Profiles and Protocols
In the Bluetooth system,
Protocol: Defines the underlying communication mechanism required to accomplish specific functions, such as data transfer, link control, security services, and service information exchange
Profile: Defines the features and functionality that the Bluetooth system provides (e.g., audio streaming, remote control, serial communication), which rely on the underlying protocols
The table below summarizes the Bluetooth Classic profiles supported by ESP-Bluedroid:
Profile |
Supported Roles |
Description |
|---|---|---|
GAP |
— |
Device discovery, connection, and security management |
A2DP |
Source, Sink |
High-quality audio streaming |
AVRCP |
Controller, Target |
Audio/video remote control |
HFP |
AG, HF |
Hands-free voice calls |
SPP |
Server, Client |
Serial data transfer |
The above profiles are implemented based on the following protocols: L2CAP, SDP, RFCOMM, AVDTP, AVCTP. The protocol stack is shown below:
┌───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Applications │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Profiles │
│ ┌───────┬───────┬───────┬───────┬───────┐ │
│ │ GAP │ A2DP │ AVRCP │ HFP │ SPP │ │
│ └───────┴───┬───┴───┬───┴───┬───┴───┬───┘ │
├─────────────┼───────┼───────┼───────┼─────────────────┤
│ │ │ │ │ Transport │
│ ┌────┴───┬───┴───┬───┴───────┴────┬───────┐ │
│ │ AVDTP │ AVCTP │ RFCOMM │ SDP │ │
│ └────┬───┴───┬───┴────────┬───────┴───┬───┘ │
├─────────────┴───────┴────────────┴───────────┴────────┤
│ L2CAP │
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ HCI │
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Bluetooth Classic Protocol Stack
Layer Functions:
L2CAP, SDP: Core protocols required for the Bluetooth Classic host stack
RFCOMM: Serial cable emulation protocol, provides transport for SPP and HFP
AVDTP, AVCTP: Audio/video transport and control protocols, provide transport for A2DP and AVRCP
Profiles: Defines application-specific functionality
Protocol
L2CAP
Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP) is the core protocol in the Bluetooth Classic host stack. Its main functions include:
Upper-layer protocol multiplexing
Data segmentation and reassembly
Quality of Service (QoS) information transfer
L2CAP allows multiple applications to share a single ACL-U logical link via channel-oriented interfaces.
L2CAP channels support the following operating modes:
Basic L2CAP mode
Flow control mode
Retransmission mode
Enhanced retransmission mode
Streaming mode
ACL-U logical links support basic L2CAP mode, enhanced retransmission mode, and streaming mode.
SDP
Service Discovery Protocol (SDP) allows applications to discover services offered by other Bluetooth devices and retrieve service characteristics. SDP involves communication between SDP servers and clients:
Server: Maintains a service record table describing available services
Client: Sends SDP requests to query the server's service records
RFCOMM
Serial Cable Emulation Protocol (RFCOMM) operates on top of L2CAP and provides a serial-like communication interface for applications. It is the foundation for SPP and HFP, simulating RS-232 control signals and data flow while supporting multiple concurrent connections.
AVDTP
Audio/Video Distribution Transport Protocol (AVDTP) is used to transport audio and video streams over L2CAP and serves as the underlying transport for A2DP. AVDTP consists of:
Signaling entity: Negotiates stream parameters
Transport entity: Transmits media streams
AVCTP
Audio/Video Control Transport Protocol (AVCTP) carries AV/C commands and responses, providing transport services for AVRCP. It supports two channels:
Control channel: Transmits control commands
Browsing channel: Transmits browsing commands
Profile
GAP
Generic Access Profile (GAP) defines basic procedures for device discovery, connection establishment, and security management. GAP is the foundation for all other profiles.
Refer to the GAP API for details.
A2DP
Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP) defines an application-level specification and procedure for high-quality audio streaming over ACL channels.
Roles:
Source (SRC): Audio source, e.g., phone, PC
Sink (SNK): Audio sink, e.g., Bluetooth speaker, headphones
Audio Codec:
SBC (Sub-Band Coding), mandatory according to A2DP specification
A2DP is based on GAP and the Generic Audio/Video Distribution Profile (GAVDP), responsible for establishing audio/video streams. See Profile Dependencies for dependencies.
Refer to the A2DP API for details.
AVRCP
Audio/Video Remote Control Profile (AVRCP) defines standard interfaces for controlling audio/video devices remotely.
Roles:
Controller (CT): Device initiating control commands
Target (TG): Device receiving and responding to commands
Supported Commands:
PASS THROUGH commands for: Play, Pause, Stop, Previous, Next, Volume control, etc.
Functional Categories:
Player/Recorder
Monitor/Amplifier (default configuration)
Tuner
Menu
A2DP and AVRCP are typically used together.
A2DP handles high-quality audio streaming
AVRCP manages remote control of audio/video devices
At the lower layer, AVDTP (for audio streams) and AVCTP (for control commands) transmit data and commands over L2CAP channels
See Profile Dependencies for the dependencies between A2DP and AVRCP.
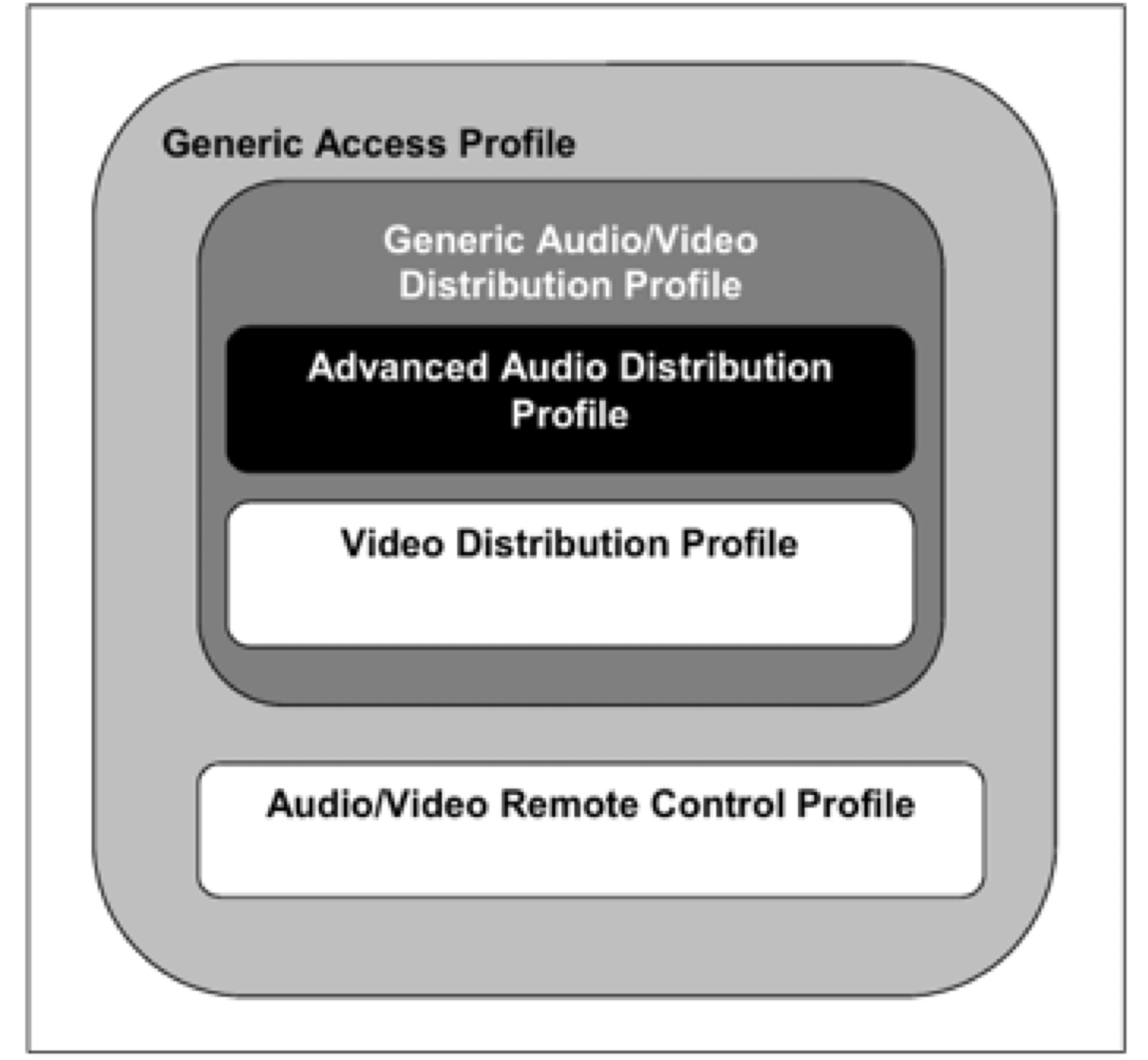
Profile Dependencies
Refer to the AVRCP API for details.
HFP
Hands-Free Profile (HFP) defines an application-level specification for communication between hands-free devices and mobile phones over Bluetooth.
Roles:
Audio Gateway (AG): Typically a phone
Hands-Free Unit (HF): E.g., car kit, Bluetooth headset
Audio Codec:
CVSD: Narrowband speech codec
mSBC: Wideband speech codec
Key Functions:
Answer/Hang up/Reject calls
Volume control
Voice dialing
Caller ID
Refer to the HFP API for details.
SPP
Serial Port Profile (SPP) defines a serial communication application based on the RFCOMM protocol, enabling RS-232-style data transmission over Bluetooth.
Roles:
Server: Device waiting for connections
Client: Device initiating connections
Use Cases:
Device configuration and debugging
Sensor data transfer
Point-to-point data exchange
Refer to the SPP API for details.