Overview
Bluetooth® wireless technology is a short-range communication standard known for its reliability, low power consumption, and cost efficiency. It is categorized into two primary types:
Bluetooth Classic: Optimized for continuous, high-throughput data streaming, suitable for applications like audio transmission.
Bluetooth Low Energy (Bluetooth LE): Designed for low-power, intermittent data transmission, ideal for devices such as sensors and wearables.
Chip Bluetooth Capability
The following table summarizes the ESP chips that support Bluetooth in ESP-IDF, and their support for Bluetooth types (Y = supported, N = not supported).
Chip Series |
Bluetooth Classic (BR/EDR) |
Bluetooth LE |
|---|---|---|
ESP32 |
Y |
Y |
ESP32-S3 |
N |
Y |
ESP32-C2 |
N |
Y |
ESP32-C3 |
N |
Y |
ESP32-C5 |
N |
Y |
ESP32-C6 |
N |
Y |
ESP32-C61 |
N |
Y |
ESP32-H2 |
N |
Y |
Bluetooth Protocol Stack
The Bluetooth protocol stack is a layered communication architecture that defines how Bluetooth devices discover each other, establish connections, exchange data, and ensure secure and reliable communication. As shown in Figure Bluetooth Core System Architecture (Source: Bluetooth Core Specification), The stack consists of two main parts: the Controller Stack and the Host Stack, which communicate via the HCI (Host Controller Interface).
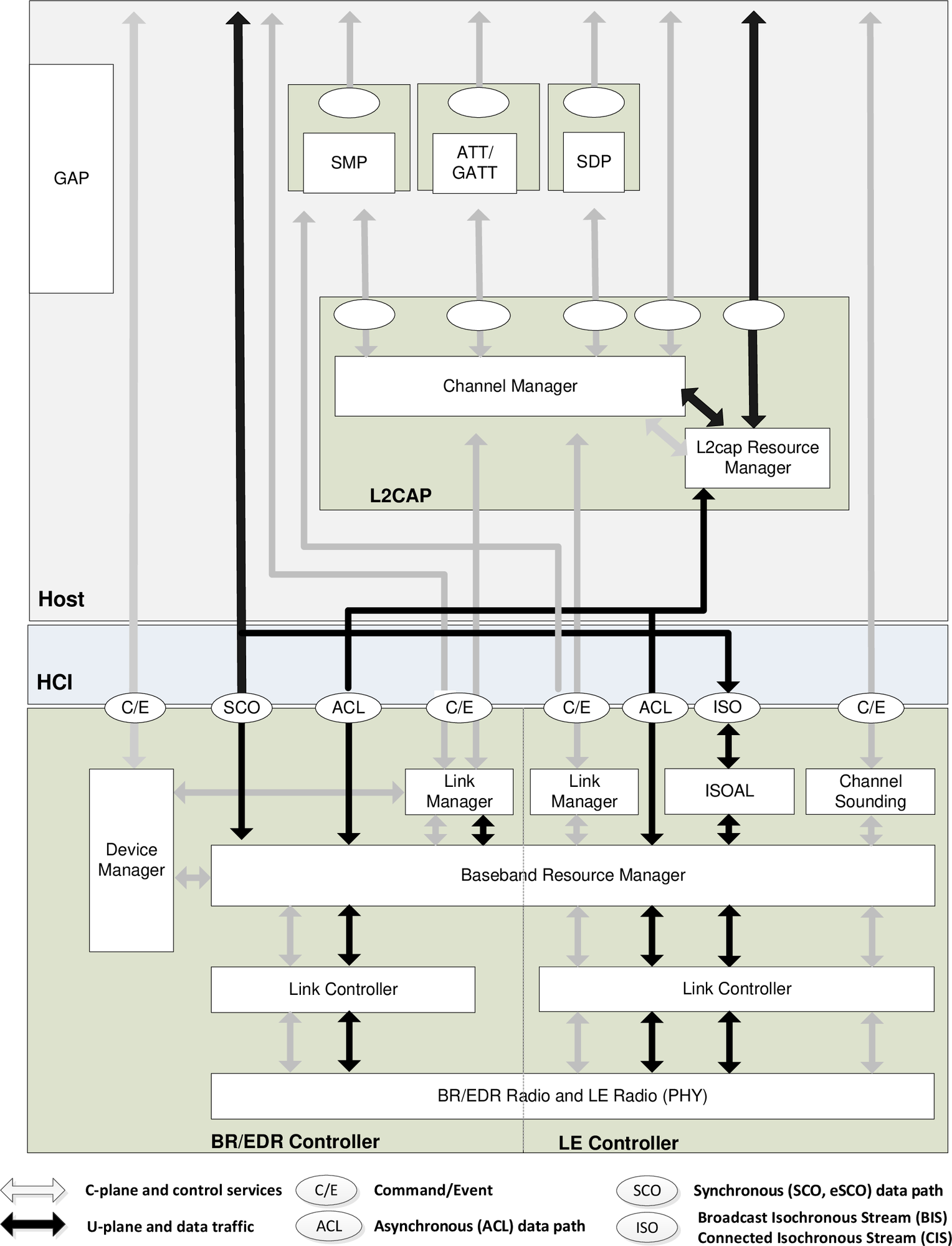
Bluetooth Core System Architecture (Source: Bluetooth Core Specification)
Controller Stack
The Controller Stack manages hardware-level operations and low-level link control. It includes:
PHY (Physical Layer): Handles transmission and reception of Bluetooth signals in the 2.4 GHz ISM band.
Baseband: Manages low-level timing and control functions, including frequency hopping, packet formatting, and error correction.
Link Controller: Handles state machine operations for device connection and disconnection, flow control, and retransmissions.
Link Manager: Manages link setup, authentication, encryption, and power control.
Device Manager: Oversees device states, handles paging and inquiry processes, and manages stored link keys for security.
Host Stack
The Host Stack implements high-level protocols for application interaction. It includes:
L2CAP (Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol): Handles data segmentation, reassembly, and multiplexing.
SMP (Security Manager Protocol): Manages authentication, encryption, and secure pairing.
GAP (Generic Access Profile): Manages device discovery, connection establishment, and defines roles and modes for Bluetooth devices.
ATT/GATT (Attribute Protocol/Generic Attribute Profile): Implements attribute-based data exchange through services and characteristics, primarily in Bluetooth LE.
SDP (Service Discovery Protocol): Allows devices to advertise and explore available services, mainly used in Bluetooth Classic.
Bluetooth Operating Environment
The ESP-IDF Bluetooth implementation operates within a FreeRTOS environment, where Bluetooth tasks are assigned based on function and priority. Controller tasks have the highest priority due to their real-time requirements, except for certain inter-process communication (IPC) tasks that coordinate operations between CPU cores.
Bluedroid
ESP-Bluedroid is a modified version of Android’s Bluedroid stack, supporting both Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth LE. It consists of two layers:
Bluetooth Upper Layer (BTU): Implements core protocols (L2CAP, GATT, SMP, etc.).
Bluetooth Transport Controller Layer (BTC): Provides application-level APIs and manages profiles.
Use Case: Recommended for applications requiring both Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth LE.
OS Adaptation
Bluedroid integrates with FreeRTOS by adapting system-related functions:
Timer (Alarm): FreeRTOS Timer has been packaged as an Alarm, and is used to start the timer which triggers certain tasks.
Task (Thread): FreeRTOS Task replaces POSIX Thread, and uses FreeRTOS Queue to trigger tasks (i.e., wake up).
Future Await/Ready (Semaphore):
xSemaphoreTakeis packaged asfuture_await, andxSemaphoreGiveasfuture_ready. These functions must not be called within the same task context.Allocator (malloc/free):
malloc/freein the standard library is packaged as theAllocatorfunction that reserves (mallocs) or frees memory.
Bluedroid Directory Structure
The ESP-IDF directory component/bt/host/bluedroid contains the following sub-folders:
├── api
├── bta
├── btc
├── common/include/common
├── config
├── device
├── external/sbc
├── hci
├── main
├── stack
└── Kconfig.in
The detailed description of each sub-folder can be found in the table below:
Sub-folder |
Description |
|---|---|
api |
The API directory, which includes all the APIs (except for those that are related to the Controller). |
bta |
The Bluetooth adaptation layer, which is suitable for the interface of some bottom layer protocols in the host. |
btc |
The Bluetooth control layer, which controls the upper-layer protocols (including profiles) and miscellaneous items in the host. |
common |
Common header file for the protocol stack. |
config |
Configure some parameters for the protocol stack. |
device |
Related to the device control of the Controller, e.g., the basic set of HCI CMD controller processes. |
external |
Codes that are not directly related to the Bluetooth, but are still usable, e.g., the SBC codec software programs. |
hci |
HCI layer protocols. |
main |
Main program (mainly to start or halt the process). |
stack |
The bottom layer protocol stacks in the Host (GAP/ ATT/ GATT/ SDP/ SMP, etc.). |
Kconfig.in |
Menuconfig files. |