Command Word
MultiNet Command Word Recognition Model
MultiNet is a lightweight model designed to recognize multiple speech command words offline based on ESP32. Currently, up to 200 speech commands, including customized commands, are supported.
Support Chinese speech commands recognition
Support user-defined commands
Support adding / deleting / modifying commands during operation
Up to 200 commands are supported
It supports single recognition and continuous recognition
Lightweight and low resource consumption
Low delay, within 500ms
The model is partitioned separately to support users to apply OTA
The MultiNet input is the audio processed by the audio-front-end algorithm (AFE), with the format of 16 KHz, 16 bit and mono. By recognizing the audio signals, speech commands can be recognized.
Please refer to Models Benchmark to check models supported by Espressif SoCs.
For details on flash models, see Section Flashing Models .
Note
Models ending with Q8 represents the 8 bit version of the model, which is more lightweight.
Commands Recognition Process
Please see the flow diagram for commands recognition below:
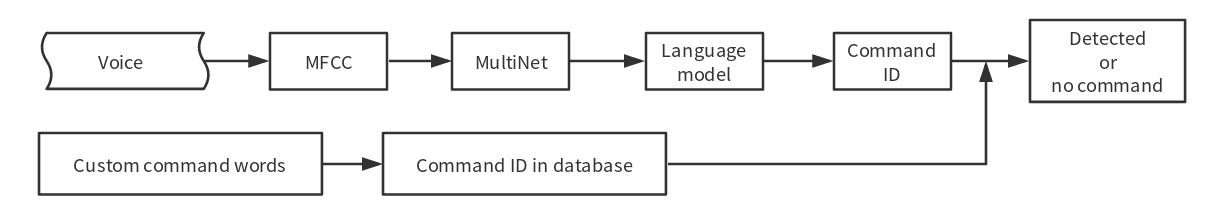
speech_command-recognition-system
Speech Commands Customization Methods
Note
Mixed Chinese and English is not supported in command words.
The command word cannot contain Arabic numerals and special characters.
Please refer to Chinese version documentation for Chinese speech commands customization methods.
MultiNet7 customize speech commands
MultiNet7 use phonemes for English speech commands. Please modify a text file model/multinet_model/fst/commands_en.txt by the following format:
# command_id,command_grapheme,command_phoneme 1,tell me a joke,TfL Mm c qbK 2,sing a song,Sgl c Sel
Column 1: command ID, it should start from 1 and cannot be set to 0.
Column 2: command_grapheme, the command sentence. It is recommended to use lowercase letters unless it is an acronym that is meant to be pronounced differently.
Column 3: command_phoneme, the phoneme sequence of the command which is optional. To fill this column, please use tool/multinet_g2p.py to do the Grapheme-to-Phoneme conversion and paste the results at the third column correspondingly (this is the recommended way).
If Column 3 is left empty, then an internal Grapheme-to-Phoneme tool will be called at runtime. But there might be a little accuracy drop in this way due the different Grapheme-to-Phoneme algorithms used.
MultiNet6 customize speech commands
MultiNet6 use grapheme for English speech commands, you can add/modify speech commands by words directly. Please modify a text file model/multinet_model/fst/commands_en.txt by the following format:
# command_id,command_grapheme 1,TELL ME A JOKE 2,MAKE A COFFEE
Column 1: command ID, it should start from 1 and cannot be set to 0.
Column 2: command_grapheme, the command sentence. It is recommended to use all capital letters.
The extra column in the default commands_en.txt is to keep it compatible with MultiNet7, there is no need to fill the third column when using MultiNet6.
MultiNet5 customize speech commands
MultiNet5 use phonemes for English speech commands. For simplicity, we use characters to denote different phonemes. Please use tool/multinet_g2p.py to do the convention.
Via
menuconfigNavigate to
idf.py menuconfig>ESP Speech Recognition>Add Chinese speech commands/Add English speech commandsto add speech commands. For details, please refer to the example in ESP-Skainet.
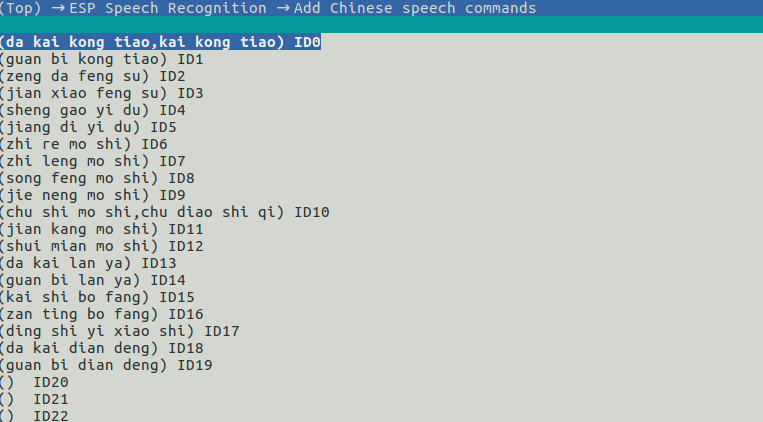
menuconfig_add_speech_commands
Please note that a single
Command IDcan correspond to more than one commands. For example, “da kai kong tiao” and “kai kong tiao” have the same meaning. Therefore, users can assign the same command id to these two commands and separate them with “,” (no space required before and after).Call the following API:
/** * @brief Update the speech commands of MultiNet by menuconfig * * @param multinet The multinet handle * * @param model_data The model object to query * * @param language The language of MultiNet * * @return * - ESP_OK Success * - ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fail */ esp_err_t esp_mn_commands_update_from_sdkconfig(esp_mn_iface_t *multinet, const model_iface_data_t *model_data);
Customize Speech Commands Via API calls
Alternatively, speech commands can be modified via API calls, this method works for MultiNet5, MultiNet6 and MultiNet7.
MutiNet5 requires the input command string to be phonemes, and MultiNet6 and MultiNet7 only accepts grapheme inputs to API calls.
Apply new changes, the add/remove/modify/clear actions will not take effect util this function is called.
/** * @brief Update the speech commands of MultiNet * * @Warning: Must be used after [add/remove/modify/clear] function, * otherwise the language model of multinet can not be updated. * * @return * - NULL Success * - others The list of error phrase which can not be parsed by multinet. */ esp_mn_error_t *esp_mn_commands_update();
Note
The modifications will not be applied, thus not printed out, until you call
esp_mn_commands_update().Add a new speech command, will return
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATEif the input string is not in the correct format./** * @brief Add one speech commands with command string and command ID * * @param command_id The command ID * @param string The command string of the speech commands * * @return * - ESP_OK Success * - ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fail */ esp_err_t esp_mn_commands_add(int command_id, char *string);
Remove a speech command, will return
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATEif the command does not exist./** * @brief Remove one speech commands by command string * * @param string The command string of the speech commands * * @return * - ESP_OK Success * - ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fail */ esp_err_t esp_mn_commands_remove(char *string);
Modify a speech command, will return
ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATEif the command does not exist./** * @brief Modify one speech commands with new command string * * @param old_string The old command string of the speech commands * @param new_string The new command string of the speech commands * * @return * - ESP_OK Success * - ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fail */ esp_err_t esp_mn_commands_modify(char *old_string, char *new_string);
Clear all speech commands.
/** * @brief Clear all speech commands in linked list * * @return * - ESP_OK Success * - ESP_ERR_INVALID_STATE Fail */ esp_err_t esp_mn_commands_clear(void);
Print cached speech commands, this function will print out all cached speech commands. Cached speech commands will be applied after
esp_mn_commands_update()is called./** * @brief Print all commands in linked list. */ void esp_mn_commands_print(void);
Print active speech commands, this function will print out all active speech commands.
/** * @brief Print all commands in linked list. */ void esp_mn_active_commands_print(void);
Use MultiNet
We suggest to use MultiNet together with audio front-end (AFE) in ESP-SR. For details, see Section AFE Introduction and Use .
After configuring AFE, users can follow the steps below to configure and run MultiNet.
Initialize MultiNet
Load and initialize MultiNet. For details, see Section flash_model
Customize speech commands. For details, see Section Speech Commands Customization Methods
Run MultiNet
Users can start MultiNet after enabling AFE and WakeNet, but must pay attention to the following limitations:
The frame length of MultiNet must be equal to the AFE fetch frame length
The audio format supported is 16 KHz, 16 bit, mono. The data obtained by AFE fetch is also in this format
Get the length of frame that needs to pass to MultiNet
int mu_chunksize = multinet->get_samp_chunksize(model_data);
mu_chunksizedescribes theshortof each frame passed to MultiNet. This size is exactly the same as the number of data points per frame obtained in AFE.Start the speech recognition
We send the data from AFE
fetchto the following API:esp_mn_state_t mn_state = multinet->detect(model_data, buff);
The length of
buffismu_chunksize * sizeof(int16_t).
MultiNet Output
Speech command recognition must be used with WakeNet. After wake-up, MultiNet detection can start.
After running, MultiNet returns the recognition output of the current frame in real time mn_state, which is currently divided into the following identification states:
ESP_MN_STATE_DETECTING
Indicates that the MultiNet is detecting but the target speech command word has not been recognized.
ESP_MN_STATE_DETECTED
Indicates that the target speech command has been recognized. At this time, the user can call
get_resultsinterface to obtain the recognition results.esp_mn_results_t *mn_result = multinet->get_results(model_data);
The recognition result is stored in the return value of the
get_resultAPI in the following format:typedef struct{ esp_mn_state_t state; int num; // The number of phrase in list, num<=5. When num=0, no phrase is recognized. int phrase_id[ESP_MN_RESULT_MAX_NUM]; // The list of phrase id. float prob[ESP_MN_RESULT_MAX_NUM]; // The list of probability. } esp_mn_results_t;
where,
stateis the recognition status of the current framenummeans the number of recognized commands,num<= 5, up to 5 possible results are returnedphrase_idmeans the Phrase ID of speech commandsprobmeans the recognition probability of the recognized entries, which is arranged from large to small
Users can use
phrase_id[0]andprob[0]get the recognition result with the highest probability.ESP_MN_STATE_TIMEOUT
Indicates the speech commands has not been detected for a long time and will exit automatically and wait to be waked up again.
Single recognition mode and Continuous recognition mode:
* Single recognition mode: exit the speech recognition when the return status is ESP_MN_STATE_DETECTED
* Continuous recognition mode: exit the speech recognition when the return status is ESP_MN_STATE_TIMEOUT
Resource Occupancy
For the resource occupancy for this model, see Resource Occupancy.