Introduction
ESP-Jumpstart: Build ESP32 Products Fast
Building production-ready firmware can be hard. It involves multiple questions and decisions about the best ways of doing things. It involves building phone applications, and integrating cloud agents to get all the features done. What if there was a ready reference, a known set of best steps, gathered from previous experience of others, that you could jumpstart with?
ESP-Jumpstart is focused on building products on ESP32 series chips. It is a quick-way to get started into your product development process. ESP-Jumpstart builds a fully functional, ready to deploy “Smart Power Outlet” in a sequence of incremental tutorial steps. Each step addresses either a user-workflow or a developer workflow. Each step is an application built with ESP-IDF, ESP32’s software development framework.
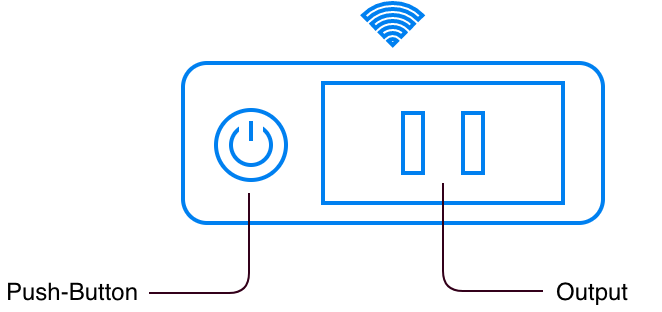
Smart Power Outlet
The ESP-Jumpstart’s Smart Power Outlet firmware assumes the device has one input push-button, and one GPIO output. It implements the following commonly required functionality.
Allows an end-user to configure their home Wi-Fi network through phone applications (iOS/Android)
Switch on or off the GPIO output
Use a push-button to physically toggle this output
Allow remote control of this output through a cloud
Implement over-the-air (OTA) firmware upgrade
Perform Reset to Factory settings on long-press of the push-button
Once you are familiar with ESP-Jumpstart, building your production firmware, is a matter of replacing the power-outlet’s device driver, with your device driver (bulb, washing machine).
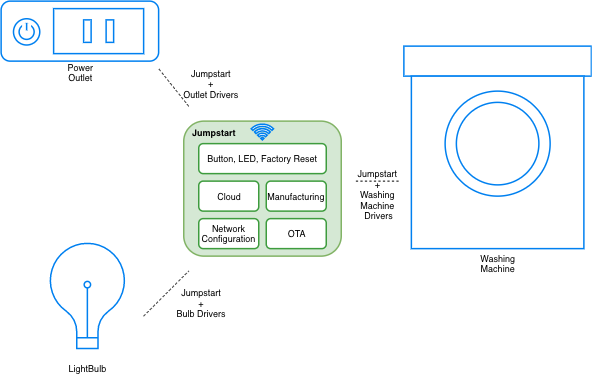
Jumpstart Applicability
Hardware Requirements
You will require the following to get started:
ESP32 Series Development Kit: ESP-Jumpstart supports multiple ESP32 variants. Choose a development kit based on your target chip:
ESP32: ESP32-DevKitC - Wi-Fi + Bluetooth Classic + BLE
ESP32-S2: ESP32-S2-DevKitC-1 - Wi-Fi only
ESP32-S3: ESP32-S3-DevKitC-1 - Wi-Fi + BLE
ESP32-C2: ESP8684-DevKitC-02 - Wi-Fi + BLE
ESP32-C3: ESP32-C3-DevKitC-02 - Wi-Fi + BLE
ESP32-C6: ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1 - Wi-Fi + BLE
All development kits are available through Espressif’s distributors. You can also use any other ESP32 series development board if you already have one.
A Development host setup (Windows, Linux or Mac) that will be used for development.
For the Restless
If you are familiar with Espressif’s hardware and/or embedded systems, and are looking for a production-reference without the incremental steps, you can do the following:
Directly use the final application in ESP-Jumpstart
If you don’t have a cloud account, configure your AWS IoT Cloud configuration as mentioned in Section AWS IoT
Create the manufacturing configuration file for your device’s unique cloud credentials, based on the instructions provided in Section Generating the Factory Data and flash it at the appropriate location
Build, flash and boot up the firmware image as you usually do
Use the reference phone-app (iOS/Android) libraries for building your phone applications. Or use the reference application to try things out as discussed in Section Network Provisioning
Use the commands discussed in Section AWS IoT for remote control
Now that you have this functional, modify to work with your driver