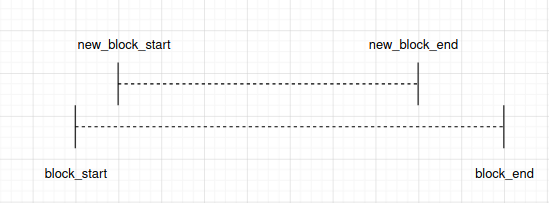基于 MMU 的存储管理
简介
ESP32-P4 的存储管理单元 (MMU) 相对简单。它可以在物理存储地址和虚拟存储地址之间进行存储地址转换,因此,CPU 可以通过虚拟存储地址来访问物理存储。虚拟存储地址有多种类型,分别具有不同的功能。
ESP-IDF 提供了一个存储器映射驱动程序,用于管理这些物理存储地址和虚拟存储地址之间的关系,实现一些功能。例如,可以通过指针从 SPI flash 中读取内容。
存储映射驱动程序实际上是一个基于属性的虚拟存储地址分配器,允许应用程序为不同的目的分配虚拟存储地址。下文将此驱动程序称为 esp_mmap 驱动程序。
ESP-IDF 还提供了一个存储器同步驱动程序来处理潜在的不同步的情况。
物理存储类型
存储映射驱动程序目前支持映射到以下物理存储类型:
SPI flash
PSRAM
虚拟存储的功能
MMU_MEM_CAP_EXEC:此功能表示虚拟存储地址具有执行权限。注意,此权限的范围仅限 MMU 硬件内部。MMU_MEM_CAP_READ:此功能表示虚拟存储地址具有读取权限。注意,此权限的范围仅限 MMU 硬件内部。MMU_MEM_CAP_WRITE:此功能表示虚拟存储地址具有写入权限。注意,此权限的范围仅限 MMU 硬件内部。MMU_MEM_CAP_32BIT:此功能表示允许访问 32 位或 32 位倍数的虚拟存储。MMU_MEM_CAP_8BIT:此功能表示允许访问 8 位或 8 位倍数的虚拟存储。
如需了解具有特定功能的最大连续可映射块大小,请调用 esp_mmu_map_get_max_consecutive_free_block_size()。
存储管理驱动程序
驱动程序
术语解释
虚拟存储池由一个或多个虚拟存储区域组成,如下图所示:
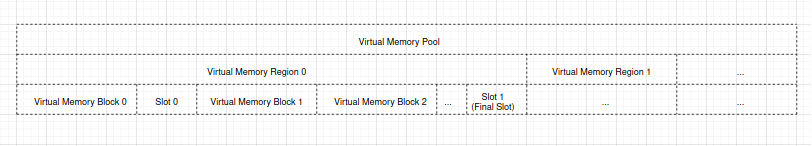
一个虚拟存储池是指可以映射到物理存储的整个虚拟地址范围。
一个虚拟存储区域是指具有相同属性的虚拟地址范围。
一个虚拟存储块是指一块动态映射的虚拟地址范围。
一个间隙是指两个虚拟存储块之间的虚拟地址范围。
一个物理存储块是指一块待映射或已映射到虚拟存储块的物理地址范围。
动态映射是指调用
esp_mmap驱动程序 APIesp_mmu_map()进行的映射,此 API 会将给定的物理存储块映射到esp_mmap驱动程序分配的虚拟存储块中。
存储块的关系
在映射物理存储块 A 时,存储块 A 与此前已映射的另一个物理存储块 B 之间可能存在以下关系之一:
驱动程序行为
存储映射
可以调用 esp_mmu_map() 进行动态映射。该 API 会根据你所选择的虚拟存储的属性分配一定大小的虚拟存储块,然后按照要求将此虚拟存储块映射到物理存储块中。esp_mmap 驱动程序支持映射到一种或多种物理存储,因此,应在映射时指定物理存储目标。
默认情况下,物理存储块和虚拟存储块是一对一映射。因此,当调用 esp_mmu_map() 时,如果存储关系不同,API 的行为也有所不同:
如果是“包含”的情形,此 API 将返回
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE。此时,由于之前已映射的虚拟存储包含待映射的虚拟存储,因此返回的out_ptr会指向之前映射的虚拟存储的起始地址。如果是“相同”的情形,此 API 的行为与“包含”的情况完全相同。
如果是“重叠”的情形,此 API 默认返回
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG。这表明,esp_mmap驱动程序在默认情况下,不允许将一个物理存储地址映射到多个虚拟存储地址。
但是,可以使用 ESP_MMU_MMAP_FLAG_PADDR_SHARED flag,代表在物理地址和虚拟地址之间的一对多映射:
如果是“重叠”的情形,此 API 将按照要求分配一个新的虚拟存储块,并将其映射到给定的物理存储块中。
取消存储映射
可以调用 esp_mmu_unmap() 来取消先前存储块的映射。如果尝试取消映射的虚拟存储块实际尚未映射到任何物理存储块,此 API 将返回 ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND。
存储地址转换
esp_mmap 驱动程序提供了两个辅助 API,用于虚拟存储地址和物理存储地址之间的转换:
esp_mmu_vaddr_to_paddr()可将虚拟存储地址转换为物理存储地址。esp_mmu_paddr_to_vaddr()可将物理存储地址转换为虚拟存储地址。
存储同步
可以通过一种或多种方法来访问支持 MMU 的物理存储。
SPI flash 可以通过 SPI1(ESP-IDF spi_flash 驱动 API)或指针进行访问。ESP-IDF spi_flash 驱动 API 中已经考虑了存储同步,因此在使用时无需额外考虑存储同步。
PSRAM 可以通过指针进行访问。当只通过指针访问 PSRAM 时,硬件可以保证数据的一致性。
线程安全
esp_mmu_map.h 中的 API 不能确保线程的安全性。
esp_cache.h 中的 API 能够确保线程的安全性。
API 参考
API 参考 - ESP MMAP 驱动
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_mmu_map.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_mmcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_mm, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_mm
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_mm
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_mmu_map(esp_paddr_t paddr_start, size_t size, mmu_target_t target, mmu_mem_caps_t caps, int flags, void **out_ptr)
Map a physical memory block to external virtual address block, with given capabilities.
备注
This API does not guarantee thread safety
- 参数
paddr_start -- [in] Start address of the physical memory block
size -- [in] Size to be mapped. Size will be rounded up by to the nearest multiple of MMU page size
target -- [in] Physical memory target you're going to map to, see
mmu_target_tcaps -- [in] Memory capabilities, see
mmu_mem_caps_tflags -- [in] Mmap flags
out_ptr -- [out] Start address of the mapped virtual memory
- 返回
ESP_OK
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Invalid argument, see printed logs
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: Only on ESP32, PSRAM is not a supported physical memory target
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: No enough size free block to use
ESP_ERR_NO_MEM: Out of memory, this API will allocate some heap memory for internal usage
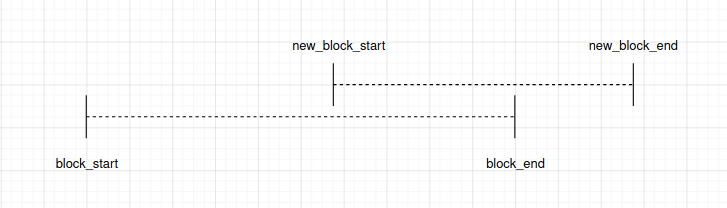
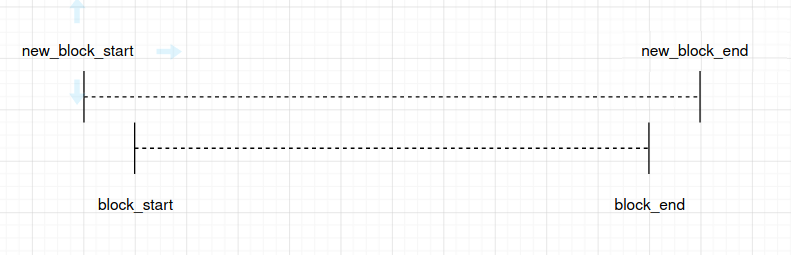
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE: Paddr is mapped already, this API will return corresponding vaddr_start of the previously mapped block. Only to-be-mapped paddr block is totally enclosed by a previously mapped block will lead to this error. (Identical scenario will behave similarly) new_block_start new_block_end |-----— New Block -----—| |------------— Block ------------—| block_start block_end
-
esp_err_t esp_mmu_unmap(void *ptr)
Unmap a previously mapped virtual memory block.
备注
This API does not guarantee thread safety
- 参数
ptr -- [in] Start address of the virtual memory
- 返回
ESP_OK
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Null pointer
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: Vaddr is not in external memory, or it's not mapped yet
-
esp_err_t esp_mmu_map_get_max_consecutive_free_block_size(mmu_mem_caps_t caps, mmu_target_t target, size_t *out_len)
Get largest consecutive free external virtual memory block size, with given capabilities and given physical target.
- 参数
caps -- [in] Bitwise OR of MMU_MEM_CAP_* flags indicating the memory block
target -- [in] Physical memory target you're going to map to, see
mmu_target_t.out_len -- [out] Largest free block length, in bytes.
- 返回
ESP_OK
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Invalid arguments, could be null pointer
-
esp_err_t esp_mmu_map_dump_mapped_blocks(FILE *stream)
Dump all the previously mapped blocks
备注
This API shall not be called from an ISR.
备注
This API does not guarantee thread safety
- 参数
stream -- stream to print information to; use stdout or stderr to print to the console; use fmemopen/open_memstream to print to a string buffer.
- 返回
ESP_OK
-
esp_err_t esp_mmu_vaddr_to_paddr(void *vaddr, esp_paddr_t *out_paddr, mmu_target_t *out_target)
Convert virtual address to physical address.
- 参数
vaddr -- [in] Virtual address
out_paddr -- [out] Physical address
out_target -- [out] Physical memory target, see
mmu_target_t
- 返回
ESP_OK
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Null pointer, or vaddr is not within external memory
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: Vaddr is not mapped yet
-
esp_err_t esp_mmu_paddr_to_vaddr(esp_paddr_t paddr, mmu_target_t target, mmu_vaddr_t type, void **out_vaddr)
Convert physical address to virtual address.
- 参数
paddr -- [in] Physical address
target -- [in] Physical memory target, see
mmu_target_ttype -- [in] Virtual address type, could be either instruction or data
out_vaddr -- [out] Virtual address
- 返回
ESP_OK
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Null pointer
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: Paddr is not mapped yet
-
esp_err_t esp_mmu_paddr_find_caps(const esp_paddr_t paddr, mmu_mem_caps_t *out_caps)
If the physical address is mapped, this API will provide the capabilities of the virtual address where the physical address is mapped to.
备注
: Only return value is ESP_OK(which means physically address is successfully mapped), then caps you get make sense.
备注
This API only check one page (see CONFIG_MMU_PAGE_SIZE), starting from the
paddr- 参数
paddr -- [in] Physical address
out_caps -- [out] Bitwise OR of MMU_MEM_CAP_* flags indicating the capabilities of a virtual address where the physical address is mapped to.
- 返回
ESP_OK: Physical address successfully mapped.
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Null pointer
ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND: Physical address is not mapped successfully.
Macros
-
ESP_MMU_MMAP_FLAG_PADDR_SHARED
Share this mapping.
MMU Memory Mapping Driver APIs for MMU supported memory
Driver Backgrounds:
Type Definitions
-
typedef uint32_t esp_paddr_t
Physical memory type.