内存同步
简介
ESP32-S2 可以通过以下方式访问其连接的 PSRAM:
CPU
DMA
默认情况下,CPU 通过 cache 访问上述内存,而 DMA 则可以直接访问内存。
这可能导致 cache 数据不一致的问题:
当 DMA 事务更改内存块的内容,并且该内容已经加载到 cache 中时:
CPU 可能会读取陈旧数据。
cache 中的陈旧数据可能会被写回到内存中,而 DMA 事务更新的新数据将被覆盖。
当 CPU 更改了地址的内容,内容已经加载至 cache 中,但还未存在于内存中(cache 会根据自己的策略将内容写回内存)时:
下一个 DMA 事务从内存中读取此内容,将会获取陈旧数据。
解决此类 cache 数据不一致问题的常见方法有三种:
基于硬件的 cache 一致性互连,ESP32-S2 没有此功能。
使用来自 non-cacheable 内存的 DMA 缓冲区(CPU 绕过 cache 访问的内存被称为 non-cacheable 内存)。
显式调用内存同步 API 将 cache 中的内容写回到内存,或使 cache 中的内容无效化。
内存同步驱动程序
建议使用 ESP-IDF 的 esp_mm 组件所提供的内存同步 API esp_cache_msync() 来处理此类 cache 数据不一致的问题。
驱动程序的概念
cache 与内存同步的方向:
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_C2M,用于从 cache 到内存的同步。ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_M2C,用于从内存到 cache 的同步。
cache 与内存同步的类型:
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_TYPE_DATA,用于同步到数据地址区域。ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_TYPE_INST,用于同步到指令地址区域。
驱动程序的行为
调用 esp_cache_msync(),可以同步 cache 和内存。第一个参数 addr 和第二个参数 size 共同描述了要同步的内存区域。关于第三个参数 flags:
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_C2M。使用此标志,指定地址区域中的内容将被写回到内存中。这一方向通常在 CPU 更新地址内容 之后 使用(例如对地址执行 memset 后),且需要在 DMA 对同一地址进行操作 之前 使用。ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_M2C。使用此标志,指定地址区域中的内容在 cache 中将无效化。这一方向通常在 DMA 更新地址内容 之后 使用,且需要在 CPU 将操作读取到同一地址 之前 使用。
上述两个标志用于选择同步的方向,不能同时使用。如果两个标志都未使用, esp_cache_msync() 将默认选择 ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_C2M。
上述两个标志能帮助选择同步地址的类型,不能同时使用,且如果没有用其中任何一个,则 esp_cache_msync() 将默认选择 ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_TYPE_DATA。
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_INVALIDATE。将特定地址区域写回内存后,可使用此标志触发区域内 cache 失效。此标志主要用于ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_C2M方向。设置ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_INVALIDATE标志对ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_M2C方向不会产生任何效果。ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_UNALIGNED。此标志会强制esp_cache_msync()API 在不检查地址对齐和大小对齐的情况下执行同步,详情请参阅下文 地址对齐的要求 章节。
地址对齐的要求
使用 esp_cache_msync() 时,对地址和大小(以字节为单位)存在来自 cache 的对齐要求。
起始地址和大小都符合 cache 与内存同步对齐要求的地址区域被称为 对齐地址区域。
起始地址或大小不符合 cache 与内存同步对齐要求的地址区域被称为 非对齐地址区域。
默认情况下,如果指定了非对齐地址区域,则 esp_cache_msync() 将报错 ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG,并告知所需的对齐方式。
有关地址对齐要求的警告
可以通过设置 ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_UNALIGNED 标志跳过此类检查。但请注意,使用此标志需谨慎,因为在非对齐地址区域内同步 cache 和内存可能会在无形中破坏内存。
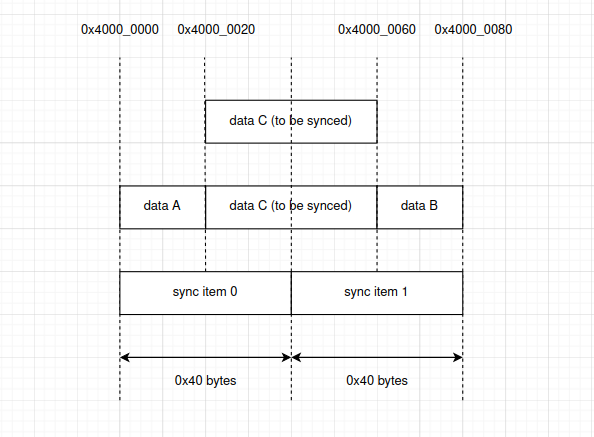
举个例子,假设:
对齐要求为 0x40 字节。
调用
esp_cache_msync(),并使用 ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_M2C | ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_UNALIGNED 标志,指定的地址区域为 0x4000_0020 ~ 0x4000_0060(详见下图中的 data C)。
上述设置将触发地址区域 0x4000_0000 ~ 0x4000_0080 cache 失效,详见下图中的 sync item0 和 sync item1。
如果 0x4000_0000 ~ 0x4000_0020 中的内容(下图中的 data A)或 0x4000_0060 ~ 0x4000_0080 中的内容(下图中的 data B)尚未写回到内存,则 data A 和 data B 将被丢弃。
API 参考
API 参考 - ESP Msync 驱动程序
Header File
This header file can be included with:
#include "esp_cache.h"
This header file is a part of the API provided by the
esp_mmcomponent. To declare that your component depends onesp_mm, add the following to your CMakeLists.txt:REQUIRES esp_mm
or
PRIV_REQUIRES esp_mm
Functions
-
esp_err_t esp_cache_msync(void *addr, size_t size, int flags)
Memory sync between Cache and storage memory.
For cache-to-memory (C2M) direction:
For cache writeback supported chips (you can refer to SOC_CACHE_WRITEBACK_SUPPORTED in soc_caps.h)
This API will do a writeback to synchronise between cache and storage memory
With ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_INVALIDATE, this API will also invalidate the values that just written
Note: although ESP32 is with PSRAM, but cache writeback isn't supported, so this API will do nothing on ESP32
For other chips, this API will do nothing. The out-of-sync should be already dealt by the SDK
For memory-to-cache (M2C) direction:
This API will by default do an invalidation
This API is cache-safe and thread-safe
备注
If you don't set direction (ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_x flags), this API is by default C2M direction
备注
If you don't set type (ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_TYPE_x flags), this API is by default doing msync for data
备注
You should not call this during any Flash operations (e.g. esp_flash APIs, nvs and some other APIs that are based on esp_flash APIs)
备注
If XIP_From_PSRAM is enabled (by enabling both CONFIG_SPIRAM_FETCH_INSTRUCTIONS and CONFIG_SPIRAM_RODATA), you can call this API during Flash operations
- 参数:
addr -- [in] Starting address to do the msync
size -- [in] Size to do the msync
flags -- [in] Flags, see
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_x
- 返回:
ESP_OK:
Successful msync
For C2M direction, if this chip doesn't support cache writeback, if the input addr is a cache supported one, this API will return ESP_OK
ESP_ERR_INVALID_ARG: Invalid argument, not cache supported addr, see printed logs
ESP_ERR_NOT_SUPPORTED: Vaddr is not in cacheable range, API will do nothing
-
size_t esp_cache_get_line_size_by_addr(const void *addr)
Get the cache line size by address.
- 参数:
addr -- [in] The buffer address to examine
- 返回:
The cache line size in bytes. Return 0 if the memory (that the address points to) is not cacheable.
Macros
-
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_INVALIDATE
Do an invalidation.
Cache msync flags
For cache-to-memory (C2M) direction: setting this flag will start an invalidation after the cache writeback operation
For memory-to-cache (M2C) direction: setting / unsetting this flag will behave similarly, trigger an invalidation
-
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_UNALIGNED
Allow msync to a address block that are not aligned to the data cache line size.
-
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_C2M
Cache msync direction: from Cache to memory.
备注
If you don't set direction (ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_x flags), it is by default cache-to-memory (C2M) direction
-
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_DIR_M2C
Cache msync direction: from memory to Cache.
-
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_TYPE_DATA
Cache msync type: data.
备注
If you don't set type (ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_TYPE_x flags), it is by default data type
-
ESP_CACHE_MSYNC_FLAG_TYPE_INST
Cache msync type: instruction.