MQTT Debugging Tool Usage Example
Note
This document is automatically translated using AI. Please excuse any detailed errors. The official English version is still in progress.
For common questions about MQTT, please refer to MQTT FAQ.
The following illustrates the troubleshooting method for ESP-IDF MQTT errors through specific cases, and shows how debugging tools can help quickly confirm the cause of the problem and the final solution.
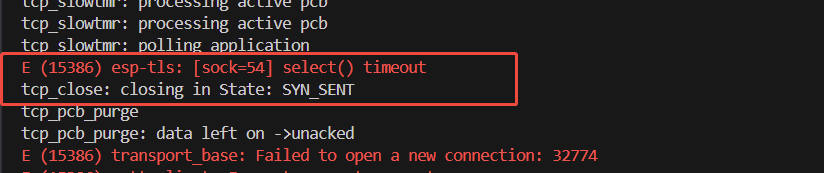
Example: esp-tls: [sock=54] select() timeout
The complete log for this issue is often:
E (15220) esp-tls: [sock=54] select() timeout
E (15220) transport_base: Failed to open a new connection: 32774
E (15220) mqtt_client: Error transport connect
I (15220) mqtt_example: MQTT_EVENT_ERROR
E (15220) mqtt_example: Last error reported from esp-tls: 0x8006
Error analysis:
TLS error code 0x8006 corresponds to
ESP_ERR_ESP_TLS_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT, indicating that the TCP connection phase timed out. The underlying socket did not receive data within the set time while waiting for the server response, causing the transport layer connection to fail.
Possible reasons:
During the TCP connection establishment phase, the client (ESP device) and the server establish a reliable transport connection through a three-way handshake. The specific process is as follows:
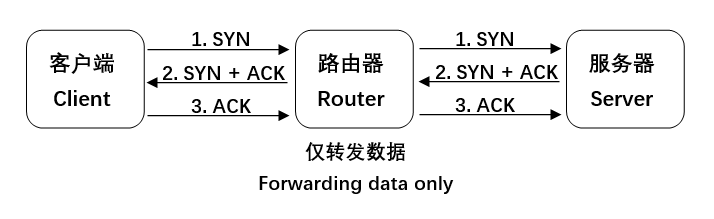
When a TCP connection timeout issue occurs, it can be investigated from the following three perspectives:
Whether the device successfully sends/receives packets
Whether the server successfully sends/receives packets
Whether the router successfully forwards packets
Note
The following shows the troubleshooting ideas and steps for this issue through two actual situations.
Situation Two: Wi-Fi failed to successfully receive and forward packets
If the device still cannot connect after changing the Broker, you need to view the communication between the device and the server through Wireless Packet Capture.
Set up a Filter, display the TCP data flow between the device and the server, and observe whether the TLS handshake is successful.
For TCP packets, you need to filter based on the device IP, server IP, and TCP.
tcp && ((ip.src == DeviceIP && ip.dst == ServerIP) || (ip.src == ServerIP && ip.dst == DeviceIP))
Observing the packet capture information reveals:
The device sent a SYN packet;
The server returned a SYN + ACK packet;
The device did not return an ACK packet.
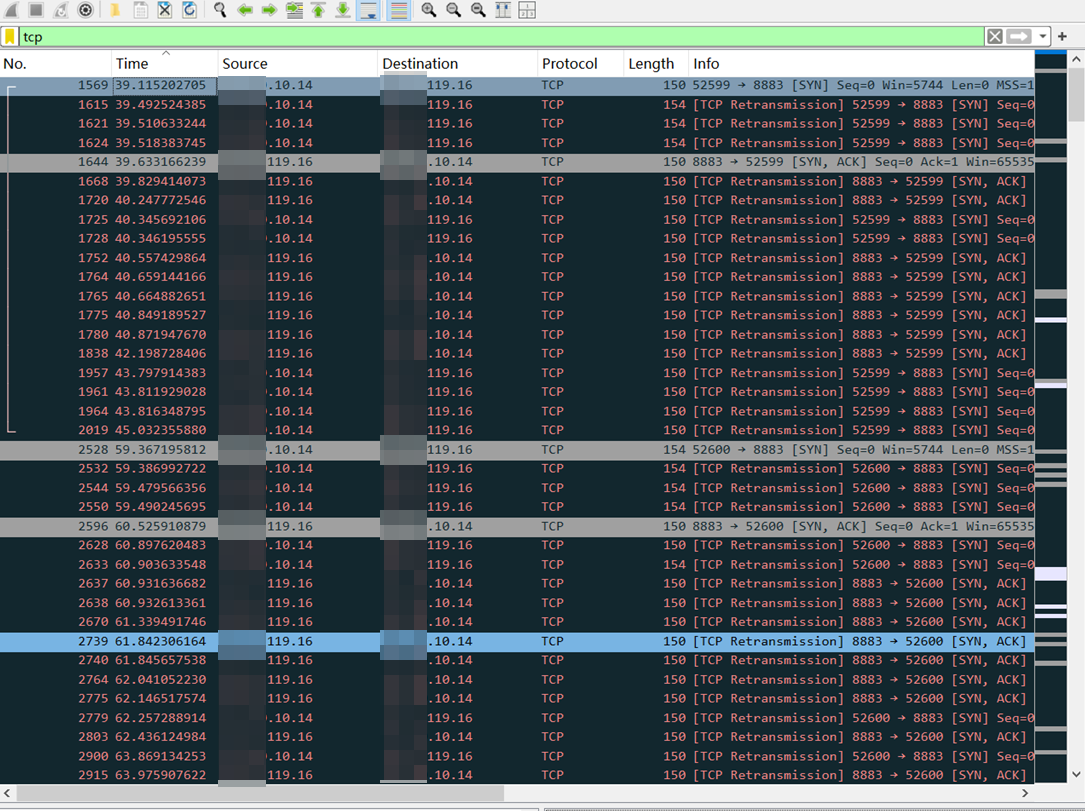
Combined with the device-side Debug Log, it does not show that the SYN + ACK packet sent by the server has been received, indicating that the data packet from the server has been successfully forwarded by the router but has not reached the device side, so it is judged that there may be a problem with the Wi-Fi link reception (RX) part.