项目配置编辑器
本扩展提供了多个设置项,用于配置 ESP-IDF 项目。若想在同一项目中启用多种配置,可以使用 项目配置编辑器 来定义多个配置文件,每个配置文件包含不同的设置。本文目录如下:
为单一构建配置扩展
典型的 ESP-IDF 项目结构 如下所示:
- /path/to/esp-project/
- CMakeLists.txt
- sdkconfig
- components/ - component1/ - CMakeLists.txt
- Kconfig
- src1.c
- component2/ - CMakeLists.txt
- Kconfig
- src1.c
- include/ - component2.h
- main/ - CMakeLists.txt
- src1.c
- src2.c
- build/
在 ESP-IDF CMake 构建系统中,项目配置通过 SDK 配置编辑器进行保存,这些配置值存储在 /path/to/esp-project/sdkconfig 文件中。默认情况下,该文件会在 ESP-IDF 项目根目录下创建,同时 /path/to/esp-project/build 目录被用作构建目录路径。
若当前 ESP-IDF 项目处于版本控制中,则 /path/to/esp-project/sdkconfig 可能会随着不同用户的构建发生变化,从而改变项目的预期行为。为避免这种情况,建议将项目相关的配置移动到 sdkconfig.defaults 文件(或文件列表)中,这些文件不会被构建系统修改。同时,可以将 /path/to/esp-project/sdkconfig 添加到 .gitignore 列表中。若使用 ESP-IDF v5.0 及以上版本,则 sdkconfig.defaults 文件可以通过命令 ESP-IDF:保存默认 SDKCONFIG 文件 (save-defconfig) 生成。
备注
构建系统在生成 sdkconfig 文件时,会使用 sdkconfig.defaults 文件来覆盖项目的默认配置。详情请参阅 ESP-IDF 文档 自定义 sdkconfig 的默认值。
通过该扩展的设置,可以修改默认的构建路径 (/path/to/esp-project/build)、sdkconfig 文件路径以及 sdkconfig.defaults 文件路径。
在此扩展中,你可以通过 idf.buildPath (Windows 系统使用 idf.buildPathWin)配置项定义构建目录,以及通过 idf.sdkconfigDefaults 配置项定义 sdkconfig 默认文件列表。扩展的构建命令将使用这些定义好的值。
例如,要为产品 1 创建配置:
你有 sdkconfig 文件
sdkconfig.prod_common和sdkconfig.prod1,并希望生成的固件输出到<your-project>/build_prod1,其中build_prod1是自定义构建目录的名称。需要在
<your-project>/.vscode/settings.json中添加以下配置:{ // ... "idf.buildPath": "${workspaceFolder}/build_prod1", "idf.sdkconfigDefaults": ["sdkconfig.prod_common", "sdkconfig.prod1"] // ... }
通过
ESP-IDF:构建项目命令构建项目。生成的文件会存放在
<your-project>/build_prod1中,SDK 配置编辑器使用的 sdkconfig 文件路径为<your-project>/build_prod1/sdkconfig。备注
ESP-IDF CMake 多配置示例在
CMakeLists.txt文件中定义了 sdkconfig 路径,这会导致idf.sdkconfigFilePath无效。修改步骤 2 中的值,即可为不同产品和配置创建不同的构建。
使用 ESP-IDF: SDK Configuration Editor 命令,你可以通过 Build Directory Path 指定构建目录,通过 SDKConfig File Path 指定 SDKConfig 文件的位置,并通过 SDKConfig Defaults 指定默认配置文件,从而在所设定路径下生成 SDKConfig 文件。
为多个构建配置扩展
前往菜单栏
查看>命令面板。输入
ESP-IDF:打开项目配置并选择该命令。在开启的项目配置向导界面中,包含以下配置项,用于管理项目配置文件:
设置 ID
功能描述
idf.cmakeCompilerArgs
CMake 编译任务的参数
idf.ninjaArgs
Ninja 构建任务的参数
idf.buildPath
扩展命令使用的自定义构建目录名(默认为 ${workspaceFolder}/build)
idf.sdkconfigFilePath
sdkconfig 文件的绝对路径
idf.sdkconfigDefaults
初始构建配置使用的 sdkconfig 默认值列表
idf.customExtraVars
添加到系统环境变量中的变量,其中 IDF_TARGET 在此处设置
idf.flashBaudRate
烧录波特率
idf.monitorBaudRate
监视器波特率(默认为空,并使用 sdkconfig 文件中定义的 CONFIG_ESP_CONSOLE_UART_BAUDRATE)
idf.openOcdDebugLevel
设置 OpenOCD 调试等级 (0~4),默认值为 2
idf.openOcdConfigs
OpenOCD 配置文件,路径相对于 OPENOCD_SCRIPTS 文件夹
idf.openOcdLaunchArgs
OpenOCD 启动参数,默认值为 []。若定义此值,则 idf.openOcdConfigs 和 idf.openOcdDebugLevel 会被忽略
idf.preBuildTask
构建任务前执行的命令字符串
idf.postBuildTask
构建任务后执行的命令字符串
idf.preFlashTask
烧录任务前执行的命令字符串
idf.postFlashTask
烧录任务后执行的命令字符串
定义配置文件及其设置后:
前往菜单栏
查看>命令面板。输入
ESP-IDF:选择项目配置命令来选择配置,从而覆盖扩展的默认配置项。
通过多个配置文件,你可以集中保存配置,并在不同设置之间轻松切换。
项目配置文件
项目配置文件是一个 JSON 文件,包含用于该扩展的配置设置。该文件在你使用 ESP-IDF:打开项目配置 命令时自动创建,并保存在 ESP-IDF 项目的根目录下。
该文件是一个包含多个配置文件的 JSON 对象。每个配置本身是一个 JSON 对象,具有以下属性:
{
"profile1": {
// profile1 settings
},
"profile2": {
// profile2 settings
}
}
配置名称是 JSON 对象的键,键对应的值是包含该配置设置的 JSON 对象。配置名称可以是任意字符串,但建议使用能够反映该配置用途的描述性名称。
配置名称用于在执行 ESP-IDF:选择项目配置 命令时标识配置,也用于在状态栏显示当前所选的配置。
配置名称不区分大小写,因此 prod1 与 Prod1 被视为同一个配置。
配置设置存储在 JSON 对象中,具有如下属性。注意:数组应包含 string 类型的元素:
{
"profileName": {
"build": {
"compileArgs": [],
"ninjaArgs": [],
"buildDirectoryPath": "",
"sdkconfigDefaults": [],
"sdkconfigFilePath": ""
},
"env": {},
"idfTarget": "",
"flashBaudRate": "",
"monitorBaudRate": "",
"openOCD": {
"debugLevel": 0,
"configs": [],
"args": []
},
"tasks": {
"preBuild": "",
"preFlash": "",
"postBuild": "",
"postFlash": ""
}
}
}
尽管每个字段的含义大致显而易见,也可以参考下表,了解配置文件设置与扩展设置的映射关系:
被替换的设置 ID |
配置文件中覆盖该设置的字段 |
|---|---|
idf.cmakeCompilerArgs |
[“profileName”].build.compileArgs |
idf.ninjaArgs |
[“profileName”].build.ninjaArgs |
idf.buildPath |
[“profileName”].build.buildDirectoryPath |
idf.sdkconfigFilePath |
[“profileName”].build.sdkconfigFilePath |
idf.sdkconfigDefaults |
[“profileName”].build.sdkconfigDefaults |
idf.customExtraVars |
[“profileName”].env and [“profileName”].idfTarget will replace idf.customExtraVars[“IDF_TARGET”] |
idf.flashBaudRate |
[“profileName”].flashBaudRate |
idf.monitorBaudRate |
[“profileName”].monitorBaudRate |
idf.openOcdDebugLevel |
[“profileName”].openOCD.debugLevel |
idf.openOcdConfigs |
[“profileName”].openOCD.configs |
idf.openOcdLaunchArgs |
[“profileName”].openOCD.args |
idf.preBuildTask |
[“profileName”].tasks.preBuild |
idf.postBuildTask |
[“profileName”].tasks.postBuild |
idf.preFlashTask |
[“profileName”].tasks.preFlash |
idf.postFlashTask |
[“profileName”].tasks.postFlash |
多配置教程
阅读本教程时,请参考 ESP-IDF CMake 多配置构建示例。
使用 ESP-IDF:打开项目配置 命令创建两个配置文件:prod1 和 prod2。在 sdkconfig defaults 字段中设置 sdkconfig.prod_common;sdkconfig.prod1 和 sdkconfig.prod_common;sdkconfig.prod2,如下所示:
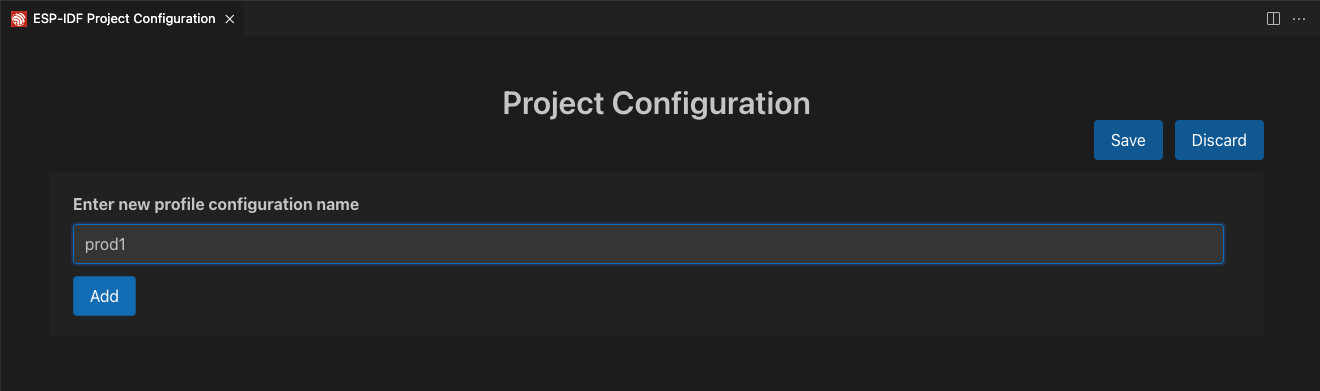
在每个配置文件中,在 sdkconfig defaults 字段输入 sdkconfig.prod_common 并点击 + 添加另一个 sdkconfig 文件。在 prod1 配置文件中输入 sdkconfig.prod1,并在 prod2 配置文件中输入 sdkconfig.prod2。
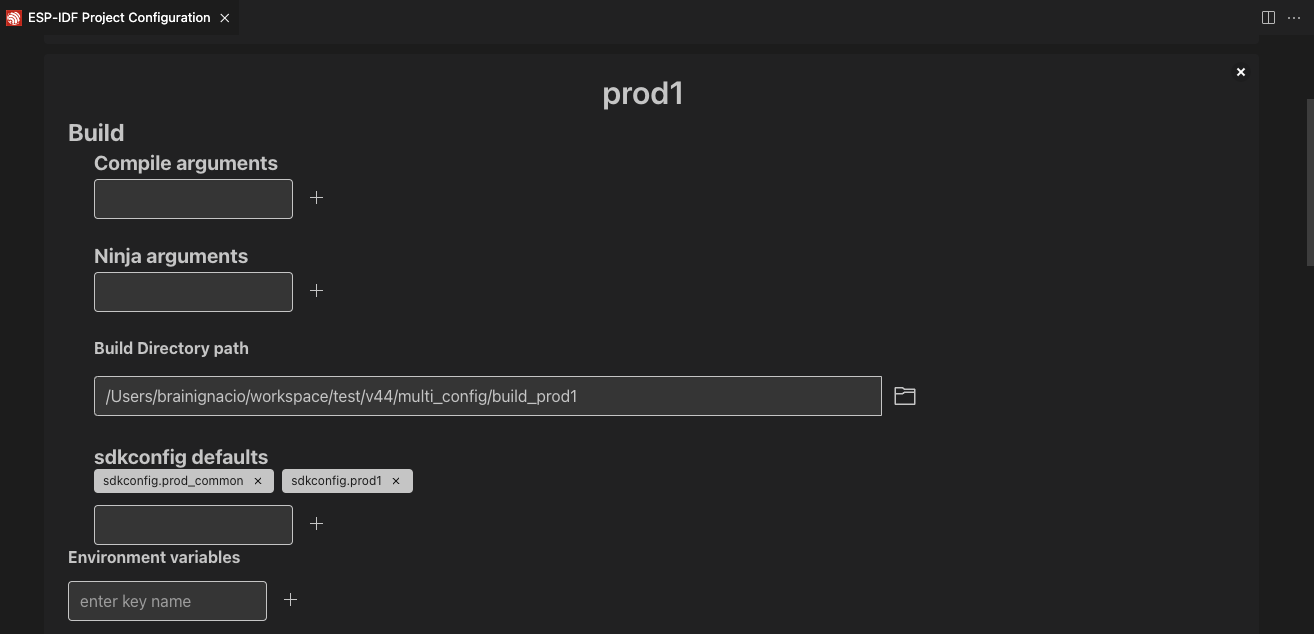

创建配置文件并设置好参数后,点击顶部的 Save 按钮。使用 ESP-IDF:选择项目配置 命令选择用来覆盖扩展设置的配置。
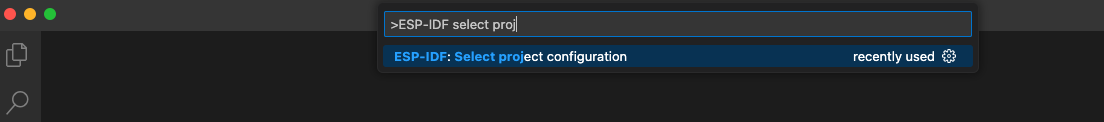
一旦选定了某个配置文件,该文件将显示在状态栏中。

使用 ESP-IDF:构建项目 命令可针对所选配置(prod1 或 prod2)构建项目。每个配置生成的二进制文件会存放在该配置中定义的路径下。使用 ESP-IDF:选择项目配置 命令可在不同配置间切换。
使用 ESP-IDF:打开项目配置 命令可以修改、添加或删除配置文件。若要停止使用这些配置文件,请删除所有配置文件。
这些配置及其设置会保存到 /path/to/esp-project/esp_idf_project_configuration.json。
ESP-IDF 项目的开发和发布配置文件
在此示例中,我们将创建 development 和 production 两个配置文件,并为其定义不同的构建目录和 sdkconfig 文件。
前往菜单栏
查看>命令面板。输入
ESP-IDF:保存默认 SDKCONFIG 文件 (save-defconfig)并选择该命令以生成sdkconfig.defaults文件。此命令需 ESP-IDF v5.0 及以上版本才可使用。你也可以手动创建sdkconfig.defaults文件。前往菜单栏
查看>命令面板。输入
ESP-IDF:打开项目配置并选择该命令,创建一个名为 production 的新配置文件。将SDKConfig Defaults设置为已有的sdkconfig.defaults文件。若要区分 production 配置文件的构建目录与默认的/path/to/esp-project/build目录,可在Build Directory Path字段中自定义目录路径,例如/path/to/esp-project/build_production。同样地,也可以在SDKConfig File Path字段中设置自定义路径,例如/path/to/esp-project/build_production/sdkconfig。创建一个名为 development 的新配置文件。为避免混淆 development 和 production 文件,可在
Build Directory Path字段中设置自定义路径(如/path/to/esp-project/build_dev),并将SDKConfig File Path设置为/path/to/esp-project/build_dev/sdkconfig。创建好两个配置文件并完成配置后,点击
Save按钮,后续可通过ESP-IDF:选择项目配置命令来选择所需的配置文件。若选择 production 配置文件并执行
ESP-IDF:构建项目命令,系统会在/path/to/esp-project/build_production目录中生成二进制文件,并创建/path/to/esp-project/build_production/sdkconfig文件。若选择 development 配置文件,系统会在
/path/to/esp-project/build_dev目录中生成二进制文件,并创建/path/to/esp-project/build_dev/sdkconfig文件。这些配置文件及其设置将保存在
/path/to/esp-project/esp_idf_project_configuration.json文件中。
如 ESP-IDF CMake multi_config 和 多配置教程 所示,上文提到的 production 配置文件可以进一步拆分为多个 production 配置文件。你可以将 sdkconfig.defaults 文件拆分为通用设置文件 sdkconfig.prod_common 和产品特定设置文件 sdkconfig.prod1 及 sdkconfig.prod2。在项目配置编辑器中,可以在 SDKConfig Defaults 字段中指定多个 sdkconfig 默认文件并以分号隔开(如 sdkconfig.prod_common;sdkconfig.prod1),这些文件将按照指定顺序依次加载。详情请参阅 此处。
以上示例展示了项目配置编辑器的功能之一。你也可以根据不同的开发场景(如测试、性能分析等)定义多个配置文件。