WakeNet Wake Word Model
WakeNet is a wake word engine built upon neural network for low-power embedded MCUs. Currently, WakeNet supports up to 5 wake words.
Overview
Please see the flow diagram of WakeNet below:
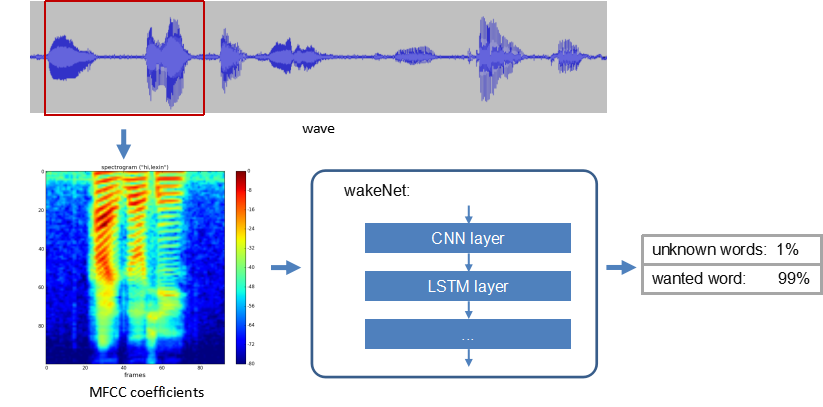
- Speech Feature
We use MFCC method to extract the speech spectrum features. The input audio file has a sample rate of 16KHz, mono, and is encoded as signed 16-bit. Each frame has a window width and step size of 30ms.
- Neural Network
Now, the neural network structure has been updated to the ninth edition, among which:
WakeNet1, WakeNet2, WakeNet3, WakeNet4, WakeNet5, WakeNet6, and WakeNet7, WakeNet8 had been out of use.
WakeNet9 and WakeNet9l support ESP32, ESP32S3, and ESP32P4 chips, which are built upon the Dilated Convolution structure. WakeNet9l further improves the recognition rate of wake words spoken at very fast speeds based on WakeNet9.
WakeNet9s supports ESP32C3, ESP32C5 and ESP32C6 chip, which is built upon the Depthwise Separable Convolution structure.
- Keyword Triggering Method:
For continuous audio stream, we calculate the average recognition results (M) for several frames and generate a smoothing prediction result, to improve the accuracy of keyword triggering. Only when the M value is larger than the set threshold, a triggering command is sent.
Use WakeNet
Select WakeNet model
To select WakeNet model, please refer to Section Flashing Models .
To customize wake words, please refer to Section Espressif Speech Wake-up Solution Customization Process
Run WakeNet
WakeNet is currently included in the AFE, which is enabled by default, and returns the detection results through the AFE fetch interface.
If users do not need WakeNet, please use:
afe_config->wakeNet_init = False.
If users want to enable/disable WakeNet temporarily, please use:
afe_handle->disable_wakenet(afe_data) afe_handle->enable_wakenet(afe_data)
Resource Occupancy
For the resource occupancy for this model, see Resource Occupancy.