ESP USB Peripheral Introduction
USB Introduction
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a universal bus standard used to connect hosts and peripheral devices. A USB host can establish a connection with USB devices through a USB interface, enabling functions such as data transfer and power supply.
USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum) is the organization responsible for establishing USB standards. It defines USB standards, including USB 1.1, USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and others. USB-IF specifies protocols for the physical layer, data link layer, transport layer, session layer, presentation layer, and more for the USB interface. It also defines USB Device Class standards, with common device classes such as HID (Human Interface Device), MSC (Mass Storage Class), CDC (Communication Device Class), Audio, Video, and more.
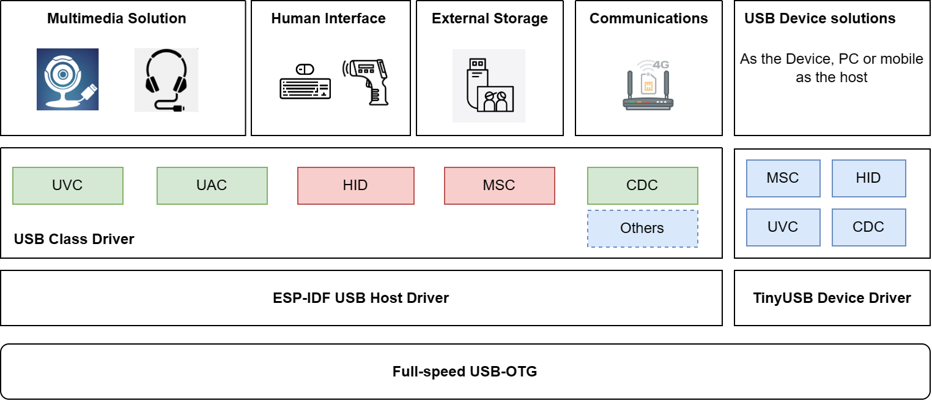
Espressif’s ESP32-S2/S3/C3/P4 chips come with built-in USB-OTG or USB-Serial-JTAG peripherals, supporting a variety of USB applications. These include USB multimedia applications, USB communication applications, USB storage applications, USB human interface applications, and more.
USB Electrical Properties
The electrical properties of the Type-A USB interface are as follows:
Pin |
Name |
Cable color |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
VBUS |
Red |
+5V |
2 |
D- |
White |
Data-(0 or 3.3V) |
3 |
D+ |
Green |
Data+(0 or 3.3V) |
4 |
GND |
Black |
Ground |
For self-powered devices, an additional IO is required to check the VBUS voltage, to detect whether the device is unplugged.
Reversing the D- D+ connection will not damage the hardware, but the host will be unable to recognize it.
USB-OTG Full-Speed Controller Introduction
USB OTG Full-Speed Controller: refers to a controller that simultaneously supports USB-OTG, USB Host, and USB Device modes, with the capability for mode negotiation and switching. It supports two speeds: Full-speed (12Mbps) and Low-speed (1.5Mbps), and is compatible with both USB 1.1 and USB 2.0 protocols.
Starting from ESP-IDF version 4.4, it includes USB Host and USB Device protocol stacks, as well as various device class drivers, supporting user secondary development.
For more information, please refer to the USB-OTG Controller Introduction.
USB-OTG High-speed Controller Introduction
USB OTG High-speed Controlleris a controller that simultaneously supports USB-OTG, USB Host, and USB Device modes, with the capability for mode negotiation and switching. It supports three speeds: High-speed (480Mbps), Full-speed (12Mbps), and Low-speed (1.5Mbps), and is compatible with USB 2.0 protocol.
Starting from ESP-IDF version 5.5, the originally independent USB PHY implementation of ESP32-P4 has been merged into the shared PHY module with S2/S3, unified driving structure, simplified maintenance.
For more information, please refer to the USB-OTG Controller Introduction.
Introduction to USB-Serial-JTAG Controller
USB-Serial-JTAG Controller: A dedicated USB controller with both USB Serial and USB JTAG capabilities. It supports firmware download, log printing, CDC transmission, and JTAG debugging through the USB interface. Secondary development such as modifying USB functions or descriptors is not supported.
For more information, please refer to the USB-Serial-JTAG Controller Introduction.
USB Full-Speed PHY Introduction
USB Full-Speed PHY: Also known as USB Full-Speed Transceiver, it is used for converting USB controller digital signals to USB bus signal levels and providing bus driving capability. The internal USB Full-speed PHY is connected to external fixed IO pins.
For more information, please refer to the USB-PHY Introduction.
ESP32-S/P/C Series USB Peripheral Support
USB OTG High-Speed |
USB OTG Full-Speed |
USB-Serial-JTAG |
Full-Speed PHY |
High-Speed PHY |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ESP32-P4 |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
√ |
ESP32-S3 |
X |
√ |
√ |
√ |
X |
ESP32-S2 |
X |
√ |
X |
√ |
X |
ESP32-C6 |
X |
X |
√ |
√ |
X |
ESP32-C3 |
X |
X |
√ |
√ |
X |
ESP32-C2 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
ESP32 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
ESP8266 |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
√ : Supported
X : Not Supported
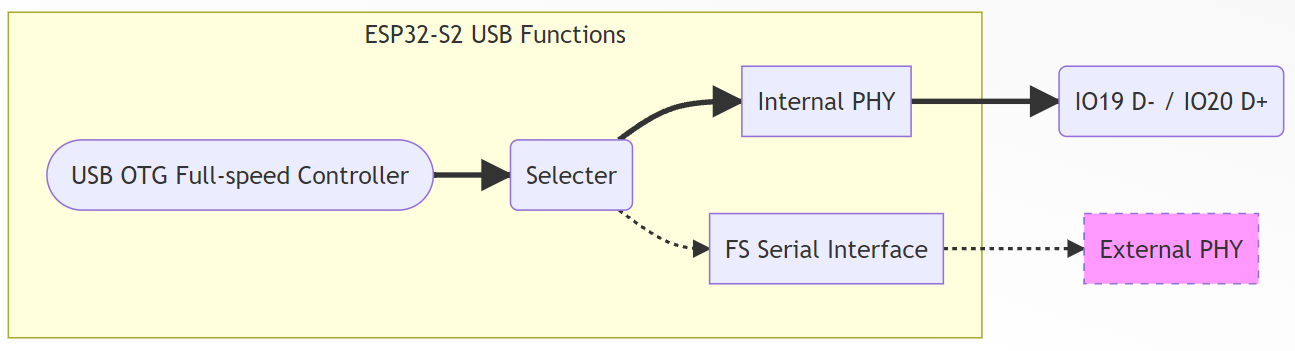
ESP32-S2 USB Function Overview
The ESP32-S2 features an integrated USB OTG Full-Speed Controller and USB Full-Speed PHY. The internal architecture is as follows:
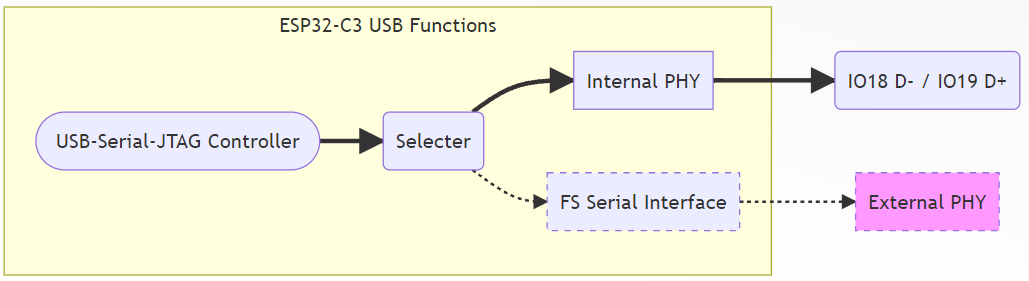
ESP32-C3 USB Function Overview
The ESP32-C3 comes equipped with a built-in USB-Serial-JTAG Controller and USB Full-Speed PHY. The internal architecture is outlined below:
ESP32-S3 USB Function Overview
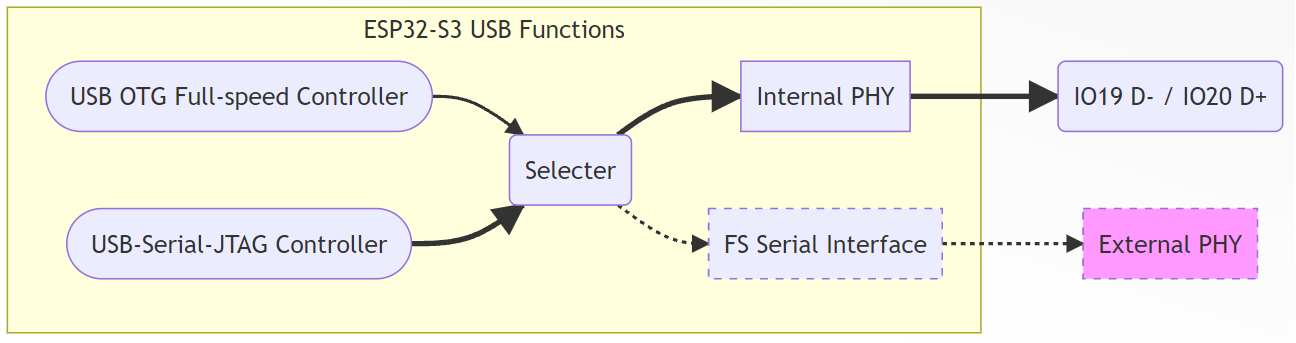
The ESP32-S3 is equipped with two built-in USB controllers. USB OTG Full-Speed Controller and USB-Serial-JTAG Controller, Additionally, there is an integrated USB Full-speed PHY. The internal USB PHY is initially connected to the USB-Serial-JTAG controller by default. It can be modified through eFuse burning to change the default configuration or dynamically switched through register configuration. It is also possible to enable both controllers simultaneously by adding an external PHY. For detailed information on switching the internal USB PHY, refer to USB PHY Switching.
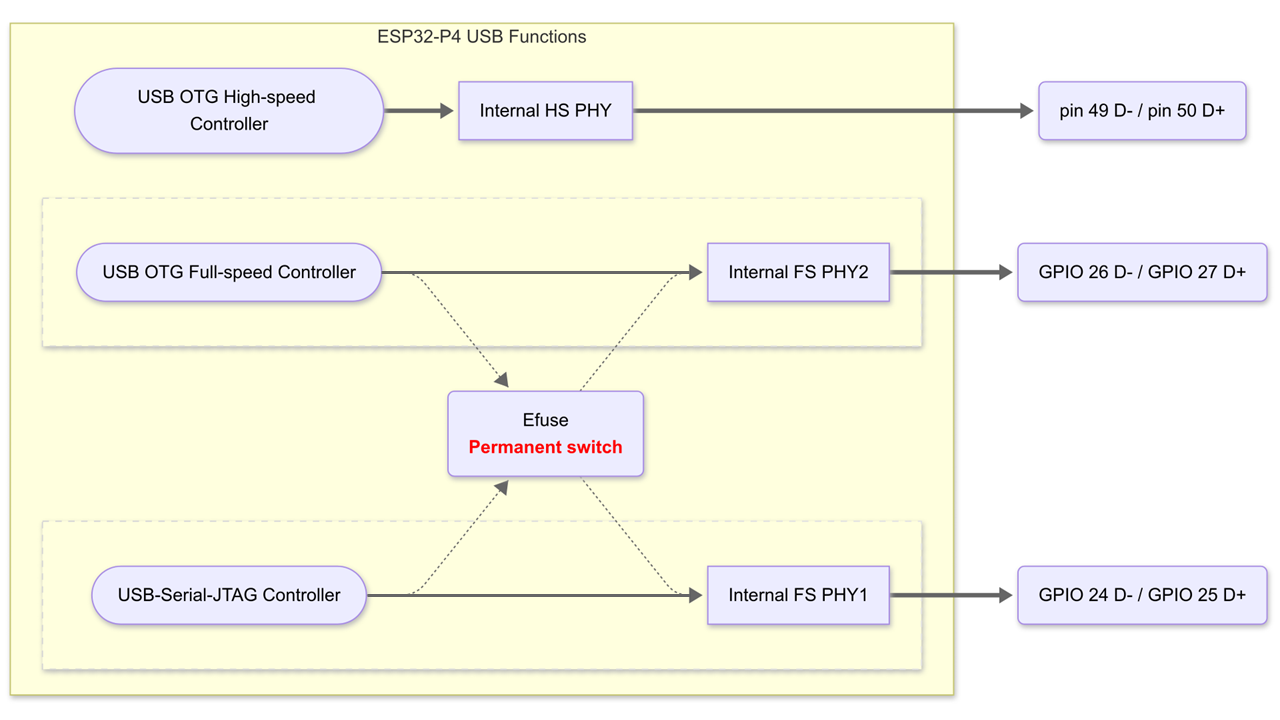
ESP32-P4 USB Function Overview
ESP32-P4 is equipped with three built-in USB controllers. USB OTG High-speed Controller , USB OTG Full-speed Controller and USB-Serial-JTAG Controller, Additionally, there is an integrated USB High-speed PHY and two USB Full-speed PHYs. The default connection is FS_PHY1 connected to the USB Serial/JTAG controller, and FS_PHY2 connected to OTG_FS. The user can change the connection relationship through EFUSE_USB_PHY_SEL.
0:FS_PHY1 connected to the USB Serial/JTAG controller, and FS_PHY2 connected to OTG_FS.
1:FS_PHY2 connected to the USB Serial/JTAG controller, and FS_PHY1 connected to OTG_FS.