MQTT Troubleshooting Tool Usage Tutorial
Note
This document is automatically translated using AI. Please excuse any detailed errors. The official English version is still in progress.
Table of Contents
This article will introduce how to troubleshoot and locate MQTT issues with local MQTT testing tools, debug logs, and wireless packet capture.
Overview
MQTT is a lightweight message transmission protocol based on the publish/subscribe model, suitable for IoT and low-bandwidth network environments. For further introduction and related examples, refer to MQTT Examples.
In actual development, developers may encounter various anomalies or failures when using MQTT, such as connection abnormalities, message loss, or subscription failure.
When an exception occurs in the program, you can first observe the WARN/ERROR logs to quickly locate the approximate link where the exception occurred:
If the following TLS error code is printed in the log, you can find the corresponding cause and possible solution by viewing the Error Troubleshooting document. You can also find the error cause corresponding to the error code through ESP TLS Return Value.
E (15139) mqtt_example: Last error reported from esp-tls: 0x8006
If the exception occurs in the connection establishment or subscription process, you can first use the Local MQTT Testing Tool to troubleshoot server environment issues.
If the MQTT server connection fails, you can get the specific error cause.
If the above methods cannot locate the problem, and the server and network environment have been confirmed to be normal, you can choose to enable more detailed logs (MQTT Debug Log) or use Wireless Packet Capture for further investigation based on the actual situation.
MQTT Debug Log
MQTT Device-side Log
When troubleshooting MQTT issues, the device-side log can view the internal state of the program and is the main source of information for analyzing the connection and transmission process.
In the default configuration, the device-side log only outputs basic process information, such as whether the connection is successful/failed, whether the message is sent or received successfully, etc., to confirm whether the core steps are executed, but it will not display more detailed internal states. Therefore, in some troubleshooting stages, it is necessary to adjust the log level according to the situation to get more details.
The log library has six levels of detail, for specific information, please refer to Log Level.
MQTT can be simply divided into the following levels:
Application layer: Generates and processes MQTT messages, executes business logic.
TLS layer: Responsible for TLS handshake, certificate verification, and data encryption and decryption, providing a secure communication channel for the upper layer.
lwIP layer: Responsible for TCP/IP encapsulation, network transmission, and connection management.
Wi-Fi layer: Responsible for wireless connection and physical data transmission and reception, it is the lowest network interface.
The application layer focuses on MQTT messages and business, the TLS layer focuses on data security, the lwIP layer focuses on network transmission, and the Wi-Fi layer focuses on wireless transmission and reception, logs provide debugging information from bottom to top.
The focus of log information at different levels is different, and the method to enable Debug Log is also different, as detailed below.
Modify the maximum log level
The global maximum log level determines the upper limit of log output, which is INFO level by default. If you need to view DEBUG or VERBOSE level debug logs, you must first raise the global maximum log level. Otherwise, even if the individual module is set to DEBUG or VERBOSE level, DEBUG or VERBOSE level logs cannot be printed.
The method to modify the maximum log level is as follows:
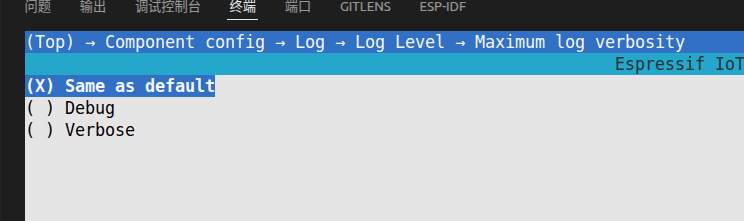
After entering
menuconfig, selectComponent config > Log > Log Level > Maximum log verbosityin order, check theDEBUGoption and save the configuration.
Steps to enable application layer Debug Log
When troubleshooting MQTT application issues, application layer logs are an important source of information for analyzing client status and message transmission and reception processes. The steps to enable the application layer Debug Log are as follows:
Modify the maximum log level to DEBUG.
Dynamically modify the log level of the module: You can dynamically modify the log level of the specified module by calling
esp_log_level_set()in the code. For the usage of this API, please refer to Log level control. The recommended modification steps are as follows:
esp_log_level_set("mqtt_client", ESP_LOG_DEBUG); // Modify the log level of the mqtt_client module to DEBUG
esp_log_level_set("mqtt_client", ESP_LOG_VERBOSE); // Modify the log level of the mqtt_client module to VERBOSE
Note
To prevent excessive log volume, it is recommended to set the key module to be debugged to DEBUG, which can output key logs and control the overall log volume.
Try to avoid setting the log level of all modules to DEBUG or VERBOSE at the same time.
The logs related to the MQTT device side mainly include the following modules (referenced from mqtt_tcp example):
mqtt_client: Handles MQTT protocol processes, including CONNECT, SUBSCRIBE, PUBLISH, ACK, etc., used to troubleshoot connection abnormalities or message transmission and reception abnormalities.mqtt_example: Business logic layer logs, observe the execution of MQTT API calls, used to troubleshoot business logic call abnormalities.transport_base: The basic module of the underlying TCP/TLS transmission encapsulation, used to troubleshoot TCP connection failures or network transmission abnormalities.transport: Transmission layer message sending/receiving and status management, used to troubleshoot message sending failures, ACK loss, or message retry abnormalities.esp-tls: TLS handshake, certificate loading and verification, used to troubleshoot TLS handshake failure, certificate verification failure, or encryption suite mismatch.outbox: The internal message queue and QoS1/QoS2 retry mechanism of the MQTT client, used for troubleshooting unsent messages, queue blockages, or retry failures.
Steps to Enable TLS Layer Debug Log
In ESP-IDF, the TLS protocol is implemented by the mbedTLS library. The steps to enable the TLS layer Debug Log are as follows:
Modify the maximum log level to DEBUG.
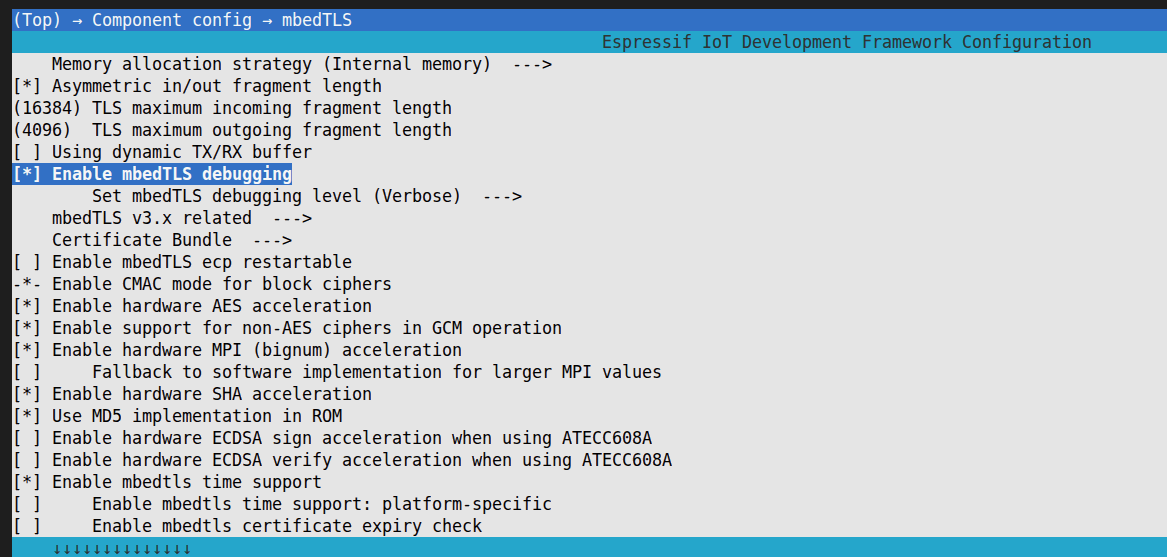
After entering
menuconfig, selectComponent config > mbedTLSin order, and press space to enableEnable mbedTLS debugging
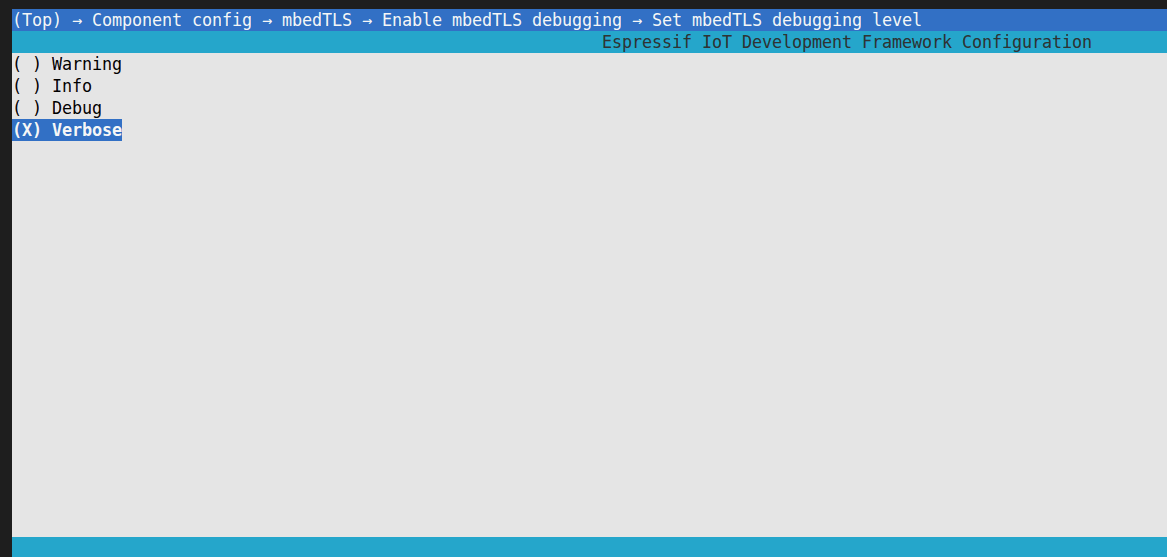
After enabling the log, you can modify the log level through
Set mbedTLS debugging level:
The default log level is VERBOSE, it is recommended to change it to DEBUG level to control the log volume.
Steps to Enable lwIP Layer Debug Log
The steps to enable the lwIP layer Debug Log are as follows:
Modify the maximum log level to DEBUG.
After entering
menuconfig, selectComponent config > LWIPin order, and press space to enableEnable LWIP Debug
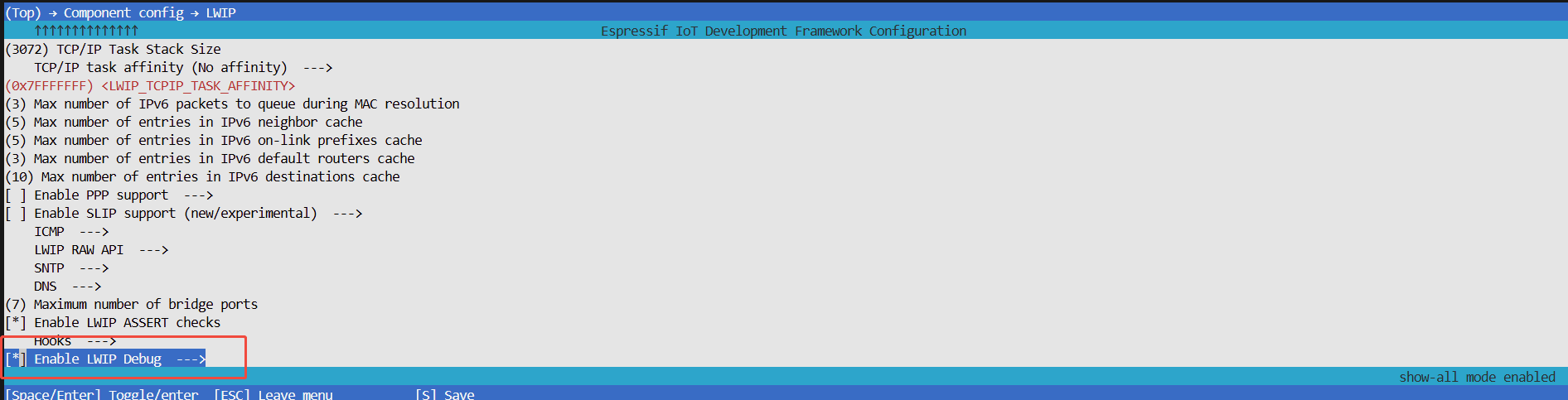
Press enter to enter the
Enable LWIP Debugpage, and enable the corresponding submodule logs as needed. The submodules include netif, pbuf, etharp, api lib, socket, IP, ICMP, DHCP, IP6, ICMP6, TCP, UDP, SNTP, DNS, bridge generic, bridge FDB, bridge forwarding.
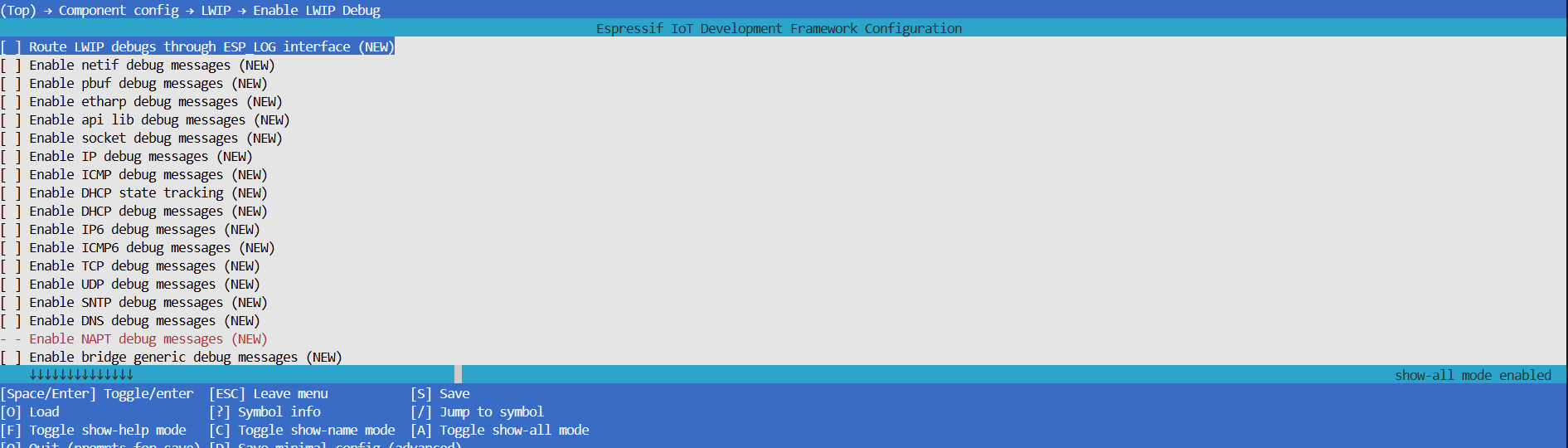
For further instructions on enabling lwIP layer debug logs, please refer to this ESP-FAQ.
Steps to Enable Wi-Fi Layer Debug Log
In ESP-IDF, Wi-Fi connection related logs are mainly distributed in the wifi and wpa modules, corresponding to link management and wireless security authentication. The steps to enable the Wi-Fi layer Debug Log are as follows:
Modify the maximum log level to DEBUG.
View wifi module debug log: The
wifimodule log is enabled by default. You can modify its log level to DEBUG by callingesp_log_level_set()in the code. For API usage, please refer to Log Level Control. The recommended modification steps are as follows:
esp_log_level_set("wifi", ESP_LOG_DEBUG);
View wpa module debug log: The
wpamodule log is disabled by default. The steps to enable it are as follows.
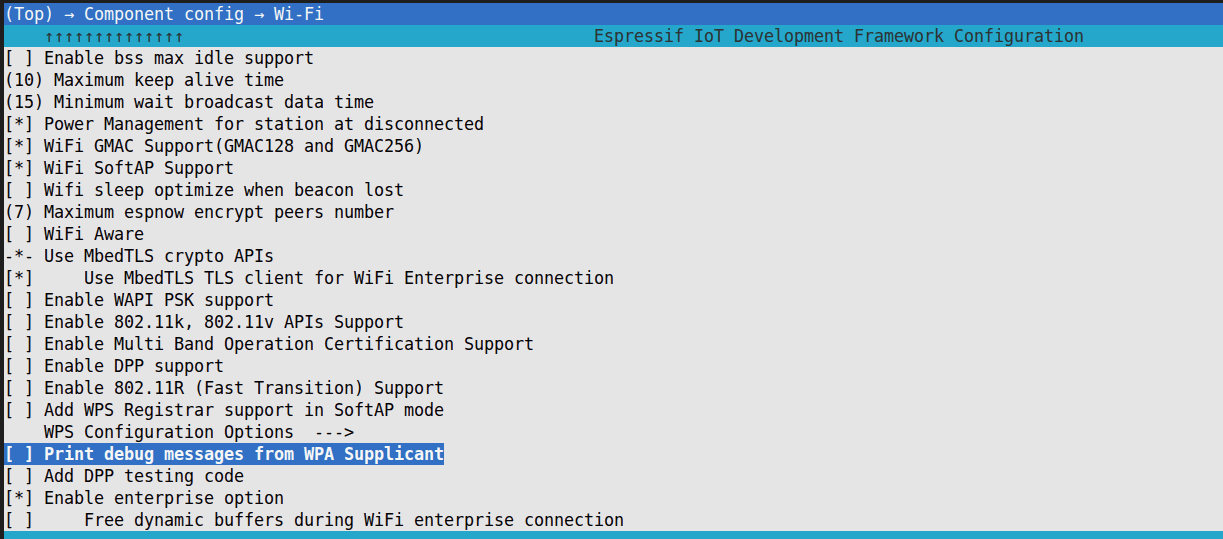
After entering
menuconfig, selectComponent config > Wi-Fiin order, and press space to enablePrint debug messages from WPA Supplicant.
Modify its log level to DEBUG by calling
esp_log_level_set()in the code. For API usage, please refer to Log Level Control. The recommended modification steps are as follows:
esp_log_level_set("wpa", ESP_LOG_DEBUG);
Local MQTT Testing Tool
Testing Tool Use Cases
The MQTT testing tool mainly serves as a client, running independently from the device side. It can be used to quickly confirm whether the MQTT server and network environment are normal, thus assisting in troubleshooting and reducing misjudgments or repeated debugging due to environmental abnormalities:
If the testing tool cannot connect to the target URI, the problem usually lies on the environment or server side.
If the testing tool connects normally, the problem usually lies on the device side code.
For problems confirmed to be on the device side, further analysis is needed in conjunction with MQTT Debug Log or Wireless Packet Capture to troubleshoot configuration and business logic issues on the device side.
In addition, some MQTT testing tools can be used as servers for quickly setting up temporary MQTT services when there is no available Broker (such as in offline environments, experimental environments, or automated testing scripts). For online or existing development environment Brokers, server mode is usually not needed.
Common Testing Tools
In MQTT development and debugging, local testing tools are mainly used to verify the connection between the client and the Broker, debug message sending and receiving, check topic and QoS configurations, and simulate client behavior. These tools can quickly help developers confirm whether message interaction is normal, and they support multi-client scenarios and batch message testing.
Common local testing tools can be divided into two categories: Graphical User Interface (GUI) tools and Command Line Interface (CLI) tools.
GUI tools provide visual operations, allowing you to intuitively view topic structures, message flow, and the status of Retain or Will messages. They are suitable for quickly verifying connections and observing message behavior.
CLI tools operate through commands or scripts, and are more suitable for batch message publishing, automated testing, or use in environments without a graphical interface.
In actual development, GUI tools are usually used for quick debugging and observing messages, while CLI tools are more suitable for script-based operations, continuous integration, or large-scale message verification.
Common local MQTT testing tools include:
MQTTX: Provides both GUI and CLI versions. The GUI intuitively displays the topic tree and message flow, and supports JSON formatting, making it easy for quick debugging and message observation; the CLI is suitable for script-based batch message publishing and automated testing, making it a comprehensive debugging tool for the development stage.
MQTT Explorer: Characterized by visual topic tree and historical message management, it is particularly suitable for handling complex topic structures and Retain messages, helping developers quickly locate problems.
Mosquitto: A lightweight, simple MQTT Broker and command line client tool. You can publish and subscribe to messages through the
mosquitto_pubandmosquitto_subcommands, suitable for automated testing, batch message verification, or use in a GUI-free environment.
Note
MQTTX and MQTT Explorer only support client mode; Mosquitto can be used as a client or server (Broker).
Test Tool Usage Instructions
Wireless Packet Capture
Wireless packet capture can directly display real network packets, mainly used for troubleshooting network layer or transport layer abnormalities, such as sending data timeout, reading data timeout, etc., to confirm whether the underlying link between the device and the Broker is stable and reliable.
Before entering the packet capture stage, the following preliminary verification needs to be completed to avoid invalid packet capture:
Use MQTT test tools to confirm that the Broker service is normal, the network link is reachable, the port / firewall configuration is effective, and the TLS authentication parameters are compatible
Use Debug Log to confirm that the connection parameters (Client ID, Topic, QoS, etc.) are correctly configured, the certificate is loaded normally, and there are no clear error codes or abnormal logs in the SDK connection process
When the test tool runs normally, and the Debug Log does not find any clear problems, but there are still unstable connections, packet loss, frequent disconnections, etc., packet capture is needed for further positioning.
The steps for wireless packet capture can be referred to Wireless Packet Capture Tutorial