启用电源管理时,系统会在进入 Light-sleep 模式前调整 APB 频率。该操作可能改变 RMT 内部计数器的分辨率。
然而,驱动程序可以通过获取 ESP_PM_APB_FREQ_MAX 类型的电源管理锁,防止系统改变 APB 频率。每当驱动创建以 RMT_CLK_SRC_APB 作为时钟源的 RMT 通道时,都会在通过 rmt_enable() 启用通道后获取电源管理锁。反之,调用 rmt_disable() 时,驱动程序释放锁。这也意味着 rmt_enable() 和 rmt_disable() 应成对出现。
如果将通道时钟源设置为其他选项,如 RMT_CLK_SRC_XTAL,则驱动程序不会为其安装电源管理锁。对于低功耗应用程序来说,只要时钟源仍然可以提供足够的分辨率,不安装电源管理锁更为合适。
IRAM 安全
默认情况下,禁用 cache 时,写入/擦除主 flash 等原因将导致 RMT 中断延迟,事件回调函数也将延迟执行。在实时应用程序中,应避免此类情况。此外,当 RMT 事务依赖 交替 中断连续编码或复制 RMT 符号时,上述中断延迟将导致不可预测的结果。
因此,可以启用 Kconfig 选项 CONFIG_RMT_ISR_IRAM_SAFE,该选项:
支持在禁用 cache 时启用所需中断
支持将 ISR 使用的所有函数存放在 IRAM 中 2
支持将驱动程序实例存放在 DRAM 中,以防其意外映射到 PSRAM 中
启用该选项可以保证 cache 禁用时的中断运行,但会相应增加 IRAM 占用。
另外一个 Kconfig 选项 CONFIG_RMT_RECV_FUNC_IN_IRAM 可以将 rmt_receive() 函数放进内部的 IRAM 中,从而当 flash cache 被关闭的时候,这个函数也能够被使用。
线程安全
RMT 驱动程序会确保工厂函数 rmt_new_tx_channel()、rmt_new_rx_channel() 和 rmt_new_sync_manager() 的线程安全。使用时,可以直接从不同的 RTOS 任务中调用此类函数,无需额外锁保护。
其他以 rmt_channel_handle_t 和 rmt_sync_manager_handle_t 作为第一个位置参数的函数均非线程安全,在没有设置互斥锁保护的任务中,应避免从多个任务中调用这类函数。
以下函数允许在 ISR 上下文中使用:
Kconfig 选项
CONFIG_RMT_ISR_IRAM_SAFE 控制默认 ISR 处理程序能否在禁用 cache 的情况下工作。详情请参阅 IRAM 安全。
CONFIG_RMT_ENABLE_DEBUG_LOG 用于启用调试日志输出,启用此选项将增加固件的二进制文件大小。
CONFIG_RMT_RECV_FUNC_IN_IRAM 用于控制 RMT 接收函数被链接到系统内存的哪个位置(IRAM 还是 Flash)。详情请参阅 IRAM 安全。
应用示例
基于 RMT 的 RGB LED 灯带自定义编码器:peripherals/rmt/led_strip
RMT 红外 NEC 协议的编码与解码:peripherals/rmt/ir_nec_transceiver
队列中的 RMT 事务:peripherals/rmt/musical_buzzer
基于 RMT 的步进电机与 S 曲线算法:: peripherals/rmt/stepper_motor
用于驱动 DShot ESC 的 RMT 无限循环:peripherals/rmt/dshot_esc
模拟 1-wire 协议的 RMT 实现(以 DS18B20 为例):peripherals/rmt/onewire
FAQ
RMT 编码器为什么会产生比预期更多的数据?
RMT 编码在 ISR 上下文中发生。如果 RMT 编码会话耗时较长(例如,记录调试信息),或者由于中断延迟导致编码会话延迟执行,则传输速率可能会超过编码速率。此时,编码器无法及时准备下一组数据,致使传输器再次发送先前的数据。由于传输器无法停止并等待,可以通过以下方法来缓解此问题:
增加
rmt_tx_channel_config_t::mem_block_symbols的值,步长为 48。将编码函数放置在 IRAM 中。
如果所用芯片支持
rmt_tx_channel_config_t::with_dma,请启用该选项。
API 参考
Header File
Functions
-
esp_err_t rmt_new_tx_channel(const rmt_tx_channel_config_t *config, rmt_channel_handle_t *ret_chan)
Create a RMT TX channel.
- 参数
config -- [in] TX channel configurations
ret_chan -- [out] Returned generic RMT channel handle
- 返回
ESP_OK: Create RMT TX channel successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Create RMT TX channel failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM: Create RMT TX channel failed because out of memory
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: Create RMT TX channel failed because all RMT channels are used up and no more free one
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: Create RMT TX channel failed because some feature is not supported by hardware, e.g. DMA feature is not supported by hardware
ESP_FAIL: Create RMT TX channel failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_transmit(rmt_channel_handle_t tx_channel, rmt_encoder_handle_t encoder, const void *payload, size_t payload_bytes, const rmt_transmit_config_t *config)
Transmit data by RMT TX channel.
备注
This function constructs a transaction descriptor then pushes to a queue. The transaction will not start immediately if there's another one under processing. Based on the setting of
rmt_transmit_config_t::queue_nonblocking, if there're too many transactions pending in the queue, this function can block until it has free slot, otherwise just return quickly.备注
The data to be transmitted will be encoded into RMT symbols by the specific
encoder.- 参数
tx_channel -- [in] RMT TX channel that created by
rmt_new_tx_channel()encoder -- [in] RMT encoder that created by various factory APIs like
rmt_new_bytes_encoder()payload -- [in] The raw data to be encoded into RMT symbols
payload_bytes -- [in] Size of the
payloadin bytesconfig -- [in] Transmission specific configuration
- 返回
ESP_OK: Transmit data successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Transmit data failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Transmit data failed because channel is not enabled
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: Transmit data failed because some feature is not supported by hardware, e.g. unsupported loop count
ESP_FAIL: Transmit data failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_tx_wait_all_done(rmt_channel_handle_t tx_channel, int timeout_ms)
Wait for all pending TX transactions done.
备注
This function will block forever if the pending transaction can't be finished within a limited time (e.g. an infinite loop transaction). See also
rmt_disable()for how to terminate a working channel.- 参数
tx_channel -- [in] RMT TX channel that created by
rmt_new_tx_channel()timeout_ms -- [in] Wait timeout, in ms. Specially, -1 means to wait forever.
- 返回
ESP_OK: Flush transactions successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Flush transactions failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_TIMEOUT: Flush transactions failed because of timeout
ESP_FAIL: Flush transactions failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_tx_register_event_callbacks(rmt_channel_handle_t tx_channel, const rmt_tx_event_callbacks_t *cbs, void *user_data)
Set event callbacks for RMT TX channel.
备注
User can deregister a previously registered callback by calling this function and setting the callback member in the
cbsstructure to NULL.备注
When CONFIG_RMT_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. The variables used in the function should be in the SRAM as well. The
user_datashould also reside in SRAM.- 参数
tx_channel -- [in] RMT generic channel that created by
rmt_new_tx_channel()cbs -- [in] Group of callback functions
user_data -- [in] User data, which will be passed to callback functions directly
- 返回
ESP_OK: Set event callbacks successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Set event callbacks failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: Set event callbacks failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_new_sync_manager(const rmt_sync_manager_config_t *config, rmt_sync_manager_handle_t *ret_synchro)
Create a synchronization manager for multiple TX channels, so that the managed channel can start transmitting at the same time.
备注
All the channels to be managed should be enabled by
rmt_enable()before put them into sync manager.- 参数
config -- [in] Synchronization manager configuration
ret_synchro -- [out] Returned synchronization manager handle
- 返回
ESP_OK: Create sync manager successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Create sync manager failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: Create sync manager failed because it is not supported by hardware
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Create sync manager failed because not all channels are enabled
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM: Create sync manager failed because out of memory
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: Create sync manager failed because all sync controllers are used up and no more free one
ESP_FAIL: Create sync manager failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_del_sync_manager(rmt_sync_manager_handle_t synchro)
Delete synchronization manager.
- 参数
synchro -- [in] Synchronization manager handle returned from
rmt_new_sync_manager()- 返回
ESP_OK: Delete the synchronization manager successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Delete the synchronization manager failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: Delete the synchronization manager failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_sync_reset(rmt_sync_manager_handle_t synchro)
Reset synchronization manager.
- 参数
synchro -- [in] Synchronization manager handle returned from
rmt_new_sync_manager()- 返回
ESP_OK: Reset the synchronization manager successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Reset the synchronization manager failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: Reset the synchronization manager failed because of other error
Structures
-
struct rmt_tx_event_callbacks_t
Group of RMT TX callbacks.
备注
The callbacks are all running under ISR environment
备注
When CONFIG_RMT_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. The variables used in the function should be in the SRAM as well.
Public Members
-
rmt_tx_done_callback_t on_trans_done
Event callback, invoked when transmission is finished
-
rmt_tx_done_callback_t on_trans_done
-
struct rmt_tx_channel_config_t
RMT TX channel specific configuration.
Public Members
-
gpio_num_t gpio_num
GPIO number used by RMT TX channel. Set to -1 if unused
-
rmt_clock_source_t clk_src
Clock source of RMT TX channel, channels in the same group must use the same clock source
-
uint32_t resolution_hz
Channel clock resolution, in Hz
-
size_t mem_block_symbols
Size of memory block, in number of
rmt_symbol_word_t, must be an even. In the DMA mode, this field controls the DMA buffer size, it can be set to a large value; In the normal mode, this field controls the number of RMT memory block that will be used by the channel.
-
size_t trans_queue_depth
Depth of internal transfer queue, increase this value can support more transfers pending in the background
-
int intr_priority
RMT interrupt priority, if set to 0, the driver will try to allocate an interrupt with a relative low priority (1,2,3)
-
uint32_t invert_out
Whether to invert the RMT channel signal before output to GPIO pad
-
uint32_t with_dma
If set, the driver will allocate an RMT channel with DMA capability
-
uint32_t io_loop_back
The signal output from the GPIO will be fed to the input path as well
-
uint32_t io_od_mode
Configure the GPIO as open-drain mode
-
uint32_t init_level
Set the initial level of the RMT channel signal
-
struct rmt_tx_channel_config_t::[anonymous] flags
TX channel config flags
-
gpio_num_t gpio_num
-
struct rmt_transmit_config_t
RMT transmit specific configuration.
Public Members
-
int loop_count
Specify the times of transmission in a loop, -1 means transmitting in an infinite loop
-
uint32_t eot_level
Set the output level for the "End Of Transmission"
-
uint32_t queue_nonblocking
If set, when the transaction queue is full, driver will not block the thread but return directly
-
struct rmt_transmit_config_t::[anonymous] flags
Transmit specific config flags
-
int loop_count
-
struct rmt_sync_manager_config_t
Synchronous manager configuration.
Public Members
-
const rmt_channel_handle_t *tx_channel_array
Array of TX channels that are about to be managed by a synchronous controller
-
size_t array_size
Size of the
tx_channel_array
-
const rmt_channel_handle_t *tx_channel_array
Header File
Functions
-
esp_err_t rmt_new_rx_channel(const rmt_rx_channel_config_t *config, rmt_channel_handle_t *ret_chan)
Create a RMT RX channel.
- 参数
config -- [in] RX channel configurations
ret_chan -- [out] Returned generic RMT channel handle
- 返回
ESP_OK: Create RMT RX channel successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Create RMT RX channel failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM: Create RMT RX channel failed because out of memory
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: Create RMT RX channel failed because all RMT channels are used up and no more free one
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: Create RMT RX channel failed because some feature is not supported by hardware, e.g. DMA feature is not supported by hardware
ESP_FAIL: Create RMT RX channel failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_receive(rmt_channel_handle_t rx_channel, void *buffer, size_t buffer_size, const rmt_receive_config_t *config)
Initiate a receive job for RMT RX channel.
备注
This function is non-blocking, it initiates a new receive job and then returns. User should check the received data from the
on_recv_donecallback that registered byrmt_rx_register_event_callbacks().备注
This function can also be called in ISR context.
备注
If you want this function to work even when the flash cache is disabled, please enable the
CONFIG_RMT_RECV_FUNC_IN_IRAMoption.- 参数
rx_channel -- [in] RMT RX channel that created by
rmt_new_rx_channel()buffer -- [in] The buffer to store the received RMT symbols
buffer_size -- [in] size of the
buffer, in bytesconfig -- [in] Receive specific configurations
- 返回
ESP_OK: Initiate receive job successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Initiate receive job failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Initiate receive job failed because channel is not enabled
ESP_FAIL: Initiate receive job failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_rx_register_event_callbacks(rmt_channel_handle_t rx_channel, const rmt_rx_event_callbacks_t *cbs, void *user_data)
Set callbacks for RMT RX channel.
备注
User can deregister a previously registered callback by calling this function and setting the callback member in the
cbsstructure to NULL.备注
When CONFIG_RMT_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. The variables used in the function should be in the SRAM as well. The
user_datashould also reside in SRAM.- 参数
rx_channel -- [in] RMT generic channel that created by
rmt_new_rx_channel()cbs -- [in] Group of callback functions
user_data -- [in] User data, which will be passed to callback functions directly
- 返回
ESP_OK: Set event callbacks successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Set event callbacks failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: Set event callbacks failed because of other error
Structures
-
struct rmt_rx_event_callbacks_t
Group of RMT RX callbacks.
备注
The callbacks are all running under ISR environment
备注
When CONFIG_RMT_ISR_IRAM_SAFE is enabled, the callback itself and functions called by it should be placed in IRAM. The variables used in the function should be in the SRAM as well.
Public Members
-
rmt_rx_done_callback_t on_recv_done
Event callback, invoked when one RMT channel receiving transaction completes
-
rmt_rx_done_callback_t on_recv_done
-
struct rmt_rx_channel_config_t
RMT RX channel specific configuration.
Public Members
-
gpio_num_t gpio_num
GPIO number used by RMT RX channel. Set to -1 if unused
-
rmt_clock_source_t clk_src
Clock source of RMT RX channel, channels in the same group must use the same clock source
-
uint32_t resolution_hz
Channel clock resolution, in Hz
-
size_t mem_block_symbols
Size of memory block, in number of
rmt_symbol_word_t, must be an even. In the DMA mode, this field controls the DMA buffer size, it can be set to a large value (e.g. 1024); In the normal mode, this field controls the number of RMT memory block that will be used by the channel.
-
uint32_t invert_in
Whether to invert the incoming RMT channel signal
-
uint32_t with_dma
If set, the driver will allocate an RMT channel with DMA capability
-
uint32_t io_loop_back
For debug/test, the signal output from the GPIO will be fed to the input path as well
-
struct rmt_rx_channel_config_t::[anonymous] flags
RX channel config flags
-
int intr_priority
RMT interrupt priority, if set to 0, the driver will try to allocate an interrupt with a relative low priority (1,2,3)
-
gpio_num_t gpio_num
-
struct rmt_receive_config_t
RMT receive specific configuration.
Header File
Functions
-
esp_err_t rmt_del_channel(rmt_channel_handle_t channel)
Delete an RMT channel.
- 参数
channel -- [in] RMT generic channel that created by
rmt_new_tx_channel()orrmt_new_rx_channel()- 返回
ESP_OK: Delete RMT channel successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Delete RMT channel failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Delete RMT channel failed because it is still in working
ESP_FAIL: Delete RMT channel failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_apply_carrier(rmt_channel_handle_t channel, const rmt_carrier_config_t *config)
Apply modulation feature for TX channel or demodulation feature for RX channel.
- 参数
channel -- [in] RMT generic channel that created by
rmt_new_tx_channel()orrmt_new_rx_channel()config -- [in] Carrier configuration. Specially, a NULL config means to disable the carrier modulation or demodulation feature
- 返回
ESP_OK: Apply carrier configuration successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Apply carrier configuration failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: Apply carrier configuration failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_enable(rmt_channel_handle_t channel)
Enable the RMT channel.
备注
This function will acquire a PM lock that might be installed during channel allocation
- 参数
channel -- [in] RMT generic channel that created by
rmt_new_tx_channel()orrmt_new_rx_channel()- 返回
ESP_OK: Enable RMT channel successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Enable RMT channel failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Enable RMT channel failed because it's enabled already
ESP_FAIL: Enable RMT channel failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_disable(rmt_channel_handle_t channel)
Disable the RMT channel.
备注
This function will release a PM lock that might be installed during channel allocation
- 参数
channel -- [in] RMT generic channel that created by
rmt_new_tx_channel()orrmt_new_rx_channel()- 返回
ESP_OK: Disable RMT channel successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Disable RMT channel failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Disable RMT channel failed because it's not enabled yet
ESP_FAIL: Disable RMT channel failed because of other error
Structures
-
struct rmt_carrier_config_t
RMT carrier wave configuration (for either modulation or demodulation)
Public Members
-
uint32_t frequency_hz
Carrier wave frequency, in Hz, 0 means disabling the carrier
-
float duty_cycle
Carrier wave duty cycle (0~100%)
-
uint32_t polarity_active_low
Specify the polarity of carrier, by default it's modulated to base signal's high level
-
uint32_t always_on
If set, the carrier can always exist even there's not transfer undergoing
-
struct rmt_carrier_config_t::[anonymous] flags
Carrier config flags
-
uint32_t frequency_hz
Header File
Functions
-
esp_err_t rmt_new_bytes_encoder(const rmt_bytes_encoder_config_t *config, rmt_encoder_handle_t *ret_encoder)
Create RMT bytes encoder, which can encode byte stream into RMT symbols.
- 参数
config -- [in] Bytes encoder configuration
ret_encoder -- [out] Returned encoder handle
- 返回
ESP_OK: Create RMT bytes encoder successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Create RMT bytes encoder failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM: Create RMT bytes encoder failed because out of memory
ESP_FAIL: Create RMT bytes encoder failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_bytes_encoder_update_config(rmt_encoder_handle_t bytes_encoder, const rmt_bytes_encoder_config_t *config)
Update the configuration of the bytes encoder.
备注
The configurations of the bytes encoder is also set up by
rmt_new_bytes_encoder(). This function is used to update the configuration of the bytes encoder at runtime.- 参数
bytes_encoder -- [in] Bytes encoder handle, created by e.g
rmt_new_bytes_encoder()config -- [in] Bytes encoder configuration
- 返回
ESP_OK: Update RMT bytes encoder successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Update RMT bytes encoder failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: Update RMT bytes encoder failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_new_copy_encoder(const rmt_copy_encoder_config_t *config, rmt_encoder_handle_t *ret_encoder)
Create RMT copy encoder, which copies the given RMT symbols into RMT memory.
- 参数
config -- [in] Copy encoder configuration
ret_encoder -- [out] Returned encoder handle
- 返回
ESP_OK: Create RMT copy encoder successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Create RMT copy encoder failed because of invalid argument
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM: Create RMT copy encoder failed because out of memory
ESP_FAIL: Create RMT copy encoder failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_del_encoder(rmt_encoder_handle_t encoder)
Delete RMT encoder.
- 参数
encoder -- [in] RMT encoder handle, created by e.g
rmt_new_bytes_encoder()- 返回
ESP_OK: Delete RMT encoder successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Delete RMT encoder failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: Delete RMT encoder failed because of other error
-
esp_err_t rmt_encoder_reset(rmt_encoder_handle_t encoder)
Reset RMT encoder.
- 参数
encoder -- [in] RMT encoder handle, created by e.g
rmt_new_bytes_encoder()- 返回
ESP_OK: Reset RMT encoder successfully
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Reset RMT encoder failed because of invalid argument
ESP_FAIL: Reset RMT encoder failed because of other error
-
void *rmt_alloc_encoder_mem(size_t size)
A helper function to allocate a proper memory for RMT encoder.
- 参数
size -- Size of memory to be allocated
- 返回
Pointer to the allocated memory if the allocation is successful, NULL otherwise
Structures
-
struct rmt_encoder_t
Interface of RMT encoder.
Public Members
-
size_t (*encode)(rmt_encoder_t *encoder, rmt_channel_handle_t tx_channel, const void *primary_data, size_t data_size, rmt_encode_state_t *ret_state)
Encode the user data into RMT symbols and write into RMT memory.
备注
The encoding function will also be called from an ISR context, thus the function must not call any blocking API.
备注
It's recommended to put this function implementation in the IRAM, to achieve a high performance and less interrupt latency.
- Param encoder
[in] Encoder handle
- Param tx_channel
[in] RMT TX channel handle, returned from
rmt_new_tx_channel()- Param primary_data
[in] App data to be encoded into RMT symbols
- Param data_size
[in] Size of primary_data, in bytes
- Param ret_state
[out] Returned current encoder's state
- Return
Number of RMT symbols that the primary data has been encoded into
-
esp_err_t (*reset)(rmt_encoder_t *encoder)
Reset encoding state.
- Param encoder
[in] Encoder handle
- Return
ESP_OK: reset encoder successfully
ESP_FAIL: reset encoder failed
-
esp_err_t (*del)(rmt_encoder_t *encoder)
Delete encoder object.
- Param encoder
[in] Encoder handle
- Return
ESP_OK: delete encoder successfully
ESP_FAIL: delete encoder failed
-
size_t (*encode)(rmt_encoder_t *encoder, rmt_channel_handle_t tx_channel, const void *primary_data, size_t data_size, rmt_encode_state_t *ret_state)
-
struct rmt_bytes_encoder_config_t
Bytes encoder configuration.
Public Members
-
rmt_symbol_word_t bit0
How to represent BIT0 in RMT symbol
-
rmt_symbol_word_t bit1
How to represent BIT1 in RMT symbol
-
uint32_t msb_first
Whether to encode MSB bit first
-
struct rmt_bytes_encoder_config_t::[anonymous] flags
Encoder config flag
-
rmt_symbol_word_t bit0
-
struct rmt_copy_encoder_config_t
Copy encoder configuration.
Enumerations
-
enum rmt_encode_state_t
RMT encoding state.
Values:
-
enumerator RMT_ENCODING_RESET
The encoding session is in reset state
-
enumerator RMT_ENCODING_COMPLETE
The encoding session is finished, the caller can continue with subsequent encoding
-
enumerator RMT_ENCODING_MEM_FULL
The encoding artifact memory is full, the caller should return from current encoding session
-
enumerator RMT_ENCODING_RESET
Header File
Structures
-
struct rmt_tx_done_event_data_t
Type of RMT TX done event data.
Public Members
-
size_t num_symbols
The number of transmitted RMT symbols, including one EOF symbol, which is appended by the driver to mark the end of a transmission. For a loop transmission, this value only counts for one round.
-
size_t num_symbols
-
struct rmt_rx_done_event_data_t
Type of RMT RX done event data.
Public Members
-
rmt_symbol_word_t *received_symbols
Point to the received RMT symbols
-
size_t num_symbols
The number of received RMT symbols
-
rmt_symbol_word_t *received_symbols
Type Definitions
-
typedef struct rmt_channel_t *rmt_channel_handle_t
Type of RMT channel handle.
-
typedef struct rmt_sync_manager_t *rmt_sync_manager_handle_t
Type of RMT synchronization manager handle.
-
typedef struct rmt_encoder_t *rmt_encoder_handle_t
Type of RMT encoder handle.
-
typedef bool (*rmt_tx_done_callback_t)(rmt_channel_handle_t tx_chan, const rmt_tx_done_event_data_t *edata, void *user_ctx)
Prototype of RMT event callback.
- Param tx_chan
[in] RMT channel handle, created from
rmt_new_tx_channel()- Param edata
[in] Point to RMT event data. The lifecycle of this pointer memory is inside this function, user should copy it into static memory if used outside this function.
- Param user_ctx
[in] User registered context, passed from
rmt_tx_register_event_callbacks()- Return
Whether a high priority task has been waken up by this callback function
-
typedef bool (*rmt_rx_done_callback_t)(rmt_channel_handle_t rx_chan, const rmt_rx_done_event_data_t *edata, void *user_ctx)
Prototype of RMT event callback.
- Param rx_chan
[in] RMT channel handle, created from
rmt_new_rx_channel()- Param edata
[in] Point to RMT event data. The lifecycle of this pointer memory is inside this function, user should copy it into static memory if used outside this function.
- Param user_ctx
[in] User registered context, passed from
rmt_rx_register_event_callbacks()- Return
Whether a high priority task has been waken up by this function
Header File
Unions
-
union rmt_symbol_word_t
- #include <rmt_types.h>
The layout of RMT symbol stored in memory, which is decided by the hardware design.
Type Definitions
-
typedef soc_periph_rmt_clk_src_t rmt_clock_source_t
RMT group clock source.
备注
User should select the clock source based on the power and resolution requirement
- 1
不同 ESP 芯片系列可能具有不同数量的 RMT 通道,详情请参阅 [TRM]。驱动程序不会禁止申请更多 RMT 通道,但会在可用硬件资源不足时报错。在进行 资源分配 时,请持续检查返回值。
- 2
回调函数,如
rmt_tx_event_callbacks_t::on_trans_done及回调函数所调用的函数也应位于 IRAM 中,用户需自行留意这一问题。