OpenThread
OpenThread is an IP stack running on the 802.15.4 MAC layer which features mesh network and low power consumption.
Modes of the OpenThread Stack
OpenThread can run under the following modes on Espressif chips:
Standalone Node
The full OpenThread stack and the application layer run on the same chip. This mode is available on chips with 15.4 radio such as ESP32-H2 and ESP32-C6.
Radio Co-Processor (RCP)
The chip is connected to another host running the OpenThread IP stack. It sends and receives 15.4 packets on behalf of the host. This mode is available on chips with 15.4 radio such as ESP32-H2 and ESP32-C6. The underlying transport between the chip and the host can be SPI or UART. For the sake of latency, we recommend using SPI as the underlying transport.
OpenThread Host
For chips without a 15.4 radio, it can be connected to an RCP and run OpenThread under host mode. This mode enables OpenThread on Wi-Fi chips such as ESP32, ESP32-S2, ESP32-S3, and ESP32-C3. The following diagram shows how devices work under different modes:
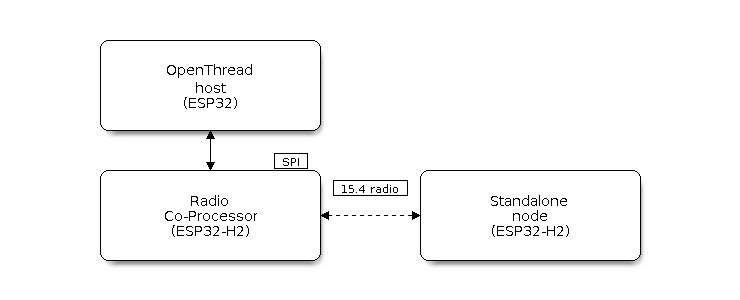
OpenThread device modes
How to Write an OpenThread Application
The OpenThread openthread/ot_cli example is a good place to start at. It demonstrates basic OpenThread initialization and simple socket-based server and client.
Before OpenThread Initialization
s1.1: The main task calls
esp_vfs_eventfd_register()to initialize the eventfd virtual file system. The eventfd file system is used for task notification in the OpenThread driver.s1.2: The main task calls
nvs_flash_init()to initialize the NVS where the Thread network data is stored.s1.3: Optional. The main task calls
esp_netif_init()only when it wants to create the network interface for Thread.s1.4: The main task calls
esp_event_loop_create()to create the system Event task and initialize an application event's callback function.
OpenThread Stack Initialization
s2.1: Call
esp_openthread_init()to initialize the OpenThread stack.
OpenThread Network Interface Initialization
The whole stage is optional and only required if the application wants to create the network interface for Thread.
s3.1: Call
esp_netif_new()withESP_NETIF_DEFAULT_OPENTHREADto create the interface.s3.2: Call
esp_openthread_netif_glue_init()to create the OpenThread interface handlers.s3.3: Call
esp_netif_attach()to attach the handlers to the interface.
The OpenThread Main Loop
s4.3: Call
esp_openthread_launch_mainloop()to launch the OpenThread main loop. Note that this is a busy loop and does not return until the OpenThread stack is terminated.
Calling OpenThread APIs
The OpenThread APIs are not thread-safe. When calling OpenThread APIs from other tasks, make sure to hold the lock with esp_openthread_lock_acquire() and release the lock with esp_openthread_lock_release() afterwards.
Deinitialization
The following steps are required to deinitialize the OpenThread stack:
Call
esp_netif_destroy()andesp_openthread_netif_glue_deinit()to deinitialize the OpenThread network interface if you have created one.Call
esp_openthread_deinit()to deinitialize the OpenThread stack.
OpenThread Macro Definitions
In the OpenThread protocol stack, defining macros to enable features and configure parameters is a common practice. Users can define macro values to enable or disable specific features and adjust parameters. ESP provides the following methods for defining OpenThread macros:
Using configuration menu (
menuconfig): Some macros are mapped to Kconfig files and can be configured throughidf.py menuconfig → Component config → OpenThread. This allows enabling or disabling features and setting related parameters.Using user-defined header files: Users can create a custom header file and enable it via
idf.py menuconfig → Component config → OpenThread → Thread Extended Features → Use a header file defined by customer. The priority of the custom header file is second only to themenuconfig.Using
openthread-core-esp32x-xxx-config.hfor configuration: Some macros have default values set in the OpenThread private header files. These cannot currently be modified through themenuconfig, but can be modified via user-defined header files.Using OpenThread stack default configurations: Other macros are assigned default values when defined in the OpenThread stack.
Note
The priority of the above configuration methods, from highest to lowest, is as follows: Configuration Menu → User-defined Header File → openthread-core-esp32x-xxx-config.h → OpenThread Stack Default Configuration
The OpenThread Border Router
The OpenThread border router connects the Thread network with other IP networks. It provides IPv6 connectivity, service registration, and commission functionality.
To launch an OpenThread border router on an ESP chip, you need to connect an RCP to a Wi-Fi capable chip such as ESP32.
Calling esp_openthread_border_router_init() during the initialization launches all the border routing functionalities.
You may refer to the openthread/ot_br example and the README for further border router details.